StringBuffer、StringBuild、FileInputStream和FileOutputStream
StirngBuffer
对字符串频繁修改(如字符串连接)时,使用StringBuffer类可以大大提高程序执行效率
// 定义
StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer("abc");
// 拼接:append()
sb.append("def");
// 在指定位置插入:insert(index,str)
sb.insert(3,g);// 输出abgcdef
// 装换成String类型:toString()
sb.toString();
// 删除delete(start,end),end的值取不到即[start,end)
sb.detele(2,4) //输出abdef
例题:
将一个数字字符串转换成逗号分隔的数字串
如:12345678——>123,456,78
public class TestStringBuffer {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入字符串:");
String str = sc.next();
StringBuffer stringBuffer = new StringBuffer(str);
for (int i = 2; i< stringBuffer.length(); i+=4) {
if(i!=stringBuffer.length()-1)
stringBuffer.insert(i+1,",");
}
System.out.println(stringBuffer);
}
}
StringBuffer与StringBuild
StringBuild的用法与StringBuffer类似,但二者有最大的区别是一个线程不安全,一个线程安全。
StringBuffer是线程安全的,但因此其速度慢
StringBuild是线程不安全的,其速度相对较快
File类
文件是相关记录或放在一起的数据的集合。Java程序通过java.io.File类访问文件属性。
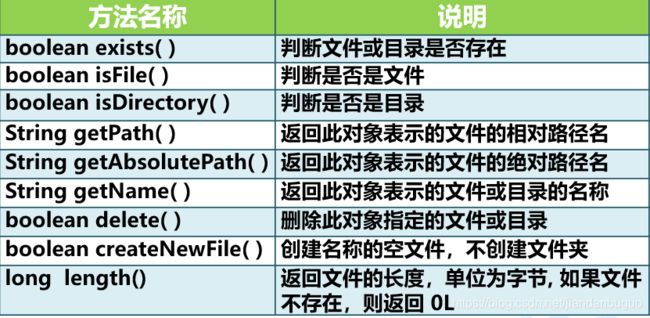
File类常用方法
public class TestFile {
public static void main(String[] args) {
File file = new File("f:/file.txt");
System.out.println(file.exists());
System.out.println(file.isFile());
System.out.println(file.isDirectory());
System.out.println("文件名称:"+file.getName());
System.out.println("相对路径:"+file.getPath());
System.out.println("绝对路径:"+file.getAbsolutePath());
System.out.println("文件大小:"+file.length()+" 字节");
File file2 = new File("f:/abc/def/hg/abc.txt");
//file2.mkdirs(); // f:/abc/def/hg/abc.txt 会将目录中的全部创建成文件
// 创建/abc/def/hg/层级文件
file2.getParentFile().mkdirs();
System.out.println(file2.exists());
try {
// 创建abc.txt
file2.createNewFile();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(file2.exists());
// 逐级删除,删除最内层即abc.txt
file2.delete();
// 相对路径,会在项目中与src同级常见abc.txt
File file3 = new File("abc.txt");
createFile("abc.txt");
}
// 创建文件
public static void createFile(String path){
File f = new File(path);
try {
f.createNewFile();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
流
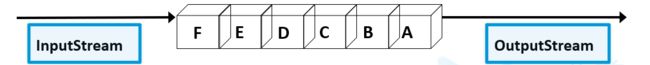
java中读写文件通过流进行。流是一组有序的数据序列,以先进先出方式发送信息的通道。
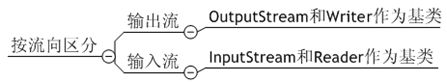
输入/输出流与数据源
输入输出流是相对程序而言的。对于程序,从文件中读取数据是输入流,程序写书其他数据源是输入流。
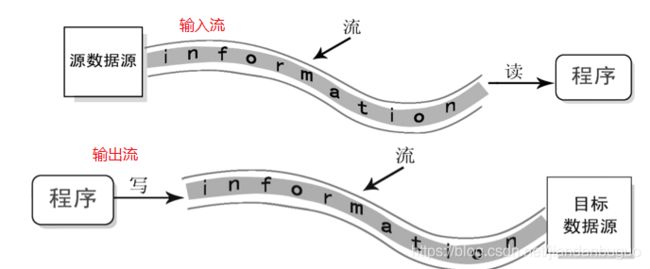
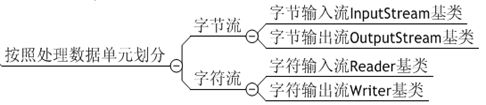
Java流的分类
FileInputStream类
FileInputStream的使用步骤:
1、FileInputStream对象和String对象声明
2、创建FileInputStream对象(文件路径或File对象)
3、读单字节或整个读到byte数组中
4、转成字符串
5、关闭FileInputStream流
6、返回结果字符串
// 定义
// 第一种
File file = new File("f:/file.txt");
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(file);
// 第二种
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("f:/file.txt");
// 文件读取
// 第一种,将文件一次性读入,放到byte型数组中
public static String readFile(String path){
FileInputStream fis = null;
String str = "";
try {
fis = new FileInputStream(path);
byte[] b = new byte[fis.available()];
fis.read(b);
str = new String(b);
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
fis.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
return str;
}
// 第二种,字符拼接,每次读取一个字符
public static String readByOne(String path){
FileInputStream fis = null;
String str = null;
try {
fis =new FileInputStream(path);
StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer();
int tmp;
while ((tmp=fis.read())>0){
char c =(char)tmp;
sb.append(c);
}
str = sb.toString();
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
fis.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
return str;
}
FileOutputStream类
FileOutputStream写文件流程
1、File对象装载文件路径
2、判断文件父级目录是否存在,不存在则创建
3、声明FileOutputStream对象
4、创建FileOutputStream对象(File对象,是否追加)
5、把要写的字符串装成byte数组,并写入输出流
6、关闭FileOutputStream流
public class TestOutputStream {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
String str = "how are you,l'm fine thank you \n and you?";
// 文件可存在可不存在
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("a.txt",true);
byte[] b = str.getBytes();
fos.write(b);
fos.close();
}
// 自定义写文件方法,参数含义:要写入的字符串,写入路径,是否覆盖
public static void writeFile(String str,String path,boolean isAppend){
File file = new File(path);
if(!file.getParentFile().exists()){
file.getParentFile().mkdirs();
}
FileOutputStream fos = null;
try {
fos = new FileOutputStream(file,isAppend);
byte[] b = str.getBytes();
fos.write(b);
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
fos.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
例题:
文件复制,将file复制到file2中
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
FileInputStream fis = null;
FileOutputStream fos = null;
try {
fis = new FileInputStream("f:/file.txt");
byte[] b = new byte[fis.available()];
fis.read(b);
fos = new FileOutputStream("f:/file2.txt");
fos.write(b);
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
try {
fis.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
try {
fos.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}