Activity的启动流程(基于Android 10.0源码)
Activity的启动一般分为普通Activity的启动,根Activity的启动.而根Activity是指应用启动的第一个Activity过程,所以也可以理解为应用的启动过程.
相关内容链接:android系统启动流程
Activity的启动过程(应用的启动流程)
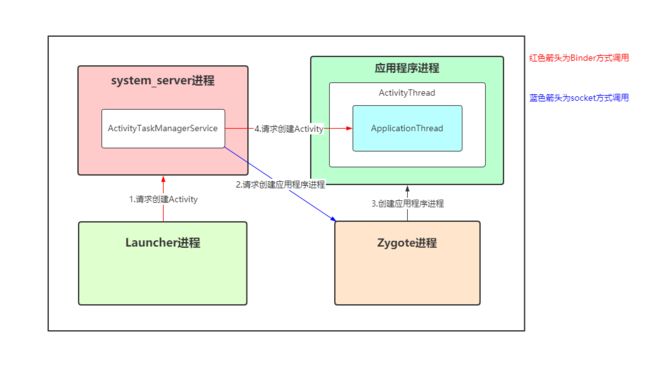
应用的启动流程大致分为如下四个阶段:
一.应用进程(Launcher)调用ATMS系统进程的过程
二.ActivityTaskManagerService到ApplicationThread的调用过程
三.AMS向Zygote发送启动应用进程的过程
四.ActivityThread启动Activity的过程
Activity启动过程涉及到进程之间的关系:
一.应用进程(Launcher)调用ATMS系统进程的过程
启动Activity时,无论是点击桌面图标还是自己写的startActivity,都是调用Activity的startActivity方法,而该方法内部又会调用startActivityForResult具体如下:
// android-29\android\app\Activity.java
public void startActivity(Intent intent, @Nullable Bundle options) {
if (options != null) {
startActivityForResult(intent, -1, options);
} else {
// Note we want to go through this call for compatibility with
// applications that may have overridden the method.
startActivityForResult(intent, -1);
}
}
源码调用如下:
类名: android.app.Activity:
1. startActivity(Intent)
2. startActivity(Intent, Bundle)
3. startActivityForResult(Intent, int, Bundle)
类名: android.app.Instrumentation:
Instrumentation主要用来监控应用程序和系统的交互
4. execStartActivity(android.content.Context, android.os.IBinder, android.os.IBinder, android.app.Activity, android.content.Intent, int, android.os.Bundle)
注释1的getService方法调用了IActivityTaskManagerSingleton的get方法,而它是一个Singleton类,在重写的create方法中获取Context.ACTIVITY_TASK_SERVICE的IBinder引用,然后转换成IActivityTaskManager类型的对象.这段代码是AIDL的写法,IActivityTaskManager类是AIDL工具在编译时自动生成,IActivityTaskManager文件的路径为framework/base/core/java/android/app/IActivityTaskManager.aidl. 要实现进程间通信,服务端也就是ActivityTaskManagerService只需要继承IActivityTaskManager.Stub类并实现相应的方法就可以了(在Android7.0使用的是ActivityManagerProxy代理模式来实现的Binder通信)
// android-29\android/app/Instrumentation.java
public ActivityResult execStartActivity(
Context who, IBinder contextThread, IBinder token, String target,
Intent intent, int requestCode, Bundle options) {
// ... ...
try {
intent.migrateExtraStreamToClipData();
intent.prepareToLeaveProcess(who);
int result = ActivityTaskManager.getService() // 注释1
.startActivity(whoThread, who.getBasePackageName(), intent,
intent.resolveTypeIfNeeded(who.getContentResolver()),
token, target, requestCode, 0, null, options);
checkStartActivityResult(result, intent);
} catch (RemoteException e) {
throw new RuntimeException("Failure from system", e);
}
return null;
}
// android-29\android\app\ActivityTaskManager.java
/** @hide */
public static IActivityTaskManager getService() {
return IActivityTaskManagerSingleton.get();
}
@UnsupportedAppUsage(trackingBug = 129726065)
private static final Singleton IActivityTaskManagerSingleton =
new Singleton() {
@Override
protected IActivityTaskManager create() {
final IBinder b = ServiceManager.getService(Context.ACTIVITY_TASK_SERVICE);
return IActivityTaskManager.Stub.asInterface(b);
}
};
// android-29\android\content\Context.java
/**
* Use with {@link #getSystemService(String)} to retrieve a
* {@link android.app.ActivityTaskManager} for interacting with the global system state.
*
* @see #getSystemService(String)
* @see android.app.ActivityTaskManager
* @hide
*/
public static final String ACTIVITY_TASK_SERVICE = "activity_task";