linux IRQ Management(七)- 中断处理流程
- 了解如何申请irq 参考此处
1.High-level interrupt-management interfaces
The generic IRQ layer provides a set of function interfaces for device drivers to grab IRQ descriptors and bind interrupt handlers, release IRQs, enable or disable interrupt lines, and so on.
1.1.Registering/Deregistering an interrupt handler
1.1.1.request_irq
typedef irqreturn_t (*irq_handler_t)(int, void *);
/**
* request_irq - allocate an interrupt line
* @irq: Interrupt line to allocate
* @handler: Function to be called when the IRQ occurs.
* @irqflags: Interrupt type flags
* @devname: An ascii name for the claiming device
* @dev_id: A cookie passed back to the handler function
*/
int request_irq(unsigned int irq, irq_handler_t handler, unsigned long flags,
const char *name, void *dev);
-
unsigned int irq:为要注册中断服务函数的中断号;
-
irq_handler_t handler:为要注册的中断服务函数;
-
unsigned long irqflags: 触发中断的参数,比如边沿触发,,定义在linux/interrupt.h。
- IRQF_SHARED: Used while binding an interrupt handler to a shared IRQ line.
描述一个interrupt line是否允许在多个设备中共享。如果中断控制器可以支持足够多的interrupt source,那么在两个外设间共享一个interrupt request line是不推荐的,毕竟有一些额外的开销(发生中断的时候要逐个询问是不是你的中断,软件上就是遍历action list),因此外设的irq handler中最好是一开始就启动判断,看看是否是自己的中断,如果不是,返回IRQ_NONE,表示这个中断不归我管。 早期PC时代,使用8259中断控制器,级联的8259最多支持15个外部中断,但是PC外设那么多,因此需要irq share。现在,ARM平台上的系统设计很少会采用外设共享IRQ方式,毕竟一般ARM SOC提供的有中断功能的GPIO非常的多,足够用的。 当然,如果确实需要两个外设共享IRQ,那也只能如此设计了。对于HW,中断控制器的一个interrupt source的引脚要接到两个外设的interrupt request line上,怎么接?直接连接可以吗?当然不行,对于低电平触发的情况,我们可以考虑用与门连接中断控制器和外设。 - IRQF_PROBE_SHARED: Set by callers when they expect sharing mismatches to occur.用来表示该interrupt action descriptor是允许和其他device共享一个interrupt line(IRQ number),但是实际上是否能够share还是需要其他条件:例如触发方式必须相同。有些驱动程序可能有这样的调用场景:我只是想scan一个irq table,看看哪一个是OK的,这时候,如果即便是不能和其他的驱动程序share这个interrupt line,我也没有关系,我就是想scan看看情况。这时候,caller其实可以预见sharing mismatche的发生,因此,不需要内核打印“Flags mismatch irq……“这样冗余的信息。
- IRQF_PERCPU: Interrupt is per CPU. 在SMP的架构下,中断有两种mode,一种中断是在所有processor之间共享的,也就是global的,一旦中断产生,interrupt controller可以把这个中断送达多个处理器。当然,在具体实现的时候不会同时将中断送达多个CPU,一般是软件和硬件协同处理,将中断送达一个CPU处理。但是一段时间内产生的中断可以平均(或者按照既定的策略)分配到一组CPU上。这种interrupt mode下,interrupt controller针对该中断的operational register是global的,所有的CPU看到的都是一套寄存器,一旦一个CPU ack了该中断,那么其他的CPU看到的该interupt source的状态也是已经ack的状态。 和global对应的就是per cpu interrupt了,对于这种interrupt,不是processor之间共享的,而是特定属于一个CPU的。例如GIC中interrupt ID等于30的中断就是per cpu的(这个中断event被用于各个CPU的local timer),这个中断号虽然只有一个,但是,实际上控制该interrupt ID的寄存器有n组(如果系统中有n个processor),每个CPU看到的是不同的控制寄存器。在具体实现中,这些寄存器组有两种形态,一种是banked,所有CPU操作同样的寄存器地址,硬件系统会根据访问的cpu定向到不同的寄存器,另外一种是non banked,也就是说,对于该interrupt source,每个cpu都有自己独特的访问地址。
- IRQF_NOBALANCING: Flag to exclude this interrupt from IRQ balancing.
这也是和multi-processor相关的一个flag。对于那些可以在多个CPU之间共享的中断,具体送达哪一个processor是有策略的,我们可以在多个CPU之间进行平衡。如果你不想让你的中断参与到irq balancing的过程中那么就设定这个flag:IRQF_IRQPOLL。 - IRQF_TIMER: Flag to mark this interrupt as a timer interrupt.
- IRQF_IRQPOLL: Interrupt is used for polling (only the interrupt that is registered first in a shared interrupt is considered for performance reasons).
- IRQF_NO_SUSPEND: Do not disable this IRQ during suspend. Does not guarantee that this interrupt will wake the system from a suspended state.
在系统suspend的时候,不用disable这个中断,如果disable,可能会导致系统不能正常的resume。 - IRQF_FORCE_RESUME: Force-enable it on resume even if IRQF_NO_SUSPEND is set.
在系统resume的过程中,强制必须进行enable的动作,即便是设定了IRQF_NO_SUSPEND这个flag。这是和特定的硬件行为相关的。 - IRQF_EARLY_RESUME: Resume IRQ early during syscore instead of at device resume time.
- IRQF_COND_SUSPEND: If the IRQ is shared with a NO_SUSPEND user, execute this interrupt handler after suspending interrupts. For system wakeup devices, users need to implement wakeup detection in their interrupt handlers.
- IRQF_ONESHOT:本身的意思的只有一次的,结合到中断这个场景,则表示中断是一次性触发的,不能嵌套。对于primary handler,当然是不会嵌套,但是对于threaded interrupt handler,有两种选择,一种是mask该interrupt source,另外一种是unmask该interrupt source。一旦mask住该interrupt source,那么该interrupt source的中断在整个threaded interrupt handler处理过程中都是不会再次触发的,也就是one shot了。这种handler不需要考虑重入问题。 具体是否要设定one shot的flag是和硬件系统有关的,比如电池驱动,电池里面有一个电量计,是使用HDQ协议进行通信的,电池驱动会注册一个threaded interrupt handler,在这个handler中,会通过HDQ协议和电量计进行通信。对于这个handler,通过HDQ进行通信是需要一个完整的HDQ交互过程,如果中间被打断,整个通信过程会出问题,因此,这个handler就必须是one shot的。
- IRQF_NO_THREAD:有些low level的interrupt是不能线程化的(例如系统timer的中断),这个flag就是起这个作用的。另外,有些级联的interrupt controller对应的IRQ也是不能线程化的(例如secondary GIC对应的IRQ),它的线程化可能会影响一大批附属于该interrupt controller的外设的中断响应延迟。
- IRQF_SHARED: Used while binding an interrupt handler to a shared IRQ line.
-
const char *devname:中断程序的名字,使用cat /proc/interrupt 可以查看中断程序名字;
-
void *dev_id:传入中断处理程序的参数,注册共享中断时不能为NULL,因为卸载时需要这个做参数,避免卸载其它中断服务函数。
其中Interrupt handler routines :
irqreturn_t handler(int irq, void *dev_id);
5 /**
6 * enum irqreturn
7 * @IRQ_NONE interrupt was not from this device or was not handled
8 * @IRQ_HANDLED interrupt was handled by this device
9 * @IRQ_WAKE_THREAD handler requests to wake the handler thread
10 */
11 enum irqreturn {
12 IRQ_NONE = (0 << 0),
13 IRQ_HANDLED = (1 << 0),
14 IRQ_WAKE_THREAD = (1 << 1),
15 };
- IRQ_NONE:The interrupt handler should return IRQ_NONE to indicate that the interrupt was not handled. It is also used to indicate that the source of the interrupt was not from its device in a shared IRQ case.
- IRQ_HANDLED:When interrupt handling has completed normally, it must return IRQ_HANDLED to indicate success.
- IRQ_WAKE_THREAD: is a special flag, returned to wake up the threaded handler.
1.1.2.free_irq
/**
* free_irq - free an interrupt allocated with request_irq
* @irq: Interrupt line to free
* @dev_id: Device identity to free
**
Remove an interrupt handler. The handler is removed and if the
* interrupt line is no longer in use by any driver it is disabled.
* On a shared IRQ the caller must ensure the interrupt is disabled
* on the card it drives before calling this function. The function
* does not return until any executing interrupts for this IRQ
* have completed.
* Returns the devname argument passed to request_irq.
*/
const void *free_irq(unsigned int irq, void *dev_id);
1.2.Threaded interrupt handlers
From the starting, it was desired for kernel to reduce the time for which processor stays in interrupt context. To solve this initially they introduced Top half and bottom half concept, in which they keep time critical task in top half and rest of the work they kept in bottom half. When processor is executing the interrupt handler it is in interrupt context with interrupts disabled on that line, which is not good because if it is a shared line, other interrupts won’t be handled during this time, which in turn effect the overall system latency.
To overcome this problem, kernel developers came up with the request_threaded_irq() method which futher reduces the time.
Processing interrupts from the hardware is a major source of latency in the kernel, because other interrupts are blocked while doing that processing. For this reason, the realtime tree has a feature, called threaded interrupt handlers, that seeks to reduce the time spent with interrupts disabled to a bare minimum—pushing the rest of the processing out into kernel threads. But it is not just realtime kernels that are interested in lower latencies, so threaded handlers are being proposed for addition to the mainline.(Moving interrupts to threads )
Handlers registered through request_irq() are executed by the interrupt-handling path of the kernel. This code path is asynchronous, and runs by suspending scheduler preemption and hardware interrupts on the local processor, and so is referred to as a hard IRQ context. Thus, it is imperative to program the driver’s interrupt handler routines to be short (do as little work as possible) and atomic (non blocking), to ensure responsiveness of the system. However, not all hardware interrupt handlers can be short and atomic: there are a magnitude of convoluted devices generating interrupt events, whose responses involve complex variable-time operations.
Conventionally, drivers are programmed to handle such complications with a splithandler design for the interrupt handler, called top half and bottom half.
- Top half routines are invoked in hard interrupt context, and these functions are programmed to execute interrupt critical operations, such as physical I/O on the hardware registers, and schedule the bottom half for deferred execution.
- Bottom half routines are usually programmed to deal with the rest of the interrupt non-critical and deferrable work, such as processing of data generated by the top half, interacting with process context, and accessing user address space. The kernel offers multiple mechanisms for scheduling and execution of bottom half routines, each with a distinct interface API and policy of execution.
As an alternative to using formal bottom-half mechanisms, the kernel supports setting up interrupt handlers that can execute in a thread context, called threaded interrupt handlers. Drivers can set up threaded interrupt handlers through an alternate interface routine called request_threaded_irq()。
1.2.1. request_threaded_irq
在 Linux 中,中断具有最高的优先级。不论在任何时刻,只要产生中断事件,内核将立即执行相应的中断处理程序,等到所有挂起的中断和软中断处理完毕后才能执行正常的任务,因此有可能造成实时任务得不到及时的处理。中断线程化之后,中断将作为内核线程运行而且被赋予不同的实时优先级,实时任务可以有比中断线程更高的优先级。这样,具有最高优先级的实时任务就能得到优先处理,即使在严重负载下仍有实时性保证。但并不是所有的中断都可以被线程化,比如时钟中断,主要用来维护系统时间以及定时器等,其中定时器是操作系统的脉搏,一旦被线程化,就有可能被挂起,这样后果将不堪设想,所以不应当被线程化。
The request_threaded_irq() function was added to allow developers to split interrupt handling code into two parts.
- One part that will execute with interrupts blocked;
- A second part that can be done by a kernel thread without interrupts blocked.
/**
* request_threaded_irq - allocate an interrupt line
* @irq: Interrupt line to allocate
* @handler: Function to be called when the IRQ occurs.
* Primary handler for threaded interrupts
* If NULL and thread_fn != NULL the default
* primary handler is installed
* @thread_fn: Function called from the irq handler thread
* If NULL, no irq thread is created
* @irqflags: Interrupt type flags
* @devname: An ascii name for the claiming device
* @dev_id: A cookie passed back to the handler function
*/
int request_threaded_irq(unsigned int irq, irq_handler_t handler,
irq_handler_t thread_fn, unsigned long irqflags,const char *devname, void *dev_id);
- “handler ” serves as the primary interrupt handler that executes in a hard IRQ context.
- “thread_fn” is executed in a thread context, and is scheduled to run when the primary handler returns IRQ_WAKE_THREAD.
request_any_context_irq:
Drivers requesting an IRQ must now know whether the handler will
run in a thread context or not, and call request_threaded_irq() or request_irq() accordingly.
The problem is that the requesting driver sometimes doesn’t know
about the nature of the interrupt, specially when the interrupt controller is a discrete chip (typically a GPIO expander connected over I2C) that can be connected to a wide variety of otherwise perfectly supported hardware.
Introduces the request_any_context_irq() function that mostly mimics the usual request_irq(), except that it checks whether the irq level is configured as nested or not, and calls the right backend. On success, it also returns either IRQC_IS_HARDIRQ or IRQC_IS_NESTED.
/**
* request_any_context_irq - allocate an interrupt line
* @irq: Interrupt line to allocate
* @handler: Function to be called when the IRQ occurs.
* Threaded handler for threaded interrupts.* @flags: Interrupt type flags
* @name: An ascii name for the claiming device
* @dev_id: A cookie passed back to the handler function
**
This call allocates interrupt resources and enables the
* interrupt line and IRQ handling. It selects either a
* hardirq or threaded handling method depending on the
* context.
* On failure, it returns a negative value. On success,
* it returns either IRQC_IS_HARDIRQ or IRQC_IS_NESTED..
*/
int request_any_context_irq(unsigned int irq,irq_handler_t handler,
unsigned long flags,const char *name,void *dev_id)
1.3.Difference between request_irq and request_threaded_irq
中断处理分上半部(硬件中断处理,必须关闭中断无法处理新的中断)跟下半部(软件中断处理),因此上半部的硬件中断处理必须尽可能简短,让系统反应速度更快。
而request_threaded_irq 是在将上半部的硬件中断处理缩短为只确定硬件中断来自我们要处理的装置,唤醒kernel thread 执行后续中断任务。
- request_irq(), one registers a handler (top half) that will be executed in atomic context, from which one can schedule a bottom half using one of a differing mechanism.
- request_thread_irq(), one can provide top and bottom halves to the function, so that the former will be run as hardirq handler, which may decide to raise the second and threaded handler, which will be run in a kernel thread.
1.3.1.代码区别
138 extern int __must_check
139 request_threaded_irq(unsigned int irq, irq_handler_t handler,
140 irq_handler_t thread_fn,
141 unsigned long flags, const char *name, void *dev);
142
143 static inline int __must_check
144 request_irq(unsigned int irq, irq_handler_t handler, unsigned long flags,
145 const char *name, void *dev)
146 {
147 return request_threaded_irq(irq, handler, NULL, flags, name, dev);
148 }
request_irq是对request_thread_irq的封装,它给request_thread_irq的thread_fn参数传进了一个NULL,也就是只申请中断处理函数,不要thread_fn。
- handler : top half handler that can only invoke limited APIs. Real-time response is expected.
- thread_fn : bottom half handler that runs in kernel thread.
1.3.2.request_threaded_irq distinction优于request_irq
-
优点:
- 减少 kernel 延迟时间
- 避免处理中断时要分辨是硬体中断或软体中断?
- 更容易为kernel 中断处理除错,可能可完全取代tasklet。
-
缺点:
- 对于非irq 中断的kernel threads ,需要在原本task_struct 新增struct irqaction 多占 4/8 bytes 空间。
1.3.3.什么时候使用request_threaded_irq/request_irq?
根据实际情况选择合适的接口,可使用request_threaded_irq的地方没必要继续使用request_irq加tasklet/workqueue或者内核线程的方式;如果中断处理简单时也不要执着使用request_threaded_irq。
1.4.Threaded interrupt handlers flags
The following are irqflags related to threaded interrupt handlers:
-
IRQF_ONESHOT: The interrupt is not re-enabled after the hard IRQ handler is finished. This is used by threaded interrupts that need to keep the IRQ line disabled until the threaded handler has been run.
-
IRQF_NO_THREAD: The interrupt cannot be threaded. This is used in shared IRQs to restrict the use of threaded interrupt handlers.
Note:
- A call to this routine with NULL assigned to handler will cause the kernel to use the default primary handler, which simply returns IRQ_WAKE_THREAD,这时IRQF_ONESHOT标识不可少,否则中断会申请失败。
- IRQF_ONESHOT的作用是保证thread_handler函数执行完整,才会接受下一个中断信号。
1.5.request_threaded_irq代码分析
使用 request_irq() 注册的是传统中断,而直接使用 request_threaded_irq() 注册的是线程化中断。线程化中断的主要目的是把中断上下文的任务迁移到线程中,减少系统关中断的时间,增强系统的实时性。
中断对应的线程命名规则为:
t = kthread_create(irq_thread, new, “irq/%d-%s”, irq, new->name);
通过 ps 命令查看系统中的中断线程,注意这些线程是实时线程 SCHED_FIFO:
root@:/ # ps | grep "irq/"
root 171 2 0 0 irq_thread 0000000000 S irq/389-charger
root 239 2 0 0 irq_thread 0000000000 S irq/296-PS_int-
root 247 2 0 0 irq_thread 0000000000 S irq/297-1124000
root 1415 2 0 0 irq_thread 0000000000 S irq/293-goodix_
root@a0255:/ #
线程化中断的创建和处理任务流程如下:
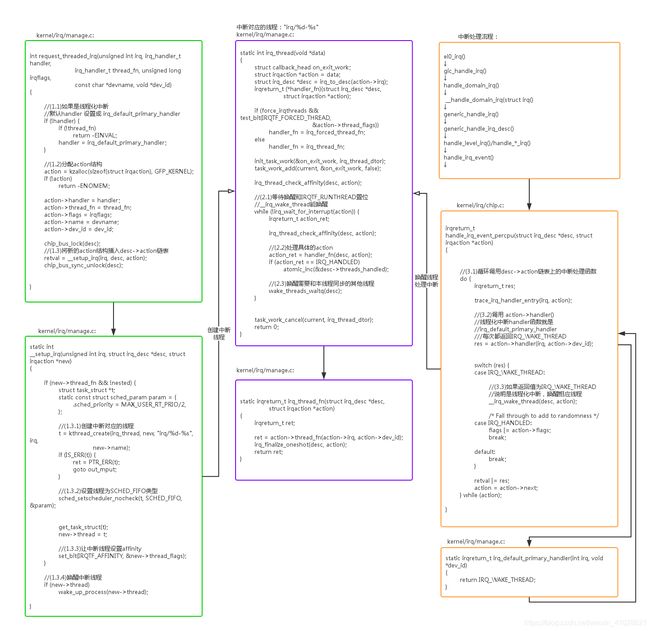
线程和 action 是一一对应的,即用户注册一个中断处理程序对应一个中断线程。
- request_threaded_irq -> __setup_irq
static int
__setup_irq(unsigned int irq, struct irq_desc *desc, struct irqaction *new)
{
struct irqaction *old, **old_ptr;
unsigned long flags, thread_mask = 0;
int ret, nested, shared = 0;
#中断描述符为null,则退出
if (!desc)
return -EINVAL;
#没有设置irq_data.chip,所以irq_data.chip 会等于no_irq_chip。这属于异常case ,退出.
if (desc->irq_data.chip == &no_irq_chip)
return -ENOSYS;
#增加这个模块的引用计数
if (!try_module_get(desc->owner))
return -ENODEV;
#更新struct irqaction *new 中的irq number
new->irq = irq;
/*
* If the trigger type is not specified by the caller,
* then use the default for this interrupt.
*/
#没有设置中断触发类型的话,则用默认值.
if (!(new->flags & IRQF_TRIGGER_MASK))
new->flags |= irqd_get_trigger_type(&desc->irq_data);
/*
* Check whether the interrupt nests into another interrupt
* thread.
*/
#检查这里是否是中断嵌套,正常情况下irq_chip 基本都不支持中断嵌套
nested = irq_settings_is_nested_thread(desc);
if (nested) {
if (!new->thread_fn) {
ret = -EINVAL;
goto out_mput;
}
new->handler = irq_nested_primary_handler;
} else {
#这里检查是否为这个中断设置一个thread,也就是说是否支持中断线程化
if (irq_settings_can_thread(desc)) {
ret = irq_setup_forced_threading(new);
if (ret)
goto out_mput;
}
}
/*
* Create a handler thread when a thread function is supplied
* and the interrupt does not nest into another interrupt
* thread.
*/
#在没有支持中断嵌套且用户用设置中断线程的情况下,这里会创建一个中断线程
if (new->thread_fn && !nested) {
ret = setup_irq_thread(new, irq, false); -----------------(1)
if (ret)
goto out_mput;
#中断线程化时是否支持第二个线程。如果支持的话,再创建一个中断线程.
if (new->secondary) {
ret = setup_irq_thread(new->secondary, irq, true);
if (ret)
goto out_thread;
}
}
#有设置oneshot 标志的话,则清掉这个标志.
if (desc->irq_data.chip->flags & IRQCHIP_ONESHOT_SAFE)
new->flags &= ~IRQF_ONESHOT;
mutex_lock(&desc->request_mutex);
chip_bus_lock(desc);
/* First installed action requests resources. */
#中断描述符的action为null的话,则通过irq_request_resources 来申请中断资源.
if (!desc->action) {
ret = irq_request_resources(desc);
if (ret) {
pr_err("Failed to request resources for %s (irq %d) on irqchip %s\n",
new->name, irq, desc->irq_data.chip->name);
goto out_bus_unlock;
}
}
raw_spin_lock_irqsave(&desc->lock, flags);
old_ptr = &desc->action;
old = *old_ptr;
#如果这个中断号对应的中断描述符中的action 不为null,说明这个中断号之前可能已经申请过中断了
#这里同样可以得出结论,同一个中断好,可以重复申请中断,但是可能会继承前一次的中断触发类型.
if (old) {
unsigned int oldtype;
if (irqd_trigger_type_was_set(&desc->irq_data)) {
oldtype = irqd_get_trigger_type(&desc->irq_data);
} else {
oldtype = new->flags & IRQF_TRIGGER_MASK;
irqd_set_trigger_type(&desc->irq_data, oldtype);
}
if (!((old->flags & new->flags) & IRQF_SHARED) ||
(oldtype != (new->flags & IRQF_TRIGGER_MASK)) ||
((old->flags ^ new->flags) & IRQF_ONESHOT))
goto mismatch;
/* All handlers must agree on per-cpuness */
if ((old->flags & IRQF_PERCPU) !=
(new->flags & IRQF_PERCPU))
goto mismatch;
/* add new interrupt at end of irq queue */
do {
thread_mask |= old->thread_mask;
old_ptr = &old->next;
old = *old_ptr;
} while (old);
shared = 1;
}
if (new->flags & IRQF_ONESHOT) {
if (thread_mask == ~0UL) {
ret = -EBUSY;
goto out_unlock;
}
new->thread_mask = 1UL << ffz(thread_mask);
} else if (new->handler == irq_default_primary_handler &&
!(desc->irq_data.chip->flags & IRQCHIP_ONESHOT_SAFE)) {
pr_err("Threaded irq requested with handler=NULL and !ONESHOT for irq %d\n",
irq);
ret = -EINVAL;
goto out_unlock;
}
#非共享中断
if (!shared) {
#初始化一个等待队列,这个等待队列包含在中断描述符中
init_waitqueue_head(&desc->wait_for_threads);
/* Setup the type (level, edge polarity) if configured: */
if (new->flags & IRQF_TRIGGER_MASK) {
ret = __irq_set_trigger(desc,
new->flags & IRQF_TRIGGER_MASK);
if (ret)
goto out_unlock;
}
#激活这个中断
ret = irq_activate(desc);
if (ret)
goto out_unlock;
desc->istate &= ~(IRQS_AUTODETECT | IRQS_SPURIOUS_DISABLED | \
IRQS_ONESHOT | IRQS_WAITING);
irqd_clear(&desc->irq_data, IRQD_IRQ_INPROGRESS);
#是不是percpu中断
if (new->flags & IRQF_PERCPU) {
irqd_set(&desc->irq_data, IRQD_PER_CPU);
irq_settings_set_per_cpu(desc);
}
if (new->flags & IRQF_ONESHOT)
desc->istate |= IRQS_ONESHOT;
/* Exclude IRQ from balancing if requested */
#不用设置irq balance
if (new->flags & IRQF_NOBALANCING) {
irq_settings_set_no_balancing(desc);
irqd_set(&desc->irq_data, IRQD_NO_BALANCING);
}
#开始中断
if (irq_settings_can_autoenable(desc)) {
irq_startup(desc, IRQ_RESEND, IRQ_START_COND);
} else {
WARN_ON_ONCE(new->flags & IRQF_SHARED);
/* Undo nested disables: */
desc->depth = 1;
}
} else if (new->flags & IRQF_TRIGGER_MASK) {
unsigned int nmsk = new->flags & IRQF_TRIGGER_MASK;
unsigned int omsk = irqd_get_trigger_type(&desc->irq_data);
if (nmsk != omsk)
/* hope the handler works with current trigger mode */
pr_warn("irq %d uses trigger mode %u; requested %u\n",
irq, omsk, nmsk);
}
*old_ptr = new;
#设置power相关
irq_pm_install_action(desc, new);
/* Reset broken irq detection when installing new handler */
desc->irq_count = 0;
desc->irqs_unhandled = 0;
if (shared && (desc->istate & IRQS_SPURIOUS_DISABLED)) {
desc->istate &= ~IRQS_SPURIOUS_DISABLED;
__enable_irq(desc);
}
raw_spin_unlock_irqrestore(&desc->lock, flags);
chip_bus_sync_unlock(desc);
mutex_unlock(&desc->request_mutex);
irq_setup_timings(desc, new);
# 如果有中断线程的话,则wakeup线程
if (new->thread)
wake_up_process(new->thread);
if (new->secondary)
wake_up_process(new->secondary->thread);
#注册irq在proc中的接口
register_irq_proc(irq, desc);
new->dir = NULL;
register_handler_proc(irq, new);
return 0;
mismatch:
if (!(new->flags & IRQF_PROBE_SHARED)) {
pr_err("Flags mismatch irq %d. %08x (%s) vs. %08x (%s)\n",
irq, new->flags, new->name, old->flags, old->name);
#ifdef CONFIG_DEBUG_SHIRQ
dump_stack();
#endif
}
ret = -EBUSY;
#一下都是异常case
out_unlock:
raw_spin_unlock_irqrestore(&desc->lock, flags);
if (!desc->action)
irq_release_resources(desc);
out_bus_unlock:
chip_bus_sync_unlock(desc);
mutex_unlock(&desc->request_mutex);
out_thread:
if (new->thread) {
struct task_struct *t = new->thread;
new->thread = NULL;
kthread_stop(t);
put_task_struct(t);
}
if (new->secondary && new->secondary->thread) {
struct task_struct *t = new->secondary->thread;
new->secondary->thread = NULL;
kthread_stop(t);
put_task_struct(t);
}
out_mput:
module_put(desc->owner);
return ret;
}
重点分析:
- setup_irq_thread(new, irq, false);
When a threaded irq handler is installed the irq thread is initially created on normal scheduling priority. Only after the the irq thread is woken up it sets its priority to RT_FIFO MAX_USER_RT_PRIO/2.
This means that interrupts that occur directly after the irq handler is installed will be handled on a normal scheduling priority instead of the realtime priority that you would expect. Fixed this by setting the RT priority on creation of the irq_thread.
setup_irq_thread 创建内核中断线程irq_thread,然后将该线程添加到new->thread = t;即irqaction结构体中thread。
内核中断线程irq_thread分析:
irq_thread在中断注册的时候,如果条件满足同时创建rq/xx-xx内核中断线程,线程优先级是49(99-50),调度策略是SCHED_FIFO。
irq_thread在irq_wait_for_interrupt()中等待,irq_wait_for_interrupt()中判断IRQTF_RUNTHREAD标志位,没有置位则schedule()换出CPU,进行睡眠;直到__irq_wake_thread()置位了IRQTF_RUNTHREAD,并且wake_up_process()后,irq_wait_for_interrupt()返回0。
static int irq_thread(void *data)
{
struct callback_head on_exit_work;
struct irqaction *action = data;
struct irq_desc *desc = irq_to_desc(action->irq);
irqreturn_t (*handler_fn)(struct irq_desc *desc,
struct irqaction *action);
if (force_irqthreads && test_bit(IRQTF_FORCED_THREAD,
&action->thread_flags))
handler_fn = irq_forced_thread_fn;
else
handler_fn = irq_thread_fn;
init_task_work(&on_exit_work, irq_thread_dtor);
task_work_add(current, &on_exit_work, false);
irq_thread_check_affinity(desc, action);
while (!irq_wait_for_interrupt(action)) {
irqreturn_t action_ret;
irq_thread_check_affinity(desc, action);
action_ret = handler_fn(desc, action);-----------执行中断内核线程函数
if (action_ret == IRQ_HANDLED)
atomic_inc(&desc->threads_handled);----------增加threads_handled计数
wake_threads_waitq(desc);------------------------唤醒wait_for_threads等待队列
}
task_work_cancel(current, irq_thread_dtor);
return 0;
}
static int irq_wait_for_interrupt(struct irqaction *action)
{
set_current_state(TASK_INTERRUPTIBLE);
while (!kthread_should_stop()) {
if (test_and_clear_bit(IRQTF_RUNTHREAD,
&action->thread_flags)) {------------判断thread_flags是否设置IRQTF_RUNTHREAD标志位,如果设置则设置当前状态TASK_RUNNING并返回0。此处和__irq_wake_thread中设置IRQTF_RUNTHREAD对应。
__set_current_state(TASK_RUNNING);
return 0;
}
schedule();-----------------------------------------换出CPU,在此等待睡眠
set_current_state(TASK_INTERRUPTIBLE);
}
__set_current_state(TASK_RUNNING);
return -1;
}
static irqreturn_t irq_thread_fn(struct irq_desc *desc,
struct irqaction *action)
{
irqreturn_t ret;
ret = action->thread_fn(action->irq, action->dev_id);---执行中断内核线程函数,为request_threaded_irq注册中断参数thread_fn。
irq_finalize_oneshot(desc, action);---------------------针对oneshot类型中断收尾处理,主要是去屏蔽中断。
return ret;
}
irq_thread调用流程:
handle_edge_irq
->handle_irq_event
->handle_irq_event_percpu
->__handle_irq_event_percpu
irqreturn_t __handle_irq_event_percpu(struct irq_desc *desc, unsigned int *flags)
{
irqreturn_t retval = IRQ_NONE;
unsigned int irq = desc->irq_data.irq;
struct irqaction *action;
record_irq_time(desc);
for_each_action_of_desc(desc, action) {
irqreturn_t res;
trace_irq_handler_entry(irq, action);
res = action->handler(irq, action->dev_id);
trace_irq_handler_exit(irq, action, res);
if (WARN_ONCE(!irqs_disabled(),"irq %u handler %pS enabled interrupts\n",
irq, action->handler))
local_irq_disable();
switch (res) {
case IRQ_WAKE_THREAD:
/*
* Catch drivers which return WAKE_THREAD but
* did not set up a thread function
*/
if (unlikely(!action->thread_fn)) {
warn_no_thread(irq, action);
break;
}
__irq_wake_thread(desc, action);
/* Fall through - to add to randomness */
case IRQ_HANDLED:
*flags |= action->flags;
break;
default:
break;
}
retval |= res;
}
return retval;
}
如果res = IRQ_WAKE_THREAD,则调用__irq_wake_thread->wake_up_process(action->thread); 即irq_thread线程;
irq_wait_for_interrupt分析:
- 设置当前进程的状态为TASK_INTERRUPTIBLE;
- IRQTF_RUNTHREAD被置位说明中断线程被唤醒,对应的中断已经触发并且经过top half的处理。检测IRQTF_RUNTHREAD,如果有,然后将该bit位清除 设置当前进程TASK_RUNNING,退出irq_wait_for_interrupt,到irq_thread的循环中,再次检测cpu affinity,然后调用handler_fn。
- IRQTF_RUNTHREAD没有置位则调用schedule让出CPU控制权。
- wake_threads_waitq唤醒该irqdesc->wait_for_threads上挂载的等待事件。
2.中断处理流程
当中断发生后,硬件中断的编码通过irq domain翻译成irq number,最终找到设备中断描述符irq_desc,继而调用highlevel irq-events(即中断控制器的中断处理程序的抽象),最终调用到对应的中断处理程序。
首先,在驱动程序中使用API request_irq()注册一个关于GPIO1_1管脚的中断处理函数。
打开中断后,当GPIO1_1出现电平变化时,中断信号从GPIO控制器经过GIC,然后进入到CPU的IRQ控制线。重点关注如下四个部分的处理:
- CPU的中断处理函数
- GIC的中断处理函数
- GPIO控制器处理函数
- 驱动程序注册的中断处理函数
2.1.CPU中断控制
2.1.1.ARM 32位系统
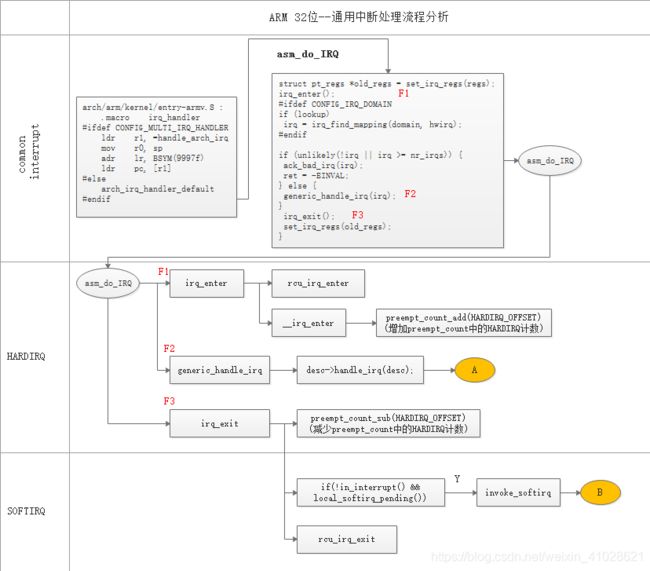
当中断发生,通过中断向量表进入真正的处理irq_handler。
arch/arm/kernel/entry-armv.S :
.macro irq_handler
#ifdef CONFIG_MULTI_IRQ_HANDLER
ldr r1, =handle_arch_irq
mov r0, sp
adr lr, BSYM(9997f)
ldr pc, [r1]
#else
arch_irq_handler_default
#endif
分两种情况:
- CONFIG_MULTI_IRQ_HANDLER,则意味着允许平台代码可以动态设置irq处理程序,平台代码可以修改全局变量:handle_arch_irq,从而可以修改irq的处理程序。
- arch_irq_handler_default
第一种:设置CONFIG_MULTI_IRQ_HANDLER
之前分析gic_of_init [参考此处]:
drivers/irqchip/irq-gic-v3.c:
gic_of_init
->gic_init_bases
->set_handle_irq(gic_handle_irq);
如上所示:set_handle_irq重新设置handle_arch_irq = gic_handle_irq;
kernel/irq/handle.c:
213 #ifdef CONFIG_GENERIC_IRQ_MULTI_HANDLER
214 int __init set_handle_irq(void (*handle_irq)(struct pt_regs *))
215 {
216 if (handle_arch_irq)
217 return -EBUSY;
218
219 handle_arch_irq = handle_irq;
220 return 0;
221 }
222 #endif
调用流程如下所示:
gic_handle_irq
->handle_domain_irq
->__handle_domain_irq
->generic_handle_irq
->desc->handle_irq(desc);
第二种:arch_irq_handler_default
4 /*
5 * Interrupt handling. Preserves r7, r8, r9
6 */
7 .macro arch_irq_handler_default
8 get_irqnr_preamble r6, lr
9 1: get_irqnr_and_base r0, r2, r6, lr
10 movne r1, sp
11 @
12 @ routine called with r0 = irq number, r1 = struct pt_regs *
13 @
14 badrne lr, 1b
15 bne asm_do_IRQ
调用流程:
arch/arm/kernel/irq.c:
->asm_do_IRQ
->handle_IRQ
->__handle_domain_irq
->generic_handle_irq
->desc->handle_irq(desc);
asm_do_IRQ 开始便进入c语言的世界,该函数有两个参数,跳转之前需要填充这两个参数,而且需要r0 = irq number, r1 = struct pt_regs *这样放,因为当参数<=4的时候,会使用r0~r4寄存器来存;参数>4时,其余的会压入栈中,入栈顺序和参数顺序相反;后入的先出,所以相反。
arch/arm/kernel/irq.c:
asm_do_IRQ
->handle_IRQ(irq, regs);
->__handle_domain_irq(NULL, irq, false, regs);
分析__handle_domain_irq:
int __handle_domain_irq(struct irq_domain *domain, unsigned int hwirq,
bool lookup, struct pt_regs *regs)
{
// 先保存中断寄存器状态
struct pt_regs *old_regs = set_irq_regs(regs);
unsigned int irq = hwirq;
int ret = 0;
irq_enter();
#ifdef CONFIG_IRQ_DOMAIN
if (lookup)
irq = irq_find_mapping(domain, hwirq);
#endif
if (unlikely(!irq || irq >= nr_irqs)) {
ack_bad_irq(irq);
ret = -EINVAL;
} else {
// 默认走到这里
generic_handle_irq(irq);
}
irq_exit();
// 恢复中断寄存器状态
set_irq_regs(old_regs);
return ret;
}
1).set_irq_regs:保存中断寄存器现场,注意old_regs是指针,指向现场全局寄存器的指针;
2).irq_enter();
调用preempt_count_add增加preempt_count中HARDIRQ的计数,标志着一个HARDIRQ的开始;
preempt_count变量不为零的时候不可以抢占。
3).irq = irq_find_mapping(domain, hwirq);
获得irq的值;
4).generic_handle_irq(irq);
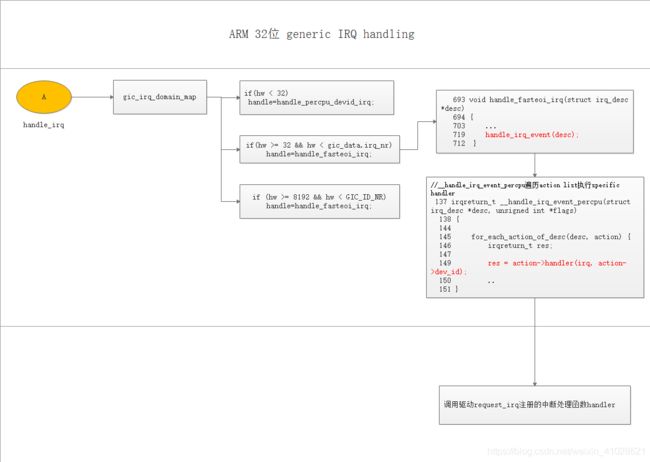
调用desc->handle_irq(desc); handle_irq 在哪里赋值?分析如下:
drivers/irqchip/irq-gic-v3.c
gic_irq_domain_map
->irq_domain_set_info
->__irq_set_handler
->__irq_do_set_handler
->desc->handle_irq = handle;
如上所示:
desc->handle_irq = handle; 此类函数有:
- 处理电平触发类型的中断handler(handle_level_irq)
- 处理边缘触发类型的中断handler(handle_edge_irq)
- 处理简单类型的中断handler(handle_simple_irq)
- 处理EOI类型的中断handler(handle_fasteoi_irq)
而此时的handle是在gic_irq_domain_map(driver/irqchip/irq-gic-v3.c) 中赋值的:
- 如果hw < 32,则handle=handle_percpu_devid_irq;
- 如果hw >= 32,则handle=handle_fasteoi_irq;
- 如果hw >= 8192,则handle=handle_fasteoi_irq。
handle_percpu_devid_irq
->res = action->handler(irq, raw_cpu_ptr(action->percpu_dev_id));
handle_fasteoi_irq
->handle_irq_event
->handle_irq_event_percpu
->__handle_irq_event_percpu
->res = action->handler(irq, action->dev_id);
如上所示,这个handler就是request_irq的第二个参数handler,终于调到自己注册的函数。
5).irq_exit
调用preempt_count_sub(HARDIRQ_OFFSET),将irq_enter增加的计数减掉,这也标志着HARDIRQ的结束,然后调用in_interrupt()判断preempt_count为0且有softirq pending,就调用invoke_softirq。
小结:ARM 32位 中断整体流程
调用注册的中断处理函数:
2.1.2.ARM 64位 中断流程

从处理流程上看,对于 gic 的每个中断源,Linux 系统分配一个 irq_desc 数据结构与之对应。irq_desc 结构中有两个中断处理函数 desc->handle_irq() 和 desc->action->handler(),这两个函数代表中断处理的两个层级:
- desc->handle_irq()。第一层次的中断处理函数,这个是系统在初始化时根据中断源的特征统一分配的,不同类型的中断源的 gic 操作是不一样的,把这些通用 gic 操作提取出来就是第一层次的操作函数。具体实现包括:
- handle_fasteoi_irq()
- handle_simple_irq()
- handle_edge_irq()
- handle_level_irq()
- handle_percpu_irq()
- handle_percpu_devid_irq()
- desc->action->handler() 第二层次的中断处理函数,由用户注册实现具体设备的驱动服务程序,都是和 GIC 操作无关的代码。同时一个中断源可以多个设备共享,所以一个 desc 可以挂载多个 action,由链表结构组织起来。

3.s3c2440 中断处理的框架及代码流程
a. 异常向量入口
arch\arm\kernel\entry-armv.S:
.section .vectors, "ax", %progbits
.L__vectors_start:
W(b) vector_rst
W(b) vector_und
W(ldr) pc, .L__vectors_start + 0x1000
W(b) vector_pabt
W(b) vector_dabt
W(b) vector_addrexcptn
W(b) vector_irq
W(b) vector_fiq
b. 中断向量: vector_irq
/*
* Interrupt dispatcher
*/
vector_stub irq, IRQ_MODE, 4 // 相当于 vector_irq: ...,
// 它会根据SPSR寄存器的值,
// 判断被中断时CPU是处于USR状态还是SVC状态,
// 然后调用下面的__irq_usr或__irq_svc
.long __irq_usr @ 0 (USR_26 / USR_32)
.long __irq_invalid @ 1 (FIQ_26 / FIQ_32)
.long __irq_invalid @ 2 (IRQ_26 / IRQ_32)
.long __irq_svc @ 3 (SVC_26 / SVC_32)
.long __irq_invalid @ 4
.long __irq_invalid @ 5
.long __irq_invalid @ 6
.long __irq_invalid @ 7
.long __irq_invalid @ 8
.long __irq_invalid @ 9
.long __irq_invalid @ a
.long __irq_invalid @ b
.long __irq_invalid @ c
.long __irq_invalid @ d
.long __irq_invalid @ e
.long __irq_invalid @ f
c. __irq_usr/__irq_svc,这2个函数的处理过程类似:
- 保存现场
- 调用 irq_handler
- 恢复现场
d. irq_handler: 将会调用C函数 handle_arch_irq
.macro irq_handler
#ifdef CONFIG_GENERIC_IRQ_MULTI_HANDLER
ldr r1, =handle_arch_irq
mov r0, sp
badr lr, 9997f
ldr pc, [r1]
#else
arch_irq_handler_default
#endif
9997:
.endm
e. handle_arch_irq的处理过程:
- 读取寄存器获得中断信息: hwirq
- 把hwirq转换为virq
- 调用 irq_desc[virq].handle_irq
对于S3C2440, s3c24xx_handle_irq 是用于处理中断的C语言入口函数。
中断处理流程:
假设中断结构如下:
sub int controller —> int controller —> cpu
-
发生中断时,cpu跳到"vector_irq", 保存现场, 调用C函数handle_arch_irq
handle_arch_irq:
a. 读 int controller, 得到hwirq
b. 根据hwirq得到virq
c. 调用 irq_desc[virq].handle_irq -
如果该中断没有子中断, irq_desc[virq].handle_irq的操作:
a. 取出irq_desc[virq].action链表中的每一个handler, 执行它
b. 使用irq_desc[virq].irq_data.chip的函数清中断 -
如果该中断是由子中断产生, irq_desc[virq].handle_irq的操作:
a. 读 sub int controller, 得到hwirq’
b. 根据hwirq’得到virq
c. 调用 irq_desc[virq].handle_irq
refer to
- http://kernel.meizu.com/linux-interrupt.html
- https://my.oschina.net/fileoptions/blog/918164