学习Content Provider
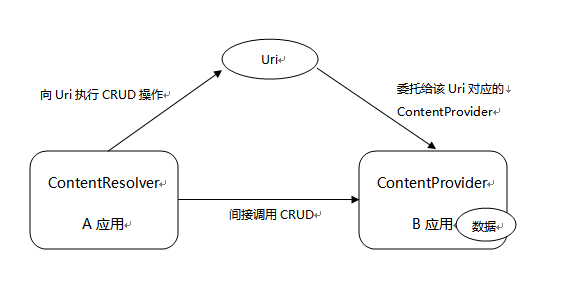
ContentProvider是Android中的四大组件之一,是不同应用程序之间进行数据交换的标准API。ContentProvider以某种Uri的形式对外提供数据,允许其他应用访问或修改数据,也就是:对外共享数据。其他应用程序使用ContentResolver根据Uri去访问操作指定数据。
在书上作者提到 "对于初学者而言,可以把ContentProvider当成Android系统内部的‘网站’,这个网站以固定的Uri对外提供服务;而ContentResolver则可以当成Android系统内部的HttpClient,它可以指定Uri发送‘请求’(实际上是调用ContentResolver的方法),这种请求最后委托给ContentProvider处理,从而实现对‘网站’(ContentProvider)内部数据进行操作”。
- ContentProvider为存储和读取数据提供了统一的接口
- 使用ContentProvider,应用程序可以实现数据共享
- android内置的许多数据都是使用ContentProvider形式,供开发者调用的(如视频,音频,图片,通讯录等)
1、注册Content Provider
在AndroidManifest.xml文件中注册一个ContentProvider,只要在
- public boolean onCreate(): 在创建ContentProvider时调用,当其他应用程序第一次访问ContentProvider时,该ContentProvider会被创建出来,并立即回调该onCreate方法。
- public Uri insert(Uri uri, ContentValues valus) :根据该Uri插入values对应的数据。
- public int delete(Uri uri, String selection, String[] selectionArgs): 根据Uri删除selection条件所匹配的全部记录。
- public int update(Uri uri, ContentValues valus, String selection,String[] selectionArgs) :根据Uri修改selection条件所匹配的全部记录。
- public Cursor query(Uri uri, String[] projection, String selection, String[] selectionArgs, String sortOrder): 根据Uri查询出selection条件所匹配的全部记录。
- public String getType(Uri): 用于返回指定的Uri中的数据的MIME类型。如果操作的数据属于集合类型,那么MIME类型字符串应该以vnd.android.cursor.dir/开头。
2、Uri简介
Uri指定了将要操作的ContentProvider,其实可以把一个Uri看作是一个网址,我们把Uri分为三部分。
content://songosng.uri.contentproviderstext/words
- content://:这个部分是Android的ContentProvider规定的,就想上网的协议默认是http://一样。
- songosng.uri.contentproviderstext:这个部分是ContentProvider的authorities。用于唯一标识这个ContentProvider,外部应用需要根据这个标识来找到它。可以看作是网址中的主机名,比如"blog.csdn.net"。
- words:资源部分,用来表示将要操作的数据。可以看作网址中细分的内容路径。
3、ContentResolver操作数据
当外部应用需要对ContentProvider中的数据进行添加、删除、修改和查询操作时,可以使用ContentResolver类来完成,要获取ContentResolver对象,可以使用Context提供的getContentResolver()方法。
Context提供了以下方法来获取ContentResolver对象。
- getContentResolver():获取该应用默认的ContentResolver。
ContentResolver cr = getContentResolver();
一旦程序性中获取得了ContentResolver对象之后,接下来就可以调用ContentResolver的以下方法来操作数据。
- insert(uri,values):向Uri对应的ContentProvider中插入values对应的数据。
- delete(uri,where,selectionArgs):删除Uri对应的contentProvider中where提交匹配的数据。
- update(uri,values,where,selectionArgs):更新Uri对应的ContentProvider中where提交匹配的数据。
- query(uri,projection,selection,selectionArgs,SortOrder):查询Uri对应的ContentProvider中where提交匹配的数据。
4、ContentResolver与ContentProvider的关系
5、开发ContentProvider子类
示例ContentProvider,实现query()、insert()、update()、delete()方法,但并未真正对底层数据进行访问,只是输出一行字符串。代码如下:
public class MyContentProvider extends ContentProvider { public MyContentProvider() { } public boolean onCreate() { System.out.println("onCreate"); return true; } public String getType(Uri uri) { return null; } public Uri insert(Uri uri, ContentValues values) { System.out.println(uri + "=insert="); System.out.println("values参数为:" + values); return null; } public int delete(Uri uri, String where, String[] selectionArgs) { System.out.println(uri + "=delete="); System.out.println("where:" + where); return 0; } public Cursor query(Uri uri, String[] projection, String where, String[] selectionArgs, String sortOrder) { System.out.println(uri + "=query="); System.out.println("where:" + where); return null; } public int update(Uri uri, ContentValues values, String where, String[] selectionArgs) { System.out.println(uri + "=update="); System.out.println("where:" + where + "values:" + values); return 0; } }
在该ContentProvider供其他应用调用之前,还需要配置该ContentProvider。
- name:指定该ContentProvider的实现类的类目。
- authorities:指定该ContentProvider对应的Uri(相当于域名)。
- android:exported:指定ContentProvider是否允许其他应用调用。(true or false)
5、使用ContentResolver调用方法
public class MainActivity extends Activity { ContentResolver contentResolver; Uri uri = Uri.parse("songsong.uri.ContentProviderText"); protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.activity_main); contentResolver = getContentResolver(); //获取ContentResolver对象 } public void query(View source) { Cursor c = contentResolver.query(uri, null, "query_where", null, null); Toast.makeText(this, "远程ContentProvider返回Cursor为:" + c, Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show(); } public void insert(View source) { ContentValues values = new ContentValues(); values.put("name", "songsong"); Uri newUri = contentResolver.insert(uri, values); Toast.makeText(this, "远程ContentProvider新插入为:" + newUri, Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show(); } public void update(View source) { ContentValues values = new ContentValues(); values.put("name", "songsong"); int count = contentResolver.update(uri, values, "update_where", null); Toast.makeText(this, "远程ContentProvider更新记录为:" + count, Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show(); } public void detele(View source) { int count = contentResolver.delete(uri, "delete_where", null); Toast.makeText(this, "远程ContentProvider更新记录为:" + count, Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show(); } }
运行上面的程序并依次单击应用的4个按钮,并观察Logcat。
--------------------------------------------