leetcode刷题笔记-DFS and BFS
212. Word Search II
在trie分类
529. Minesweeper
不会点击数字的,所以不用考虑这点
class Solution(object):
def updateBoard(self, board, click):
# 1. 如果是M雷的话,改成X结束
# 2. 如果不是M的话,附近有雷就改成数字结束。否则就是B,要DFS出附近的B
r, c = len(board), len(board[0])
x, y = click[0], click[1]
if board[x][y] == 'M':
board[x][y] = 'X'
else: # 找附近有没有雷,有就是数字,没有就是B. B的话要查附近的B
count = 0
for dx, dy in ([-1, -1], [-1, 0], [-1, 1], [0, -1], [0, 1], [1, -1], [1, 0], [1, 1]):
if 0 <= x + dx < r and 0 <= y + dy < c and board[x+dx][y+dy] == 'M':
count += 1
if count > 0:
board[x][y] = str(count)
else:
board[x][y] = 'B'
for dx, dy in ([-1, -1], [-1, 0], [-1, 1], [0, -1], [0, 1], [1, -1], [1, 0], [1, 1]):
if 0 <= x + dx < r and 0 <= y + dy < c and board[x+dx][y+dy] == 'E':
self.updateBoard(board, [x+dx, y+dy])
return board827. Making A Large Island
class Solution(object):
def largestIsland(self, grid):
def move(x, y):
for i, j in ([1, 0], [-1, 0], [0, 1], [0, -1]):
if 0 <= x+i < len(grid) and 0 <= y+j < len(grid[0]):
yield x+i, y+j
def dfs(x, y, index):
area = 0
grid[x][y] = index
for i, j in move(x, y):
if grid[i][j] == 1:
area += dfs(i, j, index)
return area + 1
index = 2
area = {}
for i in xrange(len(grid)):
for j in xrange(len(grid[0])):
if grid[i][j] == 1:
area[index] = dfs(i, j, index)
index += 1
# traverse every 0 cell and count biggest island it can conntect
res = max(area.values()+[0])
for i in xrange(len(grid)):
for j in xrange(len(grid[0])):
if grid[i][j] == 0:
possible = set(grid[x][y] for x, y in move(i, j) if grid[x][y] > 1)
res = max(res, sum(area[index] for index in possible)+1) # add 1 for the change of 0 to 1
return res
815. Bus Routes
class Solution(object):
def numBusesToDestination(self, routes, S, T):
stopToRoutes = collections.defaultdict(set)
for i, stops in enumerate(routes):
for stop in stops:
stopToRoutes[stop].add(i)
bfs = [(S, 0)]
visited = set([S])
while bfs:
curstop, bus = bfs.pop(0)
if curstop == T:
return bus
for route in stopToRoutes[curstop]:
for stop in routes[route]:
if stop not in visited:
visited.add(stop)
bfs.append((stop, bus+1))
routes[route] = []
return -1909. Snakes and Ladders
class Solution(object):
def snakesAndLadders(self, board):
n = len(board)
visited = {1: 0}
bfs = [1]
for x in bfs: # current
for i in xrange(x+1, x+7): # next x
r, c = (i-1)/n, (i-1)%n
nxt = board[~r][c if r % 2 == 0 else ~c]
if nxt > 0: i = nxt
if i == n*n: return visited[x] + 1
if i not in visited:
visited[i] = visited[x] + 1
bfs.append(i)
return -1
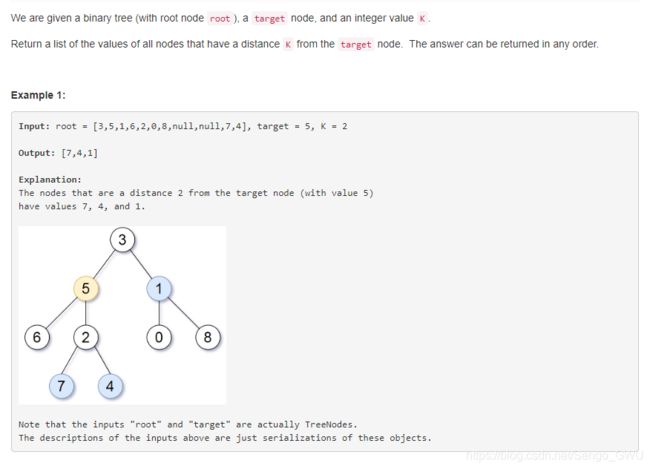
863. All Nodes Distance K in Binary Tree
class Solution(object):
def distanceK(self, root, target, K):
"""
:type root: TreeNode
:type target: TreeNode
:type K: int
:rtype: List[int]
"""
adj, res, visited = collections.defaultdict(list), [], set()
def dfs(node): # connect the nodes, convert the tree to graph
if node.left:
adj[node].append(node.left)
adj[node.left].append(node)
dfs(node.left)
if node.right:
adj[node].append(node.right)
adj[node.right].append(node)
dfs(node.right)
dfs(root)
def dfs2(node, dis):
if dis < K:
visited.add(node)
for n in adj[node]:
if n not in visited:
dfs2(n, dis+1)
else:
res.append(node.val)
dfs2(target, 0)
return res
317. Shortest Distance from All Buildings
BFS, 这个时间要728ms 应该不是最优解法,但是感觉是比较常规的解法。有的更优解法只适合自己一题的题型可能看了意义也不大。
class Solution(object):
def shortestDistance(self, grid):
"""
:type grid: List[List[int]]
:rtype: int
"""
r, c = len(grid), len(grid[0])
distance = [[0] * c for _ in xrange(r)]
reach = [[0] * c for _ in xrange(r)]
buildingNum = 0
for i in xrange(r):
for j in xrange(c):
if grid[i][j] == 1:
buildingNum += 1
q = [(i, j, 0)] # i, j, d
visited = [[0] * c for _ in xrange(r)]
# BFS
for x, y, d in q:
for j, k in ([1, 0], [-1, 0], [0, 1], [0, -1]):
X = x + j
Y = y + k
if 0 <= X < r and 0 <= Y < c and grid[X][Y] == 0 and visited[X][Y] == 0:
visited[X][Y] = 1
distance[X][Y] += d + 1
reach[X][Y] += 1
q.append((X, Y, d+1))
shortest = sys.maxint
for i in xrange(r):
for j in xrange(c):
if grid[i][j] == 0 and reach[i][j] == buildingNum:
shortest = min(shortest , distance[i][j])
return shortest if shortest < sys.maxint else -1694. Number of Distinct Islands
DFS, 用list存储遍历的方向,方向用up,left, down, right 英文表示。 记得要加back这个方向。
class Solution(object):
def numDistinctIslands(self, grid):
"""
:type grid: List[List[int]]
:rtype: int
"""
def dfs(i, j, shape, dirc):
if i < 0 or i >= len(grid) or j < 0 or j >= len(grid[0]) or grid[i][j] != 1:
return
grid[i][j] = 0
shape.append(dirc)
dfs(i-1, j, shape, 'u')
dfs(i+1, j, shape, 'd')
dfs(i, j-1, shape, 'l')
dfs(i, j+1, shape, 'r')
shape.append('b') # back 没有back 就失败了
return shape
re = set()
for i in xrange(len(grid)):
for j in xrange(len(grid[0])):
if grid[i][j]:
shape = dfs(i, j, [], 'o')
re.add(''.join(shape))
return len(re)559. Maximum Depth of N-ary Tree
easy
BFS
Given a n-ary tree, find its maximum depth.
The maximum depth is the number of nodes along the longest path from the root node down to the farthest leaf node.
For example, given a 3-ary tree:
![]()
We should return its max depth, which is 3.
Note:
- The depth of the tree is at most
1000. - The total number of nodes is at most
5000.
思路:The solution uses 'X' to indicate the end of all nodes on a level in the queue. The 'X' gets added only after all the nodes from the same level are enqueued.
"""
# Definition for a Node.
class Node(object):
def __init__(self, val, children):
self.val = val
self.children = children
"""
class Solution(object):
def maxDepth(self, root):
"""
:type root: Node
:rtype: int
"""
if not root: return 0
if not root.children: return 1
depth = 0
q = [root, 'X']
while len(q):
node = q.pop(0)
if node == 'X':
depth += 1
if len(q):
q.append('X')
continue
if node.children:
for n in node.children:
q.append(n)
return depth
690. Employee Importance
easy
You are given a data structure of employee information, which includes the employee's unique id, his importance value and his directsubordinates' id.
For example, employee 1 is the leader of employee 2, and employee 2 is the leader of employee 3. They have importance value 15, 10 and 5, respectively. Then employee 1 has a data structure like [1, 15, [2]], and employee 2 has [2, 10, [3]], and employee 3 has [3, 5, []]. Note that although employee 3 is also a subordinate of employee 1, the relationship is not direct.
Now given the employee information of a company, and an employee id, you need to return the total importance value of this employee and all his subordinates.
Example 1:
Input: [[1, 5, [2, 3]], [2, 3, []], [3, 3, []]], 1
Output: 11
Explanation:
Employee 1 has importance value 5, and he has two direct subordinates: employee 2 and employee 3. They both have importance value 3. So the total importance value of employee 1 is 5 + 3 + 3 = 11.
"""
# Employee info
class Employee(object):
def __init__(self, id, importance, subordinates):
# It's the unique id of each node.
# unique id of this employee
self.id = id
# the importance value of this employee
self.importance = importance
# the id of direct subordinates
self.subordinates = subordinates
"""
class Solution(object):
def getImportance(self, employees, id):
"""
:type employees: Employee
:type id: int
:rtype: int
"""
d = {e.id: e for e in employees}
res = 0
q = [d[id]]
while q:
e = q.pop()
res += e.importance
for s in e.subordinates:
q.append(d[s])
return res733. Flood Fill
easy DFS
An image is represented by a 2-D array of integers, each integer representing the pixel value of the image (from 0 to 65535).
Given a coordinate (sr, sc) representing the starting pixel (row and column) of the flood fill, and a pixel value newColor, "flood fill" the image.
To perform a "flood fill", consider the starting pixel, plus any pixels connected 4-directionally to the starting pixel of the same color as the starting pixel, plus any pixels connected 4-directionally to those pixels (also with the same color as the starting pixel), and so on. Replace the color of all of the aforementioned pixels with the newColor.
At the end, return the modified image.
Example 1:
Input:
image = [[1,1,1],[1,1,0],[1,0,1]]
sr = 1, sc = 1, newColor = 2
Output: [[2,2,2],[2,2,0],[2,0,1]]
Explanation:
From the center of the image (with position (sr, sc) = (1, 1)), all pixels connected
by a path of the same color as the starting pixel are colored with the new color.
Note the bottom corner is not colored 2, because it is not 4-directionally connected
to the starting pixel.class Solution(object):
def floodFill(self, image, sr, sc, newColor):
"""
:type image: List[List[int]]
:type sr: int
:type sc: int
:type newColor: int
:rtype: List[List[int]]
"""
visited = [[0]*len(image[0]) for i in image]
return self.helper(image, visited, sr, sc, newColor, image[sr][sc])
def helper(self, image, visited, sr, sc, newColor, oldColor):
if not ( 0 <= sr < len(image) and 0 <= sc < len(image[0])) or visited[sr][sc] or image[sr][sc] != oldColor:
return image
image[sr][sc] = newColor
visited[sr][sc] = 1
offset = ((0, 1), (0, -1), (1, 0), (-1, 0))
for off in offset:
image = self.helper(image, visited, sr+off[0], sc+off[1], newColor, oldColor)
return image108. Convert Sorted Array to Binary Search Tree
Given an array where elements are sorted in ascending order, convert it to a height balanced BST.
For this problem, a height-balanced binary tree is defined as a binary tree in which the depth of the two subtrees of every node never differ by more than 1.
Example:
Given the sorted array: [-10,-3,0,5,9],
One possible answer is: [0,-3,9,-10,null,5], which represents the following height balanced BST:
0
/ \
-3 9
/ /
-10 5思路:
For a sorted array, the left half will be in the left subtree, middle value as the root, right half in the right subtree. This holds through for every node:
[1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7] -> left: [1, 2, 3], root: 4, right: [5, 6, 7][1, 2, 3] -> left: [1], root: 2, right: [3][5, 6, 7] -> left: [5], root: 6, right: [7]
Many of the approaches here suggest slicing an array recursively and passing them. However, slicing the array is expensive. It is better to pass the left and right bounds into recursive calls instead.
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode(object):
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.left = None
# self.right = None
class Solution(object):
def sortedArrayToBST(self, nums):
"""
:type nums: List[int]
:rtype: TreeNode
"""
def helper(left, right):
if left > right:
return None
mid = (right + left) // 2
node = TreeNode(nums[mid])
node.left = helper(left, mid-1)
node.right = helper(mid+1, right)
return node
return helper(0, len(nums)-1)257. Binary Tree Paths
easy DFS stack
Given a binary tree, return all root-to-leaf paths.
Note: A leaf is a node with no children.
Example:
Input:
1
/ \
2 3
\
5
Output: ["1->2->5", "1->3"]
Explanation: All root-to-leaf paths are: 1->2->5, 1->3# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode(object):
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.left = None
# self.right = None
class Solution(object):
def binaryTreePaths(self, root):
"""
:type root: TreeNode
:rtype: List[str]
"""
if not root:
return []
res, queue = [], [(root, "")]
while queue:
node, string = queue.pop(0)
if node.right:
queue.append((node.right, string+str(node.val)+'->'))
if node.left:
queue.append((node.left, string+str(node.val)+'->'))
if not node.left and not node.right:
res.append(string + str(node.val))
return res110. Balanced Binary Tree
Given a binary tree, determine if it is height-balanced.
For this problem, a height-balanced binary tree is defined as:
a binary tree in which the depth of the two subtrees of every node never differ by more than 1.
Example 1:
Given the following tree [3,9,20,null,null,15,7]:
3
/ \
9 20
/ \
15 7Return true.
Example 2:
Given the following tree [1,2,2,3,3,null,null,4,4]:
1
/ \
2 2
/ \
3 3
/ \
4 4
Return false.
class Solution(object):
def isBalanced(self, root):
"""
:type root: TreeNode
:rtype: bool
"""
if not root:
return True
return abs(self.countHeight(root.left) - self.countHeight(root.right)) < 2 \
and self.isBalanced(root.left) and self.isBalanced(root.right)
def countHeight(self, node):
if not node:
return 0
return max(self.countHeight(node.left), self.countHeight(node.right)) + 1111. Minimum Depth of Binary Tree
Given a binary tree, find its minimum depth.
The minimum depth is the number of nodes along the shortest path from the root node down to the nearest leaf node.
Note: A leaf is a node with no children.
Example:
Given binary tree [3,9,20,null,null,15,7],
3
/ \
9 20
/ \
15 7return its minimum depth = 2.
DFS:
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode(object):
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.left = None
# self.right = None
class Solution(object):
def minDepth(self, root):
"""
:type root: TreeNode
:rtype: int
"""
if not root:
return 0
if None in (root.left, root.right):
return max(self.minDepth(root.left), self.minDepth(root.right)) + 1
else:
return min(self.minDepth(root.left), self.minDepth(root.right)) + 1513. Find Bottom Left Tree Value
Given a binary tree, find the leftmost value in the last row of the tree.
Example 1:
Input:
2
/ \
1 3
Output:
1
Example 2:
Input:
1
/ \
2 3
/ / \
4 5 6
/
7
Output:
7# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode(object):
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.left = None
# self.right = None
class Solution(object):
def findBottomLeftValue(self, root):
"""
:type root: TreeNode
:rtype: int
"""
# BFS
queue = [root]
for node in queue:
queue += filter(None, [node.right, node.left])
return node.val515. Find Largest Value in Each Tree Row
You need to find the largest value in each row of a binary tree.
Example:
Input:
1
/ \
3 2
/ \ \
5 3 9
Output: [1, 3, 9]结合了前面题目的方法。
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode(object):
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.left = None
# self.right = None
class Solution(object):
def largestValues(self, root):
"""
:type root: TreeNode
:rtype: List[int]
"""
res = []
if not root:
return res
q = [root, "X"]
maxValue = float('-inf')
while q:
node = q.pop(0)
if node == 'X':
res.append(maxValue)
maxValue = float('-inf')
if len(q):
q.append('X')
else:
q += filter(None, [node.left, node.right])
maxValue = max(maxValue, node.val)
return res别人的解法,妈呀唉:
def findValueMostElement(self, root):
maxes = []
row = [root]
while any(row):
maxes.append(max(node.val for node in row))
row = [kid for node in row for kid in (node.left, node.right) if kid]
return maxes547. Friend Circles
There are N students in a class. Some of them are friends, while some are not. Their friendship is transitive in nature. For example, if A is a direct friend of B, and B is a direct friend of C, then A is an indirect friend of C. And we defined a friend circle is a group of students who are direct or indirect friends.
Given a N*N matrix M representing the friend relationship between students in the class. If M[i][j] = 1, then the ith and jth students are direct friends with each other, otherwise not. And you have to output the total number of friend circles among all the students.
Example 1:
Input:
[[1,1,0],
[1,1,0],
[0,0,1]]
Output: 2
Explanation:The 0th and 1st students are direct friends, so they are in a friend circle.
The 2nd student himself is in a friend circle. So return 2.
Example 2:
Input:
[[1,1,0],
[1,1,1],
[0,1,1]]
Output: 1
Explanation:The 0th and 1st students are direct friends, the 1st and 2nd students are direct friends,
so the 0th and 2nd students are indirect friends. All of them are in the same friend circle, so return 1.人都是0到N
class Solution(object):
def findCircleNum(self, M):
"""
:type M: List[List[int]]
:rtype: int
"""
visited = set()
circle = 0
def dfs(people):
visited.add(people)
for friend in xrange(len(M)):
if M[people][friend] and friend not in visited:
dfs(friend)
for people in xrange(len(M)):
if people not in visited:
circle += 1
dfs(people)
return circle638. Shopping Offers
In LeetCode Store, there are some kinds of items to sell. Each item has a price.
However, there are some special offers, and a special offer consists of one or more different kinds of items with a sale price.
You are given the each item's price, a set of special offers, and the number we need to buy for each item. The job is to output the lowest price you have to pay for exactly certain items as given, where you could make optimal use of the special offers.
Each special offer is represented in the form of an array, the last number represents the price you need to pay for this special offer, other numbers represents how many specific items you could get if you buy this offer.
You could use any of special offers as many times as you want.
Example 1:
Input: [2,5], [[3,0,5],[1,2,10]], [3,2]
Output: 14
Explanation:
There are two kinds of items, A and B. Their prices are $2 and $5 respectively.
In special offer 1, you can pay $5 for 3A and 0B
In special offer 2, you can pay $10 for 1A and 2B.
You need to buy 3A and 2B, so you may pay $10 for 1A and 2B (special offer #2), and $4 for 2A.
Example 2:
Input: [2,3,4], [[1,1,0,4],[2,2,1,9]], [1,2,1]
Output: 11
Explanation:
The price of A is $2, and $3 for B, $4 for C.
You may pay $4 for 1A and 1B, and $9 for 2A ,2B and 1C.
You need to buy 1A ,2B and 1C, so you may pay $4 for 1A and 1B (special offer #1), and $3 for 1B, $4 for 1C.
You cannot add more items, though only $9 for 2A ,2B and 1C.
Note:
- There are at most 6 kinds of items, 100 special offers.
- For each item, you need to buy at most 6 of them.
- You are not allowed to buy more items than you want, even if that would lower the overall price.
这个写法太好了,很简洁直接。
class Solution(object):
def shoppingOffers(self, price, special, needs):
"""
:type price: List[int]
:type special: List[List[int]]
:type needs: List[int]
:rtype: int
"""
d = {}
def dfs(curNeeds):
val = sum(curNeeds[i]*price[i] for i in xrange(len(needs))) # cost without special
for spec in special:
tmpNeeds = [curNeeds[j] - spec[j] for j in xrange(len(needs))]
if min(tmpNeeds) >= 0:
val = min(val, d.get(tuple(tmpNeeds), dfs(tmpNeeds)) + spec[-1])
d[tuple(curNeeds)] = val
return val
return dfs(needs)337. House Robber III
The thief has found himself a new place for his thievery again. There is only one entrance to this area, called the "root." Besides the root, each house has one and only one parent house. After a tour, the smart thief realized that "all houses in this place forms a binary tree". It will automatically contact the police if two directly-linked houses were broken into on the same night.
Determine the maximum amount of money the thief can rob tonight without alerting the police.
Example 1:
Input: [3,2,3,null,3,null,1]
3
/ \
2 3
\ \
3 1
Output: 7
Explanation: Maximum amount of money the thief can rob = 3 + 3 + 1 = 7.Example 2:
Input: [3,4,5,1,3,null,1]
3
/ \
4 5
/ \ \
1 3 1
Output: 9
Explanation: Maximum amount of money the thief can rob = 4 + 5 = 9.
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode(object):
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.left = None
# self.right = None
class Solution(object):
def rob(self, root):
"""
:type root: TreeNode
:rtype: int
"""
def superRob(node):
# returns tuple of size two (now, later)
# now: max money earned if input node is robbed
# later: max money earned if input node is not robbed
if not node: return (0, 0)
left, right = superRob(node.left), superRob(node.right)
# rob now
now = node.val + left[1] + right[1]
# rob later
later = max(left) + max(right)
return now, later
return max(superRob(root))199. Binary Tree Right Side View
Given a binary tree, imagine yourself standing on the right side of it, return the values of the nodes you can see ordered from top to bottom.
Example:
Input: [1,2,3,null,5,null,4]
Output: [1, 3, 4]
Explanation:
1 <---
/ \
2 3 <---
\ \
5 4 <---和之前的题目方法一样,每层的Node放到queue中
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode(object):
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.left = None
# self.right = None
class Solution(object):
def rightSideView(self, root):
"""
:type root: TreeNode
:rtype: List[int]
"""
if not root:
return []
q = [root]
res = []
while q:
res.append(q[-1].val)
q = [kid for node in q for kid in (node.left, node.right) if kid]
return res129. Sum Root to Leaf Numbers
Given a binary tree containing digits from 0-9 only, each root-to-leaf path could represent a number.
An example is the root-to-leaf path 1->2->3 which represents the number 123.
Find the total sum of all root-to-leaf numbers.
Note: A leaf is a node with no children.
Example:
Input: [1,2,3]
1
/ \
2 3
Output: 25
Explanation:
The root-to-leaf path 1->2 represents the number 12.
The root-to-leaf path 1->3 represents the number 13.
Therefore, sum = 12 + 13 = 25.
Example 2:
Input: [4,9,0,5,1]
4
/ \
9 0
/ \
5 1
Output: 1026
Explanation:
The root-to-leaf path 4->9->5 represents the number 495.
The root-to-leaf path 4->9->1 represents the number 491.
The root-to-leaf path 4->0 represents the number 40.
Therefore, sum = 495 + 491 + 40 = 1026.
标准的DFS:
class Solution(object):
def sumNumbers(self, root):
"""
:type root: TreeNode
:rtype: int
"""
if not root:
return 0
# dfs
stack = [[root, root.val]]
res = 0
while stack:
node, value = stack.pop()
if node.left:
stack.append([node.left, value*10+node.left.val])
if node.right:
stack.append([node.right, value*10+node.right.val])
if not node.left and not node.right:
res += value
return resBFS
class Solution(object):
def sumNumbers(self, root):
"""
:type root: TreeNode
:rtype: int
"""
if not root:
return 0
# dfs
stack = [[root, root.val]]
res = 0
while stack:
node, value = stack.pop(0)
if node.left:
stack.append([node.left, value*10+node.left.val])
if node.right:
stack.append([node.right, value*10+node.right.val])
if not node.left and not node.right:
res += value
return res
200. Number of Islands
Given a 2d grid map of '1's (land) and '0's (water), count the number of islands. An island is surrounded by water and is formed by connecting adjacent lands horizontally or vertically. You may assume all four edges of the grid are all surrounded by water.
Example 1:
Input:
11110
11010
11000
00000
Output: 1
Example 2:
Input:
11000
11000
00100
00011
Output: 3第一次解法超时:
class Solution(object):
def numIslands(self, grid):
"""
:type grid: List[List[str]]
:rtype: int
"""
def dfs(row, col):
if row < 0 or row >= len(grid) or col < 0 or col >= len(grid[0]):
return
if visited[row][col]:
return
else:
visited[row][col] = 1
if grid[row][col] == 0: return
for i, j in ([0, 1], [0, -1], [1, 0], [-1, 0]):
dfs(row+i, col+j)
visited = [[0]*len(grid[0]) for i in grid]
count = 0
for row in xrange(len(grid)):
for col in xrange(len(grid[0])):
if grid[row][col] and visited[row][col] == 0:
count += 1
dfs(row, col)
return count参考别人的解法后不用visited来判断是否访问过,直接在原grid上把访问过的改成‘#’,其他思路一样
class Solution(object):
def numIslands(self, grid):
"""
:type grid: List[List[str]]
:rtype: int
"""
if not grid:
return 0
def dfs(row, col):
if row < 0 or row >= len(grid) or col < 0 or col >= len(grid[0]) or grid[row][col] != '1':
return
grid[row][col] = '#'
for i, j in ([0, 1], [0, -1], [1, 0], [-1, 0]):
dfs(row+i, col+j)
count = 0
for row in xrange(len(grid)):
for col in xrange(len(grid[0])):
if grid[row][col] == '1':
count += 1
dfs(row, col)
return count473. Matchsticks to Square
Remember the story of Little Match Girl? By now, you know exactly what matchsticks the little match girl has, please find out a way you can make one square by using up all those matchsticks. You should not break any stick, but you can link them up, and each matchstick must be used exactly one time.
Your input will be several matchsticks the girl has, represented with their stick length. Your output will either be true or false, to represent whether you could make one square using all the matchsticks the little match girl has.
Example 1:
Input: [1,1,2,2,2]
Output: true
Explanation: You can form a square with length 2, one side of the square came two sticks with length 1.
Example 2:
Input: [3,3,3,3,4]
Output: false
Explanation: You cannot find a way to form a square with all the matchsticks.why we need sort(reverse=True), e.g. sum=7*4=28 [6,6,4,4,4,3,1] should return False. 如果排序的话,[7,7,7,7] 先减去大的,6 和4后剩下【1,1,3,3】 剩下【4,3,1】,直接就返回false。 不排序的话,会减去很多个小的后才发现不能满足,导致TLE。
class Solution(object):
def makesquare(self, nums):
"""
:type nums: List[int]
:rtype: bool
"""
s = sum(nums)
if s % 4 or len(nums) < 4 or max(nums) > s / 4:
return False
def dfs(nums, index, target):
if index == len(nums): return True
for i in xrange(4):
if target[i] >= nums[index]:
target[i] -= nums[index]
if dfs(nums, index + 1, target): return True
target[i] += nums[index]
return False
s /= 4
n = len(nums)
nums.sort(reverse=True)
target = [s] * 4
return dfs(nums, 0, target)class Solution(object):
def makesquare(self, nums):
"""
:type nums: List[int]
:rtype: bool
"""
s = sum(nums)
side = s / 4
if s % 4 or len(nums) < 4 or max(nums) > side :
return False
_sum = [0] * 4
def dfs(index):
if index == len(nums): # 不用减1
return _sum[0] == _sum[1] == _sum[2] == side
for i in xrange(4):
if _sum[i] + nums[index] <= side: # 这里要加nums[index]
_sum[i] += nums[index]
if dfs(index + 1):
return True
_sum[i] -= nums[index]
return False
nums.sort(reverse=True)
return dfs(0)
417. Pacific Atlantic Water Flow
Given an m x n matrix of non-negative integers representing the height of each unit cell in a continent, the "Pacific ocean" touches the left and top edges of the matrix and the "Atlantic ocean" touches the right and bottom edges.
Water can only flow in four directions (up, down, left, or right) from a cell to another one with height equal or lower.
Find the list of grid coordinates where water can flow to both the Pacific and Atlantic ocean.
Note:
- The order of returned grid coordinates does not matter.
- Both m and n are less than 150.
Example:
Given the following 5x5 matrix:
Pacific ~ ~ ~ ~ ~
~ 1 2 2 3 (5) *
~ 3 2 3 (4) (4) *
~ 2 4 (5) 3 1 *
~ (6) (7) 1 4 5 *
~ (5) 1 1 2 4 *
* * * * * Atlantic
Return:
[[0, 4], [1, 3], [1, 4], [2, 2], [3, 0], [3, 1], [4, 0]] (positions with parentheses in above matrix).思路倒是很简单,但是结果老是不对,对条件的判断容易错,导致花费了好几个小时在这题上。
class Solution(object):
def pacificAtlantic(self, matrix):
"""
:type matrix: List[List[int]]
:rtype: List[List[int]]
"""
if not matrix:
return []
n, m, res = len(matrix), len(matrix[0]), []
pVisited, aVisited = [[0]*m for i in matrix], [[0]*m for i in matrix]
def DFS(row, col, preHeight, visited):
if row < 0 or col < 0 or row > n-1 or col > m-1 or visited[row][col]:
return
height = matrix[row][col]
if height < preHeight:
return
visited[row][col] = 1
offsets = ([0, 1], [0, -1], [-1, 0], [1, 0])
for i,j in offsets:
DFS(row+i, col+j, height, visited)
for i in xrange(n):
DFS(i, 0, 0, pVisited)
DFS(i, m-1, 0, aVisited)
for j in xrange(m):
DFS(0, j, 0, pVisited)
DFS(n-1, j, 0, aVisited)
for i in xrange(n):
for j in xrange(m):
if aVisited[i][j] and pVisited[i][j]:
res.append([i, j])
return res116. Populating Next Right Pointers in Each Node
Given a binary tree
struct TreeLinkNode {
TreeLinkNode *left;
TreeLinkNode *right;
TreeLinkNode *next;
}
Populate each next pointer to point to its next right node. If there is no next right node, the next pointer should be set to NULL.
Initially, all next pointers are set to NULL.
Note:
- You may only use constant extra space.
- Recursive approach is fine, implicit stack space does not count as extra space for this problem.
- You may assume that it is a perfect binary tree (ie, all leaves are at the same level, and every parent has two children).
Example:
Given the following perfect binary tree,
1
/ \
2 3
/ \ / \
4 5 6 7
After calling your function, the tree should look like:
1 -> NULL
/ \
2 -> 3 -> NULL
/ \ / \
4->5->6->7 -> NULLclass Solution:
# @param root, a tree link node
# @return nothing
def connect(self, root):
if not root:
return root
q = [root]
right = None
while q:
for node in q:
node.next = right
right = node
right = None
q = [kid for node in q for kid in (node.right, node.left) if kid]
O(1) space
class Solution:
# @param root, a tree link node
# @return nothing
def connect(self, root):
if not root:
return None
cur = root # cur _next 存最左的那个node
_next = root.left
while cur.left:
cur.left.next = cur.right
if cur.next:
cur.right.next = cur.next.left
cur = cur.next
else:
cur = _next
_next = cur.left
117. Populating Next Right Pointers in Each Node II
Given a binary tree
struct TreeLinkNode {
TreeLinkNode *left;
TreeLinkNode *right;
TreeLinkNode *next;
}
Populate each next pointer to point to its next right node. If there is no next right node, the next pointer should be set to NULL.
Initially, all next pointers are set to NULL.
Note:
- You may only use constant extra space.
- Recursive approach is fine, implicit stack space does not count as extra space for this problem.
Example:
Given the following binary tree,
1
/ \
2 3
/ \ \
4 5 7
After calling your function, the tree should look like:
1 -> NULL
/ \
2 -> 3 -> NULL
/ \ \
4-> 5 -> 7 -> NULLO(1)space
class Solution:
# @param root, a tree link node
# @return nothing
def connect(self, node):
tail = dummy = TreeLinkNode(0)
while node:
tail.next = node.left
if tail.next:
tail = tail.next
tail.next = node.right
if node.right:
tail = tail.next
node = node.next
if not node:
tail = dummy # 这里要指向dummy,下一次的node = dummy.next 才会是下一层
node = dummy.next
class Solution:
# @param root, a tree link node
# @return nothing
def connect(self, root):
if not root:
return root
q = [root]
right = None
while q:
for node in q:
node.next = right
right = node
right = None
q = [kid for node in q for kid in (node.right, node.left) if kid]542. 01 Matrix
Given a matrix consists of 0 and 1, find the distance of the nearest 0 for each cell.
The distance between two adjacent cells is 1.
Example 1:
Input:
0 0 0
0 1 0
0 0 0
Output:
0 0 0
0 1 0
0 0 0
Example 2:
Input:
0 0 0
0 1 0
1 1 1
Output:
0 0 0
0 1 0
1 2 1看了讨论里面的答案,无以言表的好,太棒了!
class Solution(object):
def updateMatrix(self, matrix):
"""
:type matrix: List[List[int]]
:rtype: List[List[int]]
"""
n, m = len(matrix), len(matrix[0])
q = []
for i in xrange(n):
for j in xrange(m):
if matrix[i][j] != 0:
matrix[i][j] = 0x7fffff
else:
q.append((i, j))
for i, j in q:
z = matrix[i][j] + 1
for r, c in ((i+1, j), (i-1, j), (i, j+1), (i, j-1)):
if 0 <= r < n and 0 <= c < m and matrix[r][c] > z:
matrix[r][c] = z
q.append((r,c))
return matrix
把没处理过的设置为‘#’, 它等于周边处理过的加1
class Solution(object):
def updateMatrix(self, matrix):
"""
:type matrix: List[List[int]]
:rtype: List[List[int]]
"""
n, m = len(matrix), len(matrix[0])
q = []
for i in xrange(n):
for j in xrange(m):
if matrix[i][j] != 0:
matrix[i][j] = '#'
else:
q.append((i, j))
for i, j in q:
z = matrix[i][j] + 1
for r, c in ((i+1, j), (i-1, j), (i, j+1), (i, j-1)):
if 0 <= r < n and 0 <= c < m and matrix[r][c] == '#':
matrix[r][c] = z
q.append((r,c))
return matrix
98. Validate Binary Search Tree
Given a binary tree, determine if it is a valid binary search tree (BST).
Assume a BST is defined as follows:
- The left subtree of a node contains only nodes with keys less than the node's key.
- The right subtree of a node contains only nodes with keys greater than the node's key.
- Both the left and right subtrees must also be binary search trees.
Example 1:
Input:
2
/ \
1 3
Output: true
Example 2:
5
/ \
1 4
/ \
3 6
Output: false
Explanation: The input is: [5,1,4,null,null,3,6]. The root node's value
is 5 but its right child's value is 4.class Solution(object):
def isValidBST(self, root, smallerThan=float('inf'), largerThan=float('-inf')):
"""
:type root: TreeNode
:rtype: bool
"""
if not root:
return True
if root.val <= largerThan or root.val >= smallerThan:
return False
return self.isValidBST(root.left, min(smallerThan, root.val), largerThan) and self.isValidBST(root.right, smallerThan, max(largerThan, root.val))130. Surrounded Regions
Given a 2D board containing 'X' and 'O' (the letter O), capture all regions surrounded by 'X'.
A region is captured by flipping all 'O's into 'X's in that surrounded region.
Example:
X X X X
X O O X
X X O X
X O X X
After running your function, the board should be:
X X X X
X X X X
X X X X
X O X X
Explanation:
Surrounded regions shouldn’t be on the border, which means that any 'O' on the border of the board are not flipped to 'X'. Any 'O' that is not on the border and it is not connected to an 'O' on the border will be flipped to 'X'. Two cells are connected if they are adjacent cells connected horizontally or vertically.
从边缘做DFS
class Solution(object):
def solve(self, board):
"""
:type board: List[List[str]]
:rtype: void Do not return anything, modify board in-place instead.
"""
if not board:
return
self.n, self.m = len(board), len(board[0])
def dfs(board, i, j):
if board[i][j] != 'O':
return
else:
board[i][j] = 'Z'
for x, y in ((i+1, j), (i-1, j), (i, j+1), (i, j-1)):
if 0 <= x < self.n and 0 <= y < self.m:
dfs(board, x, y)
for i in xrange(self.n):
dfs(board, i, 0)
dfs(board, i, self.m-1)
for j in xrange(self.m):
dfs(board, 0, j)
dfs(board, self.n-1, j)
for i in xrange(self.n):
for j in xrange(self.m):
if board[i][j] == 'O':
board[i][j] = 'X'
elif board[i][j] == 'Z':
board[i][j] = 'O'
79. Word Search
class Solution(object):
def exist(self, board, word):
"""
:type board: List[List[str]]
:type word: str
:rtype: bool
"""
for i in xrange(len(board)):
for j in xrange(len(board[0])):
if self.dfs(board, word, i, j):
return True
return False
def dfs(self, board, word, i, j):
if word[0] != board[i][j]:
return
board[i][j] = '#'
w, word = word[0], word[1:]
if not word:
return True
for x, y in ((i + 1, j), (i - 1, j), (i, j + 1), (i, j - 1)):
if 0 <= x < len(board) and 0 <= y < len(board[0]):
if self.dfs(board, word, x, y):
return True
board[i][j] = w127. Word Ladder
class Solution(object):
def ladderLength(self, beginWord, endWord, wordList):
"""
:type beginWord: str
:type endWord: str
:type wordList: List[str]
:rtype: int
"""
wordList = set(wordList)
queue = collections.deque([[beginWord, 1]])
while queue:
word, length = queue.popleft()
if word == endWord:
return length
for i in xrange(len(beginWord)):
for c in 'abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz':
next_word = word[:i] + c + word[i+1:]
if next_word in wordList:
queue.append([next_word, length+1])
wordList.remove(next_word)
return 0
126. Word Ladder II
class Solution(object):
def findLadders(self, beginWord, endWord, wordList):
"""
:type beginWord: str
:type endWord: str
:type wordList: List[str]
:rtype: List[List[str]]
"""
wordList = set(wordList)
layer = {}
layer[beginWord] = [[beginWord]]
res = []
while layer:
newLayer = collections.defaultdict(list)
for w in layer:
if w == endWord:
return layer[endWord]
else:
for i in xrange(len(w)):
for c in "abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz":
neww = w[:i] + c + w[i+1:]
if neww in wordList:
newLayer[neww] += [l + [neww] for l in layer[w]]
wordList -= set(newLayer.keys())
layer = newLayer
return res
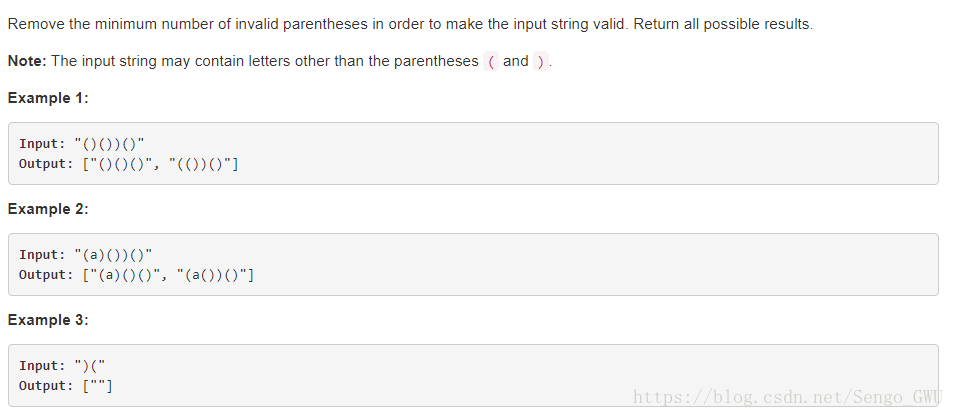
301. Remove Invalid Parentheses
class Solution(object):
def removeInvalidParentheses(self, s):
def isValid(s):
l = 0
for c in s:
if c == '(':
l += 1
elif c == ')':
l -= 1
if l < 0: # 注意这里别漏了
return False
return l == 0
level = {s} # set
while True:
re = filter(isValid, level)
if re: return re
else:
level = {s[:i] + s[i+1:] for s in level for i in xrange(len(s))} # 注意是set785. Is Graph Bipartite?
思路:把边的另外一个点涂成另外一个颜色。
我的: 写完通过懒得优化代码了。
class Solution(object):
def isBipartite(self, graph):
"""
:type graph: List[List[int]]
:rtype: bool
"""
self.re = True
self.checked = {}
for i in xrange(len(graph)):
self.bfs(graph, i, 'blue', {}, {})
return self.re
def bfs(self, graph, node, color, blue, red):
if color == 'blue':
if node in red:
self.re = False
return
if node in blue:
return
blue[node] = True
else:
if node in blue:
self.re = False
return
if node in red:
return
red[node] = True
if node not in self.checked:
self.checked[node] = True
else:
return
adjNodes = graph[node]
for n in adjNodes:
_color = 'blue' if color != 'blue' else 'red'
self.bfs(graph, n, _color, blue, red)别人的:
def isBipartite(self, graph):
color = {}
def dfs(pos):
for i in graph[pos]:
if i in color:
if color[i] == color[pos]: return False
else:
color[i] = 1 - color[pos]
if not dfs(i): return False
return True
for i in range(len(graph)):
if i not in color: color[i] = 0
if not dfs(i): return False
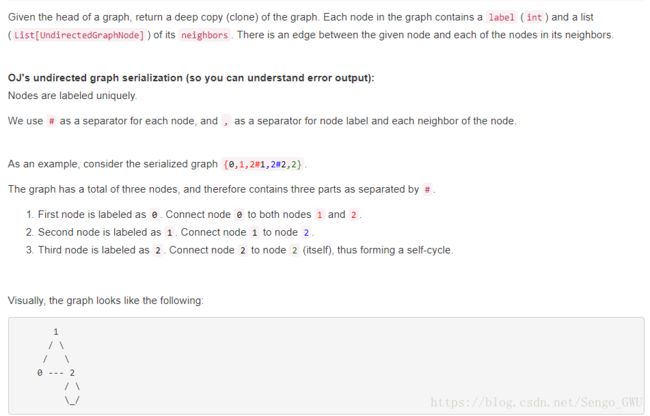
return True133. Clone Graph
class Solution:
# @param node, a undirected graph node
# @return a undirected graph node
def cloneGraph(self, node):
if not node: return
nodeCopy = UndirectedGraphNode(node.label)
dic = {node:nodeCopy} # 类型题的重点
queue = [node]
while queue:
node = queue.pop(0)
neighbors = node.neighbors
for nei in neighbors:
if nei not in dic:
neiCopy = UndirectedGraphNode(nei.label)
dic[nei] = neiCopy
dic[node].neighbors.append(neiCopy)
queue.append(nei)
else:
dic[node].neighbors.append(dic[nei])
return nodeCopy