C++项目实战(一)——简单商品销售系统实现
本项目通过使用win32控制台应用程序实现一个非常简单的商品销售系统,主要涉及的知识点包含有:类的设计与使用、文件流操作、标准模板库的使用。
简单商品销售系统:
需求分析:
我们需要实现一个 能进货、能售货的简单商品销售系统,根据面向对象的理念,思路如下:
1、设计一个 commodity 类,用来实现 商品的基本属性、获取商品基本属性的接口。(即 包含有:商品的种类、 商品的库存量、商品的进货价、商品的售出价,获取商品基本属
性的接口等)
2、设计一个 trade 类,用来实现 商品的数据链表、获取商品操作以及保存信息的接口。(即
包含有:商品数据链表,获取本地商品信息、商品进货及售出交易信息、更新商品库存信
息等)
3、在 main 主程序中使用 win32 控制台实现用户与操作系统间的界面交互,主要为:各种商
品操作提示信息,运用以上两个类操作简单商品销售系统等。
代码实现:
头文件:
1、commodity.h
#include
class commodity
{
private:
int static kinds; //商品种类
int ID; //商品编号
int stock; //商品库存量
float buyValue; //商品进货单价
float sellValue; //商品售出单价
char name[30]; //商品名称
public:
int getID(); //获取商品编号
int getStock(); //获取商品库存量
float getBuyValue(); //获取进货单价
float getsellValue(); //获取售出单价
char* getName(); //获取商品名称
void UpdateStock(int n); //更新商品库存量
friend class trade; //将自身数据提供给友元 trade 类使用
//两个有参构造函数
commodity(char name[], float buyValue, float sellValue) //构造函数1:加入一种全新的商品
{
kinds++;
ID = kinds;
this->stock = 0;
this->buyValue = buyValue;
this->sellValue = sellValue;
strcpy(this->name, name);
}
commodity(int ID, char name[], float buyValue, float sellValue, int stock) //构造函数2保留
{
kinds++;
this->ID = ID;
this->stock = stock;
this->buyValue = buyValue;
this->sellValue = sellValue;
strcpy(this->name, name);
}
};
2、trade.h
#include "stdafx.h"
#include
#include "commodity.h" //加入commodity.h
using std::list; //使用 list 命名空间
class trade
{
struct record //商品交易记录结构体
{
char name[30]; //商品名称
int count; //交易数量
char sTime[70]; //交易时间
record(char* name, int count, char* time)
{
strcpy(this->name, name);
this->count = count;
strcpy(sTime, time);
}
};
//成员变量
private:
list dataList; //使用 commodity类 实现一个商品数据链表
list buyRecordList; //使用 record结构体 实现一个商品进货记录链表
list sellRecordList; //使用 record结构体 实现一个商品售货记录链表
//成员函数
public:
bool GetInformathion(int index); //获取并输出商品信息
void GetIndex(); //获取并输出商品目录
bool init(); //从本地文件获取商品信息
void save(); //将商品信息保存到本地文件中
bool Buy(int ID, int count); //购买商品的操作与数据检查
bool Sell(int n, int ID); //售出商品的操作与数据检查
void AddNew(char name[], float buyValue, float sellValue); //添加新的商品
/*获得商品的购入和销售记录*/
void getSellRecord();
void getBuyRecord();
};
至此,上述完成了两个类的声明部分,下main在源文件中实现类的定义,以及main函数实现简单商品销售系统的实现。
源文件:
1、commodity.cpp
#include "stdafx.h"
#include "commodity.h"
//初始化ID
int commodity::kinds = 0;
void commodity::UpdateStock(int n) //更新商品库存
{
stock += n;
}
int commodity::getStock() //获取商品库存
{
return stock;
}
int commodity::getID() //获取货品编号
{
return ID;
}
float commodity::getBuyValue() //获取购入价
{
return buyValue;
}
float commodity::getsellValue() //获取售出价
{
return sellValue;
}
char* commodity::getName() //获取商品名称
{
return name;
}
2、trade.cpp
#include "stdafx.h"
#include "trade.h"
#include //加入文件流操作头文件
#include //加入时间操作头文件
#define CAP 5
#define TLEN 10
#define ALEN 30
using std::ofstream;
using std::ifstream;
bool trade::Buy(int ID, int count) //购买商品的操作与数据检查
{
for (auto iter = dataList.begin(); iter != dataList.end(); iter++)
{
if (iter->getID() == ID)
{
iter->UpdateStock(count);
time_t t = time(0);
char temp[50];
strftime(temp, sizeof(temp), "%Y年 %m月 %d日 %X %A", localtime(&t));
buyRecordList.push_back(record(iter->name, count, temp));
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
bool trade::Sell(int ID, int count) //售出商品的操作与数据检查
{
for (auto iter = dataList.begin(); iter != dataList.end(); iter++)
{
if (iter->getID() == ID && !(iter->getStock() + count < 0))
{
iter->UpdateStock(-count);
time_t t = time(0);
char temp[50];
strftime(temp, sizeof(temp), "%Y年 %m月 %d日 %X %A", localtime(&t));
sellRecordList.push_back(record(iter->name, count, temp));
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
void trade::AddNew(char name[], float buyValue, float sellValue) //加入一种全新的商品
{
dataList.push_back(commodity(name, buyValue, sellValue));
}
void trade::GetIndex() //获取并输出商品目录
{
for (auto iter = dataList.begin(); iter != dataList.end(); iter++)
{
printf("\t 商品编号: %i 商品名称: %s\n", iter->getID(), iter->getName());
}
}
bool trade::GetInformathion(int index) //获取并输出商品信息
{
for (auto iter = dataList.begin(); iter != dataList.end(); iter++)
{
if (iter->getID() == index)
{
printf("商品编号:%d\n商品名称:%s\n购入价格:%f\n出售价格:%f\n剩余:%d\n", index,
iter->getName(),
iter->getBuyValue(),
iter->getsellValue(),
iter->getStock());
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
void trade::save() //将商品信息保存到本地文件中
{
ofstream file;
file.open("stock.txt");
if (!file.fail())
{
file << " ════════════════════════════ \n";
file << " ***** 商品信息 ***** \n";
file << " ════════════════════════════ \n";
for (auto iter = dataList.begin(); iter != dataList.end(); iter++)
{
file << "ID:" << iter->getID()
<< "\tNAME:" << iter->getName()
<< "\tBUYCOST:" << iter->getBuyValue()
<< "\tSELLVALUE:" << iter->getsellValue()
<< "\tSTOCK:" << iter->getStock()
<< "\n";
}
}
else
{
printf("记录文件创建失败");
}
file.close();
file.open("sellRecord.txt");
if (!file.fail())
{
file << " ════════════════════════════ \n";
file << " ***** 销售信息 ***** \n";
file << " ════════════════════════════ \n";
for (auto iter = sellRecordList.begin(); iter != sellRecordList.end(); iter++)
{
file << "NAME:" << iter->name
<< "\tTIME:" << iter->sTime
<< "\tCOUNT:" << iter->count
<< "\n";
}
}
else
{
printf("销售记录文件创建失败");
}
file.close();
file.open("buyRecord.txt");
if (!file.fail())
{
file << " ════════════════════════════ \n";
file << " ***** 购入信息 ***** \n";
file << " ════════════════════════════ \n";
for (auto iter = buyRecordList.begin(); iter != buyRecordList.end(); iter++)
{
file << "NAME:" << iter->name
<< "\tTIME:" << iter->sTime
<< "\tCOUNT:" << iter->count
<< "\n";
}
}
else
{
printf("购入记录文件创建失败");
}
}
bool trade::init() //从本地文件获取商品信息
{
ifstream file("stock.txt");
if (!file.fail())
{
char titles[CAP][TLEN] = { "ID:", "NAME:", "COST:", "VALUE:", "STOCK:" };
char saves[CAP][ALEN] = {};
int tIndex = 0;
char buf[128];
int kinds = 0; //商品种类计数
for (int i = 0; i<3; i++) //忽略标题,也就是忽略前三行标题消息
{
file.getline(buf, 128);
}
while (!file.eof())
{
char temp[TLEN] = ""; //读取文件内容的字符数组
for (int i = 0; i < TLEN && !file.eof(); i++) //for NO.1
{
file.get(temp[i]);
if (strcmp(temp, titles[tIndex]) == 0)
{
for (int j = 0; j < ALEN && !file.eof(); j++) //for NO.2
{
char c;
file.get(c);
if (c != '\t' && c != '\n')
{
saves[tIndex][j] = c;
}
else if (c != '\n')
{
if (tIndex>4)
{
return false; //行参数结尾后仍然有字符存在,失效
}
tIndex++;
break; //break NO.2
}
else
{
dataList.push_back(commodity(atoi(saves[0]), saves[1],
atof(saves[2]), atof(saves[3]), atoi(saves[4])));
tIndex = 0;
kinds++;
break; //break NO.2
}
if (j == ALEN - 1)
{
return false; //超过了参数长度,初始化失败
}
} //end NO.2
break;//break NO.1
}
if (i == TLEN - 1)
{
return false; //没有匹配到参数名称,初始化失败
}
} //end NO.1
} //end While,读取结束
commodity::kinds = kinds;
return true;
}
return false; //文件不存在,初始化失败
}
void trade::getSellRecord() //获得商品的销售记录
{
for (auto iter = sellRecordList.begin(); iter != sellRecordList.end(); iter++)
{
printf("\t出售商品名称:%s\n", iter->name);
printf("\t交易日期:%s\n", iter->sTime);
printf("\t出售数目:%d\n", iter->count);
printf("\t ════════════════════════════ \n");
}
}
void trade::getBuyRecord()//获得商品的购入记录
{
for (auto iter = buyRecordList.begin(); iter != buyRecordList.end(); iter++)
{
printf("\t购入商品名称:%s\n", iter->name);
printf("\t交易日期:%s\n", iter->sTime);
printf("\t购入数目:%d\n", iter->count);
printf("\t ════════════════════════════ \n");
}
}
3、trade_commodity.cpp,也就是 main 函数
// trade_commodity.cpp : 定义控制台应用程序的入口点。
#include "stdafx.h"
#include "trade.h"
#include
using std::cout;
using std::cin;
using std::endl;
void ToBuy(int& ID, int& count)
{
cout << "请输入购买商品的编号" << endl;
cin >> ID;
getchar();
cout << "请输入购买商品的数量:" << endl;
cin >> count;
getchar();
}
void ToSell(int& ID, int& count)
{
cout << "请输入卖出商品的编号" << endl;
cin >> ID;
getchar();
cout << "请输入卖出商品的数量:" << endl;
cin >> count;
getchar();
}
void operate()
{
printf("按任意键继续");
getchar();
system("cls"); //清空屏幕
}
void drawIndex()
{
system("cls");
printf("\t ════════════════════════════ \n");
printf("\t ***** 商品目录 ***** \n");
printf("\t ════════════════════════════ \n");
}
void drawLine()
{
printf("\t ════════════════════════════ \n");
}
void DrawMainMenu()
{
printf("\t╔═══════════════════════════╗\n");
printf("\t║ 欢迎使用销售系统 ║\n");
printf("\t╠═══════════════════════════╣\n");
printf("\t║ 1 - 购进商品 ║\n");
printf("\t║ 2 - 卖出商品 ║\n");
printf("\t║ 3 - 添加新品 ║\n");
printf("\t║ 4 - 查看商品信息 ║\n");
printf("\t║ 5 - 查看采购记录 ║\n");
printf("\t║ 6 - 查看销售记录 ║\n");
printf("\t║ 7 - 退出 ║\n");
printf("\t╚═══════════════════════════╝\n");
}
void drawBuyRecord()
{
system("cls");
printf("\t ════════════════════════════ \n");
printf("\t ***** 采购记录 ***** \n");
printf("\t ════════════════════════════ \n");
}
void drawSellRecord()
{
system("cls");
printf("\t ════════════════════════════ \n");
printf("\t ***** 销售记录 ***** \n");
printf("\t ════════════════════════════ \n");
}
int main(int argc, _TCHAR* argv[])
{
trade myTrade;
if (!myTrade.init())
{
myTrade = trade();
}
bool quitFlag = false;
while (!quitFlag)
{
DrawMainMenu();
printf("请输入您的选项:");
int selection;
cin >> selection;
getchar();
int ID;
int count;
switch (selection)
{
case 1:
drawIndex();
myTrade.GetIndex();
drawLine();
ToBuy(ID, count);
if (myTrade.Buy(ID, count))
{
system("cls");
printf("操作成功,");
}
else
{
system("cls");
printf("您的输入有误,");
}
operate();
break;
case 2:
drawIndex();
myTrade.GetIndex();
drawLine();
ToSell(ID, count);
if (myTrade.Sell(ID, count))
{
system("cls");
printf("操作成功,");
}
else
{
system("cls");
printf("您的输入有误,");
}
operate();
break;
case 3:
char name[30];
float value;
float cost;
system("cls");
cout << "请输入新品的名称" << endl;
cin >> name;
getchar();
cout << "请输入购入价格" << endl;
cin >> cost;
getchar();
cout << "请输入出售价格" << endl;
cin >> value;
getchar();
myTrade.AddNew(name, cost, value);
system("cls");
printf("操作成功,");
operate();
break;
case 4:
drawIndex();
myTrade.GetIndex();
drawLine();
cout << "请输入商品编号:";
int index;
cin >> index;
getchar();
system("cls");
if (!myTrade.GetInformathion(index))
{
cout << "无效的商品编号,";
operate();
}
else{
operate();
}
break;
case 5:
drawBuyRecord();
myTrade.getBuyRecord();
operate();
break;
case 6:
drawSellRecord();
myTrade.getSellRecord();
operate();
break;
case 7:
quitFlag = true;
break;
default:
system("cls");
printf("无效的选项,");
operate();
}
}
myTrade.save();
return 0;
}
运行结果:
1、窗口界面:

资源文件:
可能程序会在本地创建“stock.txt”、“sellRecord.txt”、“buyRecord.txt”失败,所以读者最好自行创建一下,确保程序正确运行。以下举例创建 stock.txt ,供读者参考。

本地stock.txt内容:
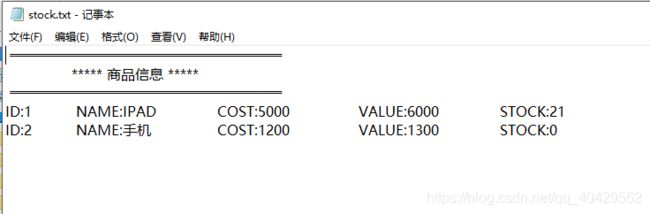
2、运行结果说明:
简单商品销售系统实现最后的结果让人较为满意,成功实现了简单商品销售系统所有操作功能。当然该项目作为入门项目比较简单,但能够让读者对类的设计与使用、文件流操作、标准模板库的使用等的知识点更加的熟悉。