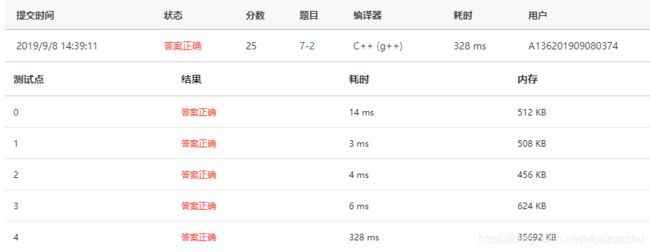
PAT-2019年秋季考试-甲级 7-2 Merging Linked Lists (25 分)
7-2 Merging Linked Lists (25 分)
Given two singly linked lists L1 = a1→a2→⋯→an−1→an and L2 = b1→b2→⋯→bm−1→bm . If n≥2m, you are supposed to reverse and merge the shorter one into the longer one to obtain a list like a1→a2→bm→a3→a4→bm−1⋯. For example, given one list being 6→7 and the other one 1→2→3→4→5, you must output 1→2→7→3→4→6→5.
Input Specification:
Each input file contains one test case. For each case, the first line contains the two addresses of the first nodes of L1 and L2 , plus a positive N (≤105) which is the total number of nodes given. The address of a node is a 5-digit nonnegative integer, and NULL is represented by -1.
Then N lines follow, each describes a node in the format:
Address Data Next
where Address is the position of the node, Data is a positive integer no more than 105 , and Next is the position of the next node. It is guaranteed that no list is empty, and the longer list is at least twice as long as the shorter one.
Output Specification:
For each case, output in order the resulting linked list. Each node occupies a line, and is printed in the same format as in the input.
Sample Input:
00100 01000 7
02233 2 34891
00100 6 00001
34891 3 10086
01000 1 02233
00033 5 -1
10086 4 00033
00001 7 -1
Sample Output:
01000 1 02233
02233 2 00001
00001 7 34891
34891 3 10086
10086 4 00100
00100 6 00033
00033 5 -1
题意
给你两条链表,将短的链表逆置后合并两条链表。合并方式:当长链表的序号比短链表的序号的两倍大时,同时将短链表的该序号元素插入长链表中
思路
根据输入将链表保存在map中,遍历map,使用容器保存两条链表
判断长度后将短链表逆置
从后往前遍历长链表,满足n大于或等于短链表长度的两倍时插入短链表最后一个元素并从短链表中删除,插入长链表元素
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#define maxsize 10000
using namespace std;
struct Node
{
string add, next;
int v;
};
int n;
string firstL1, firstL2;
unordered_map l;
vector l1, l2, out;
void comu(vector a, vector b)
{
int j = b.size() - 1;
for (int i = 0; i < b.size(); i++, j--)
{
if (i >= j)
break;
swap(b[i], b[j]);
}
for (int i = a.size() - 1; i >= 0; i--)
{
j = i + 1;
if (j <= (2 * b.size()))
{
out.push_back(b[b.size() - 1]);
b.pop_back();
}
out.push_back(a[i]);
}
}
int main()
{
std::iostream::sync_with_stdio(false);
std::cin.tie(0);
cin >> firstL1 >> firstL2 >> n;
string a, b;
int v;
Node tmpNode;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
cin >> tmpNode.add >> tmpNode.v >> tmpNode.next;
l.insert(make_pair(tmpNode.add, tmpNode));
}
a = firstL1;
while (l.find(a) != l.end())
{
tmpNode = l.find(a)->second;
l1.push_back(tmpNode);
if (tmpNode.next == "-1")
break;
a = tmpNode.next;
}
a = firstL2;
while (l.find(a) != l.end())
{
tmpNode = l.find(a)->second;
l2.push_back(tmpNode);
if (tmpNode.next == "-1")
break;
a = tmpNode.next;
}
int s1 = l1.size(), s2 = l2.size();
if (s1 >= (2 * s2))
comu(l1, l2);
else
comu(l2, l1);
for (int i = out.size() - 1; i >= 1; i--)
cout << out[i].add << " " << out[i].v << " " << out[i - 1].add << endl;
cout << out[0].add << " " << out[0].v << " " << -1 << endl;
return 0;
}