java语言语法高级部分常用API(一)学习总结
java语言语法高级部分常用API(一)学习总结如下:
- 一:Scanner类
- 二:Random类
- 三:ArrayList类
- 四:String类
- 五:static关键字
- 六:Math工具类
- 七:ArrayList工具类
- 八:匿名对象
一:Scanner类
1、什么是Scanner类?
一个可以解析基本类型和字符串的简单文本扫描器。
2、通过 Scanner 类可以获取用户的输入,创建 Scanner 对象的基本语法如下:
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
备注:System.in 系统输入指的是通过键盘录入数据。
3、导包:
java.util.Scanner;
4、常用方法如下:
-
nextInt()、next()和nextLine()
- nextInt():
(nextInt()只读取数值,剩下”\n”还没有读取,并将cursor放在本行中) - next():
next() 方法遇见第一个有效字符(非空格,非换行符)时,开始扫描,当遇见第一个分隔符或结束符(空格或换行符)时,结束扫描,获取扫描到的内容,即获得第一个扫描到的不含空格、换行符的单个字符串。 - nextLine():
nextLine()时,则可以扫描到一行内容并作为一个字符串而被获取到。
- nextInt():
补充一个方法:
Java中List转换为数组,数组转List
List转换为Array可以这样处理:
ArrayList list=new ArrayList();
String[] strings = new String[list.size()];
list.toArray(strings);
反过来,如果要将数组转成List怎么办呢?如下:
String[] s = {“a”,“b”,“c”}; List list = java.util.Arrays.asList(s);
实践代码如下:
import java.util.Scanner;
public class ScannerMethod {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
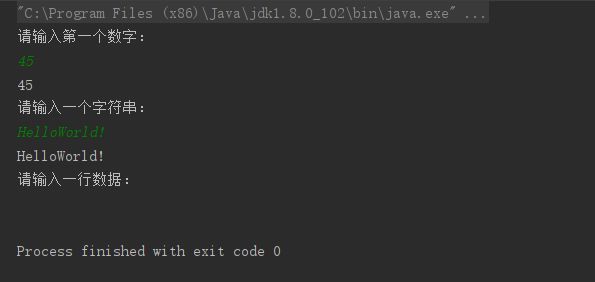
System.out.println("请输入第一个数字:");
int num = sc.nextInt();
System.out.println(num);
System.out.println("请输入一个字符串:");
String str1 = sc.next();
System.out.println(str1);
System.out.println("请输入一行数据:");
String str2 = sc.nextLine();
System.out.println(str2);
}
}
|
import java.util.Scanner;
public class ScannerMethod {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入第一个数字:");
int num = sc.nextInt();
System.out.println(num);
System.out.println("请输入一个字符串:");
String str1 = sc.next();
System.out.println(str1);
sc.nextLine();//在这里在增加一行sc.nextLine();将被next()等去掉的enter结束符过滤掉。
System.out.println("请输入一行数据:");
String str2 = sc.nextLine();
System.out.println(str2);
}
}
02
二:Random类
此类的实例用于生成伪随机数。
Random r = new Random();
int i = r.nextInt();
查看成员方法
public int nextInt(int n) :返回一个伪随机数,范围在 0 (包括)和 指定值 n (不包括)之间的 int 值。
猜数字小游戏代码展示:
//猜字小游戏
Random r = new Random();
int realNum = r.nextInt(10);
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
while(true){
System.out.println("答案为:"+realNum);
System.out.println("请你猜一个数字:");
int input = sc.nextInt();
if(input<realNum){
System.out.println("你输入的数字小啦!请重新输入");
}
else if(input>realNum){
System.out.println("你输入的数字大啦!请重新输入");
}
else{
System.out.println("恭喜你猜对了!");
break;
}
}
03
三:ArrayList类
java.util.ArrayList 是大小可变的数组的实现,存储在内的数据称为元素。此类提供一些方法来操作内部存储 的元素。 ArrayList 中可不断添加元素,其大小也自动增长。
导包语句:
import java.util.ArrayList;
java.util.ArrayList :该类需要 import导入使后使用。
ArrayList<String>,ArrayList<Student>
ArrayList<Integer> list1 = new ArrayList<>();
常用方法和遍历
对于元素的操作,基本体现在——增、删、查。常用的方法有: public boolean add(E e) :将指定的元素添加到此集合的尾部。
public E remove(int index) :移除此集合中指定位置上的元素。返回被删除的元素。 public E get(int index) :返回此集合中指定位置上的元素。返回获取的元素。
public int size() :返回此集合中的元素数。遍历集合时,可以控制索引范围,防止越界。 这些都是基本的方法,操作非常简单,代码如下:
实践代码如下:
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Random;
public class ArrayList1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add("赵丽颖");
System.out.println(list);
list.add("迪丽热巴");
list.add("古力娜扎");
list.add("玛尔拉哈");
System.out.println(list);
System.out.println(list.get(0));
// System.out.println(list.remove(3));
// System.out.println(list.get(3));
int size1 = list.size();
System.out.println(list.size());
for(int i = 0;i<list.size();i++){
System.out.println(list.get(i));
}
//遍历集合
ArrayList<Integer> list1 = new ArrayList<>();
Random r = new Random();
for(int i = 0;i<100;i++){
list1.add(r.nextInt(10));
}
for(int i = 0 ;i<list1.size();i++){
System.out.print("-->"+list1.get(i));
if(i%25 == 0&&i!=0){
System.out.println();
}
}
//添加四个对象的list集合中并且遍历对象数组
ArrayList<Student> list2 = new ArrayList<>();
Student one = new Student("洪七公",52);
Student two = new Student("欧阳锋",52);
Student three = new Student("黄药师",52);
Student four = new Student("杨过",28);
list2.add(one);
list2.add(two);
list2.add(three);
list2.add(four);
System.out.println();
for(int i = 0;i<list2.size();i++){
System.out.println("姓甚名谁:"+list2.get(i).getName()+" 年龄:"+list2.get(i).getAge());
}
//使用{}扩起集合,使用@分割每个元素。
printArrayList1(list);
ArrayList<Integer> list4 = new ArrayList();
Random r1 = new Random();
for(int i = 0;i<20;i++){
list4.add(r1.nextInt(10));
}
System.out.println(list4);
oushu(list4);
System.out.println(list4);
}
//格式如下:{赵丽颖@迪丽热巴@古力娜扎@玛尔拉哈}
//方法
public static void printArrayList(ArrayList<String> list){
String[] a = new String[list.size()];
list.toArray(a);
for(int i = 0;i<a.length;i++){
if(i==0){
System.out.print("{");
}
System.out.print(a[i]);
if(i!=a.length-1){
System.out.print("@");
}
}
System.out.println("}");
}
public static void printArrayList1(ArrayList<String> list){
System.out.print("{");
for(int i = 0;i<list.size();i++){
System.out.print(list.get(i));
if(i!=list.size()-1){
System.out.print("@");
}
}
System.out.print("}");
}
//用list.remove 方法遇到的问题
public static void oushu(ArrayList<Integer> list){
for(int i = list.size()-1;i>=0;i--){
if(list.get(i)%2==1){
list.remove(i);
}
}
System.out.println(list);
}
}
原因:List每remove掉一个元素以后,后面的元素都会向前移动,此时如果执行i=i+1,则刚刚移过来的元素没有被读取。
解决方法:
1.倒过来遍历list
for (int i = list.size()-1; i > =0; i--) {
if (((String) list.get(i)).startsWith("abcde")) {
list.remove(i);
}
}
2.每移除一个元素以后再把i移回来
for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) {
if (((String) list.get(i)).startsWith("abcde")) {
list.remove(i);
i=i-1;
}
}
3.使用iterator.remove()方法删除
for (Iterator it = list.iterator(); it.hasNext();) {
String str = (String)it.next();
if (str.equals("chengang")){
it.remove();
}
}
04
四:String类
java.lang.String 类代表字符串。
1、特点:
(1). 字符串不变:字符串的值在创建后不能被更改。(具体详见代码)
public class StringMethod {
public static void main(String[] args) {
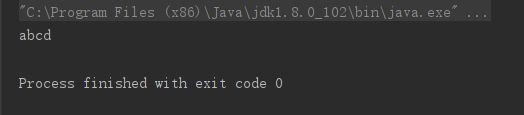
String s1 = "abc";
s1+="d";
System.out.println(s1);
// 内存中有"abc","abcd"两个对象,s1从指向"abc",改变指向,指向了"abcd"。
}
}
结果如下:
(2). 因为String对象是不可变的,所以它们可以被共享。
String s1 = "abc";
String s2 = "abc";
// 内存中只有一个"abc"对象被创建,同时被s1和s2共享。
(3). “abc” 等效于 char[] data={ ‘a’ , ‘b’ , ‘c’ } 。
//例如
String str = "abc";
// 相当于
char[] data = {
'a','b','c'};
String str = new String(data);
// String底层是靠字符数组实现的。
2、方法使用:
(1)java.lang.String :此类不需要导入包。
(2)查看构造方法:
public String() :初始化新创建的 String对象,以使其表示空字符序列。
public String(char[] value) :通过当前参数中的字符数组来构造新的String。
public String(byte[] bytes) :通过使用平台的默认字符集解码当前参数中的字节数组来构造新的 String。 构造举例,代码如下:
public class StringMethod {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//无参构造
String str = new String();
//通过字符数组构造
char[] data = {
'a','b','c'};
String str2 = new String(data);
//通过字节数组构造
byte[] bytes = {
97,98,99};
String str3 = new String(bytes);
System.out.println(str2);
System.out.println(str3);
}
}
(3)获取功能的方法:
public int length () :返回此字符串的长度。 public String concat (String str) :将指定的字符串连接到该字符串的末尾。 public char charAt (int index) :返回指定索引处的 char值。 public int indexOf (String str) :返回指定子字符串第一次出现在该字符串内的索引。
public String substring (int beginIndex) :返回一个子字符串,从beginIndex开始截取字符串到字符 串结尾。
public String substring (int beginIndex, int endIndex) :返回一个子字符串,从beginIndex到 endIndex截取字符串。含beginIndex,不含endIndex。
(4)转换功能的方法:
public char[] toCharArray () :将此字符串转换为新的字符数组。
public byte[] getBytes () :使用平台的默认字符集将该 String编码转换为新的字节数组。
public String replace (CharSequence target,CharSequence replacement) :将与target匹配的字符串使 用replacement字符串替换。
(5)分割功能的方法:
public String[] split(String regex) :将此字符串按照给定的regex(规则)拆分为字符串数组。
小练:键盘录入一个字符串数据,统计字符串中大小写字母及数字字符个数。
代码如下:
import java.util.Scanner;
public class StringMethod {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//键盘录入一个字符串数据,统计字符串中大小写字母及数字字符个数
System.out.println("请从键盘输入一个字符串数据:");
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
String str = sc.next();
int bigCount = 0;//定义了如下三个计数器分别统计大写字母与小写字母和数字的个数。
int smallCount = 0;
int numberCount = 0;
for(int i = 0; i<str.length();i++){
char ch = str.charAt(i);
if(ch>='a'&&ch<='z'){
smallCount++;
}
else if(ch>='A'&&ch<='Z'){
bigCount++;
}
else if(ch>='0'&&ch<='9'){
numberCount++;
}
else{
System.out.println("该字符非法:"+ch);
}
}
System.out.println("小写字母的个数为:"+smallCount);
System.out.println("大写字母的个数为:"+bigCount);
System.out.println("数字的个数为:"+numberCount);
}
}
05
五:static关键字
1、 概述
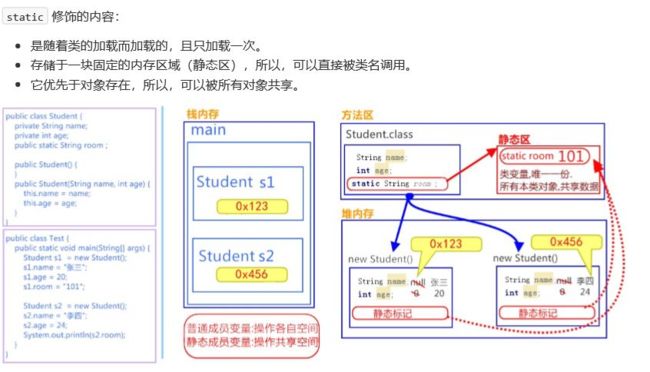
关于 static 关键字的使用,它可以用来修饰的成员变量和成员方法,被修饰的成员是属于类的,而不是单单是属 于某个对象的。也就是说,既然属于类,就可以不靠创建对象来调用了。
2、类变量
当 static 修饰成员变量时,该变量称为类变量。该类的每个对象都共享同一个类变量的值。任何对象都可以更改该类变量的值,但也可以在不创建该类的对象的情况下对类变量进行操作。(多个对象共享同一份数据)
类变量:使用 static关键字修饰的成员变量。
格式:static 数据类型 变量名;
3、应用场景
比如说,基础班新班开班,学员报到。现在想为每一位新来报到的同学编学号(sid),从第一名同学开始,sid为 1,以此类推。学号必须是唯一的,连续的,并且与班级的人数相符,这样以便知道,要分配给下一名新同学的学 号是多少。这样我们就需要一个变量,与单独的每一个学生对象无关,而是与整个班级同学数量有关。
所以,我们可以这样定义一个静态变量num,代码如下:
public class Student {
private String name;
private int age;
private int sid;//我们定义一个sid来记录每一个学生的学号,并让它实现自增长
//即每当创建一个对象的时候,让其加一。
//因为sid是每一个人都有的且各不相同,所以我们不能将此变量设置为共享变量。
//我们设置另一个变量为共享变量达到控制sid实现自增长。
public static int num = 0;//static修饰的共享变量!
public Student() {
}
public int getSid() {
return sid;
}
public void setSid(int sid) {
this.sid = sid;
}
public Student(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.sid =++num;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
}
public class StudentDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
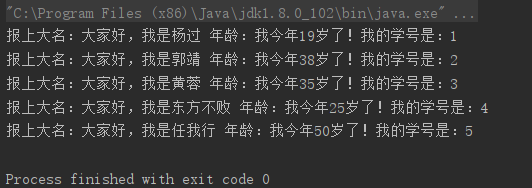
Student stu1 = new Student("杨过",19);
Student stu2 = new Student("郭靖",38);
Student stu3 = new Student("黄蓉",35);
Student stu4 = new Student("东方不败",25);
Student stu5 = new Student("任我行",50);
System.out.println("报上大名:大家好,我是"+stu1.getName()+" 年龄:我今年"+ stu1.getAge()+"岁了!"+"我的学号是:"+stu1.getSid());
System.out.println("报上大名:大家好,我是"+stu2.getName()+" 年龄:我今年"+ stu2.getAge()+"岁了!"+"我的学号是:"+stu2.getSid());
System.out.println("报上大名:大家好,我是"+stu3.getName()+" 年龄:我今年"+ stu3.getAge()+"岁了!"+"我的学号是:"+stu3.getSid());
System.out.println("报上大名:大家好,我是"+stu4.getName()+" 年龄:我今年"+ stu4.getAge()+"岁了!"+"我的学号是:"+stu4.getSid());
System.out.println("报上大名:大家好,我是"+stu5.getName()+" 年龄:我今年"+ stu5.getAge()+"岁了!"+"我的学号是:"+stu5.getSid());
}
}
4、静态方法
当 static 修饰成员方法时,该方法称为类方法 。静态方法在声明中有 static ,建议使用类名来调用,而不需要 创建类的对象。调用方式非常简单。
类方法:使用 static关键字修饰的成员方法,习惯称为静态方法。
定义格式:
public static void showNum(){
System.out.println("一共有多少个学生:"+num);
}
静态方法调用的注意事项: 静态方法可以直接访问类变量和静态方法。 静态方法不能直接访问普通成员变量或成员方法。反之,成员方法可以直接访问类变量或静态方法。 静态方法中,不能使用this关键字。
Do you know?:静态方法只能访问静态成员。
调用格式 :
被static修饰的成员可以并且建议通过类名直接访问。虽然也可以通过对象名访问静态成员,原因即多个对象均属 于一个类,共享使用同一个静态成员,但是不建议,会出现警告信息。
格式:
// 访问类变量 类名.类变量名;
// 调用静态方法 类名.静态方法名(参数);
5、静态代码块:
静态代码块:定义在成员位置,使用static修饰的代码块{ }。 位置:类中方法外。 执行:随着类的加载而执行且执行一次,优先于main方法和构造方法的执行。
格式:
//静态代码块格式:
public class ClassName(){
static{
//执行语句
}
}
public class Test{
public static int number;
public static ArrayList<String> list;
static{
//给类变量进行赋值
number = 66;
list = new ArrayList<String>();
//添加元素到集合中
list.add("风清扬");
list.add("东方不败");
System.out.println(list);
}
}
锦囊妙计:
static 关键字,可以修饰变量、方法和代码块。在使用的过程中,其主要目的还是想在不创建对象的情况 下,去调用方法。下面将介绍两个工具类,来体现static 方法的便利。
06
六:Math工具类
1、 概述
java.lang.Math 类包含用于执行基本数学运算的方法,如初等指数、对数、平方根和三角函数。类似这样的工具 类,其所有方法均为静态方法,并且不会创建对象,调用起来非常简单。
2、 基本运算的方法
(1)public static double abs(double a) :返回 double 值的绝对值。
double d1 = Math.abs(‐5); //d1的值为5
double d2 = Math.abs(5); //d2的值为5
(2)public static double ceil(double a) :返回大于等于参数的小的整数。
double d1 = Math.ceil(3.3); //d1的值为 4.0
double d2 = Math.ceil(‐3.3); //d2的值为 ‐3.0
double d3 = Math.ceil(5.1); //d3的值为 6.0
(3)public static double floor(double a) :返回小于等于参数大的整数。
double d1 = Math.floor(3.3); //d1的值为3.0
double d2 = Math.floor(‐3.3); //d2的值为‐4.0
double d3 = Math.floor(5.1); //d3的值为 5.0
(4)public static long round(double a) :返回接近参数的 long。(相当于四舍五入方法)
long d1 = Math.round(5.5); //d1的值为6.0
long d2 = Math.round(5.4); //d2的值为5.0
07
七:ArrayList工具类
1、概述
java.util.Arrays 此类包含用来操作数组的各种方法,比如排序和搜索等。其所有方法均为静态方法,调用起来 非常简单。
2、 操作数组的方法
(1)public static String toString(int[] a) :返回指定数组内容的字符串表示形式。
public class StudentDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] nums = {
5,56,45,487,666,13};
//将数组内容转换为字符串
String str = Arrays.toString(nums);
System.out.println(str);//[5, 56, 45, 487, 666, 13]此为输出内容,带格式输出。
}
}
(2)public static void sort(int[] a) :对指定的 int 型数组按数字升序进行排序。
public class StudentDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] data = {
2,8,65,4,3,45};
Arrays.sort(data);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(data));//排序后[2, 3, 4, 8, 45, 65]
}
}
08
八:匿名对象
创建对象时,只有创建对象的语句,却没有把对象地址值赋值给某个变量。虽然是创建对象的简化写法,但是应用 场景非常有限。
1、匿名对象 :没有变量名的对象。
2、格式:
new 类名(参数列表);
new Scanner(System.in);
3、应用场景:
(1). 创建匿名对象直接调用方法,没有变量名。
new Scanner(System.in).nextInt();
(2).一旦调用两次方法,就是创建了两个对象,造成浪费,请看如下代码。
new Scanner(System.in).nextInt();
new Scanner(System.in).nextInt();
小贴士:一个匿名对象,只能使用一次。(因为new一下,就是另外一个对象了)
(3). 匿名对象可以作为方法的参数和返回值
System.out.println("Scanner的使用方法和匿名对象的使用方法如下:");
System.out.println("普通使用方式:");
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int s1 = sc.nextInt();
String s2 = sc.next();
System.out.println("输入的数字是:"+s1);
System.out.println("输入的字符是:"+s2);
System.out.println("匿名对象使用方式:");
int num = new Scanner(System.in).nextInt();
System.out.println("输入的数字是:"+num);
System.out.println("普通使用方式传参:");
Scanner sc1 = new Scanner(System.in);
methodParam(sc1);
System.out.println("匿名对象方式传参:");
methodParam(new Scanner(System.in));
System.out.println("匿名对象作为返回值:");
Scanner sc2 = methodReturn();
int num2 = sc2.nextInt();
System.out.println("匿名对象作为返回值:"+num2);
//下面是定义的两个方法
public static void methodParam(Scanner sc){
int num = sc.nextInt();
System.out.println("输入的字符是:"+num);
}
public static Scanner methodReturn(){
return new Scanner(System.in);
}