java进阶之常见对象(二)
1:StringBuffer
(1)用字符串做拼接,比较耗时并且也耗内存,而这种拼接操作又是比较常见的,为了解决这个问题,Java就提供了
一个字符串缓冲区类。StringBuffer供我们使用。
(2)StringBuffer的构造方法
A:StringBuffer()//无参构造方法
B:StringBuffer(int size)//指定容量的字符串缓冲区对象
C:StringBuffer(String str)//指定字符串内容的字符串缓冲区对象
(3)StringBuffer的常见功能(自己补齐方法的声明和方法的解释)
A:添加功能
public StringBuffer append(String str)
可以把任意类型数据添加到字符串缓冲区里面,并返回字符串缓冲区本身
public StringBuffer insert(int offset,String str)
在指定位置把任意类型的数据插入到字符串缓冲区里面,并返回字符串缓冲区本身
B:删除功能
public StringBuffer deleteCharAt(int index)
删除指定位置的字符,并返回本身
public StringBuffer delete(int start,int end)
删除从指定位置开始指定位置结束的内容,并返回本身
C:替换功能
public StringBuffer replace(int start,int end,String str)
从start开始到end用str替换
D:反转功能
public StringBuffer reverse()
E:截取功能(注意这个返回值)
public String substring(int start)
返回值为String型
public String substring(int start,int end)
包左不包右,返回值为String型
(4)StringBuffer的方法
public int capacity():返回当前容量。 理论值
构造方法创建时不传容量参数,值为16
构造方法创建对象时指定容量,值为指定值
构造方法创建时指定字符串内容,值为16+内容长度
public int length():返回长度(字符数)。 实际值
有多少个字符长度为多少,无参数构造方法创建对象时,值为0
(5)面试题
小细节:
StringBuffer:同步的,数据安全,效率低。
StringBuilder:不同步的,数据不安全,效率高。
A:String,StringBuffer,StringBuilder的区别
B:StringBuffer和数组的区别?
(6)注意的问题:
String作为形式参数,StringBuffer作为形式参数。
开发原则:只要是对象,我们就要判断该对象是否为null。
1.String,StringBuffer,StringBuilder的区别?
- A:String是内容不可变的,而StringBuffer,StringBuilder都是内容可变的。
- B:StringBuffer是同步的,数据安全,效率低;StringBuilder是不同步的,数据不安全,效率高
2:StringBuffer和数组的区别?
- 二者都可以看出是一个容器,装其他的数据。
- 但是呢,StringBuffer的数据最终是一个字符串数据。
- 而数组可以放置多种数据,但必须是同一种数据类型的。
注意:
形式参数:基本类型、引用类型
-
基本类型:形式参数的改变不影响实际参数:long、short、int、float、byte、double、char、boolean、8种 -
引用类型:形式参数的改变直接影响实际参数:类、字符串型、接口类型、数组类型、枚举类型、注解类型 -
String虽然为引用类型,作为参数传递,效果和基本类型作为参数传递是一样的。
3.StringBuffer和String的区别?
- 前者长度和内容可变,后者不可变。
- 如果使用前者做字符串的拼接,不会浪费太多的资源。
2:数组高级以及Arrays
(1)排序
A:冒泡排序
相邻元素两两比较,大的往后放,第一次完毕,最大值出现在了最大索引处。同理,其他的元素就可以排好。
public static void bubbleSort(int[] arr) {
for(int x=0; x<arr.length-1; x++) {
for(int y=0; y<arr.length-1-x; y++) {
if(arr[y] > arr[y+1]) {
int temp = arr[y];
arr[y] = arr[y+1];
arr[y+1] = temp;
}
}
}
}
B:选择排序
把0索引的元素,和索引1以后的元素都进行比较,第一次完毕,最小值出现在了0索引。同理,其他的元素就可以排好。
public static void selectSort(int[] arr) {
for(int x=0; x<arr.length-1; x++) {
for(int y=x+1; y<arr.length; y++) {
if(arr[y] < arr[x]) {
int temp = arr[x];
arr[x] = arr[y];
arr[y] = temp;
}
}
}
}
(2)查找
A:基本查找
针对数组无序的情况
public static int getIndex(int[] arr,int value) {
int index = -1;
for(int x=0; x<arr.length; x++) {
if(arr[x] == value) {
index = x;
break;
}
}
return index;
}
B:二分查找(折半查找)
针对数组有序的情况(千万不要先排序,在查找)
public static int binarySearch(int[] arr,int value) {
int min = 0;
int max = arr.length-1;
int mid = (min+max)/2;
while(arr[mid] != value) {
if(arr[mid] > value) {
max = mid - 1;
}else if(arr[mid] < value) {
min = mid + 1;
}
if(min > max) {
return -1;
}
mid = (min+max)/2;
}
return mid;
}
(3)Arrays工具类
A:是针对数组进行操作的工具类。包括排序和查找等功能。
B:要掌握的方法
把数组转成字符串:见下面案例
排序:见下面案例
二分查找:见下面案例
(4)Arrays工具类的源码解析
(5)把字符串中的字符进行排序
举例:
"edacbgf"
得到结果
"abcdefg"
3:Integer
(1)为了让基本类型的数据进行更多的操作,Java就为每种基本类型提供了对应的包装类类型
byte Byte
short Short
int Integer
long Long
float Float
double Double
char Character
boolean Boolean
(2)Integer的构造方法
A:Integer i = new Integer(100);
B:Integer i = new Integer("100");
注意:这里的参数可以是字符串型,但字符串必须是由数字字符组成
(3)String和int的相互转换
A:String -- int
Integer.parseInt("100");
B:int -- String
String.valueOf(100);
(4)其他的功能
进制转换
(5)JDK5的新特性
自动装箱 基本类型--引用类型
自动拆箱 引用类型--基本类型
把下面的这个代码理解即可:
Integer i = 100;
i += 200;
(6)面试题
-128到127之间的数据缓冲池问题
4:Character
(1)Character构造方法
Character ch = new Character('a');
(2)要掌握的方法:(自己补齐)
A:判断给定的字符是否是大写
public static boolean isUpperCase(char ch)
B:判断给定的字符是否是小写
public static boolean isLowerCase(char ch)
C:判断给定的字符是否是数字字符
public static boolean isDigit(char ch)
D:把给定的字符转成大写
public static char toUpperCase(char ch)
E:把给定的字符转成小写
public static char toLowerCase(char ch)
案例
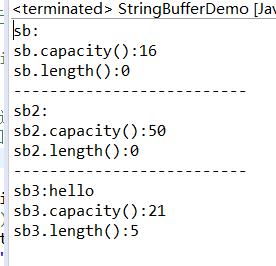
比较StringBuffer的capacity()和length()方法
public class StringBufferDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// public StringBuffer():无参构造方法
StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer();
System.out.println("sb:" + sb);
System.out.println("sb.capacity():" + sb.capacity());
System.out.println("sb.length():" + sb.length());
System.out.println("--------------------------");
// public StringBuffer(int capacity):指定容量的字符串缓冲区对象
StringBuffer sb2 = new StringBuffer(50);
System.out.println("sb2:" + sb2);
System.out.println("sb2.capacity():" + sb2.capacity());
System.out.println("sb2.length():" + sb2.length());
System.out.println("--------------------------");
// public StringBuffer(String str):指定字符串内容的字符串缓冲区对象
StringBuffer sb3 = new StringBuffer("hello");
System.out.println("sb3:" + sb3);
System.out.println("sb3.capacity():" + sb3.capacity());
System.out.println("sb3.length():" + sb3.length());
}
}
public class StringBufferTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// String -- StringBuffer
String s = "hello";
// 注意:不能把字符串的值直接赋值给StringBuffer
// StringBuffer sb = "hello";
// StringBuffer sb = s;
// 方式1:通过构造方法
StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer(s);
// 方式2:通过append()方法
StringBuffer sb2 = new StringBuffer();
sb2.append(s);
System.out.println("sb:" + sb);
System.out.println("sb2:" + sb2);
System.out.println("---------------");
// StringBuffer -- String
StringBuffer buffer = new StringBuffer("java");
// String(StringBuffer buffer)
// 方式1:通过构造方法
String str = new String(buffer);
// 方式2:通过toString()方法
String str2 = buffer.toString();
System.out.println("str:" + str);
System.out.println("str2:" + str2);
}
}
public class StringBufferTest2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 定义一个数组
int[] arr = {
44, 33, 55, 11, 22 };
// 定义功能
// 方式1:用String做拼接的方式
String s1 = arrayToString(arr);
System.out.println("s1:" + s1);
// 方式2:用StringBuffer做拼接的方式
String s2 = arrayToString2(arr);
System.out.println("s2:" + s2);
}
// 用StringBuffer做拼接的方式
public static String arrayToString2(int[] arr) {
StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer();
sb.append("[");
for (int x = 0; x < arr.length; x++) {
if (x == arr.length - 1) {
sb.append(arr[x]);
} else {
sb.append(arr[x]).append(", ");
}
}
sb.append("]");
return sb.toString();
}
// 用String做拼接的方式
public static String arrayToString(int[] arr) {
String s = "";
s += "[";
for (int x = 0; x < arr.length; x++) {
if (x == arr.length - 1) {
s += arr[x];
} else {
s += arr[x];
s += ", ";
}
}
s += "]";
return s;
}
}
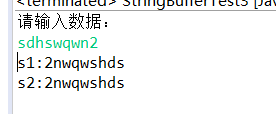
public class StringBufferTest3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 键盘录入数据
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入数据:");
String s = sc.nextLine();
// 方式1:用String做拼接
String s1 = myReverse(s);
System.out.println("s1:" + s1);
// 方式2:用StringBuffer的reverse()功能
String s2 = myReverse2(s);
System.out.println("s2:" + s2);
}
// 用StringBuffer的reverse()功能
public static String myReverse2(String s) {
// StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer();
// sb.append(s);
// StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer(s);
// sb.reverse();
// return sb.toString();
// 简易版
return new StringBuffer(s).reverse().toString();
}
// 用String做拼接
public static String myReverse(String s) {
String result = "";
char[] chs = s.toCharArray();
for (int x = chs.length - 1; x >= 0; x--) {
// char ch = chs[x];
// result += ch;
result += chs[x];
}
return result;
}
}
判断一个字符串是否是对称字符串
例如"abc"不是对称字符串,“aba”、“abba”、“aaa”、"mnanm"是对称字符串
public class StringBufferTest4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建键盘录入对象
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入一个字符串:");
String s = sc.nextLine();
// 一个一个的比较
boolean b = isSame(s);
System.out.println("b:" + b);
//用字符串缓冲区的反转功能
boolean b2 = isSame2(s);
System.out.println("b2:"+b2);
}
public static boolean isSame2(String s) {
return new StringBuffer(s).reverse().toString().equals(s);
}
public static boolean isSame(String s) {
boolean flag = true;
// 把字符串转成字符数组
char[] chs = s.toCharArray();
for (int start = 0, end = chs.length - 1; start <= end; start++, end--) {
if (chs[start] != chs[end]) {
flag = false;
break;
}
}
return flag;
}
}
public class StringBufferDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s1 = "hello";
String s2 = "world";
System.out.println(s1 + "---" + s2);// hello---world
change(s1, s2);
System.out.println(s1 + "---" + s2);// hello---world
StringBuffer sb1 = new StringBuffer("hello");
StringBuffer sb2 = new StringBuffer("world");
System.out.println(sb1 + "---" + sb2);// hello---world
change(sb1, sb2);
System.out.println(sb1 + "---" + sb2);// hello---worldworld
}
public static void change(StringBuffer sb1, StringBuffer sb2) {
sb1 = sb2;//赋值不变
sb2.append(sb1);//作为方法改变
}
public static void change(String s1, String s2) {
s1 = s2;
s2 = s1 + s2;
}
}
把100这个数据的二进制,八进制,十六进制计算出来,以及int的范围是多大,重点考察integer对象的方法。
- 常用的基本进制转换
- public static String toBinaryString(int i)
- public static String toOctalString(int i)
- public static String toHexString(int i)
public class IntegerDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 不麻烦的就来了
// public static String toBinaryString(int i)
System.out.println(Integer.toBinaryString(100));
// public static String toOctalString(int i)
System.out.println(Integer.toOctalString(100));
// public static String toHexString(int i)
System.out.println(Integer.toHexString(100));
// public static final int MAX_VALUE
System.out.println(Integer.MAX_VALUE);
// public static final int MIN_VALUE
System.out.println(Integer.MIN_VALUE);
}
}

其他进制到10进制的转换,其他进制到十进制的转换
进制的范围:2-36(0-9,a-z故为10+26)
- 十进制到其他进制
- public static String toString(int i,int radix)
- 其他进制到十进制
- public static int parseInt(String s,int radix)
public class IntegerDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 十进制到二进制,八进制,十六进制
System.out.println(Integer.toBinaryString(100));
System.out.println(Integer.toOctalString(100));
System.out.println(Integer.toHexString(100));
System.out.println("-------------------------");
// 十进制到其他进制
System.out.println(Integer.toString(100, 10));
System.out.println(Integer.toString(100, 2));
System.out.println(Integer.toString(100, 8));
System.out.println(Integer.toString(100, 16));
System.out.println(Integer.toString(100, 5));
System.out.println(Integer.toString(100, 7));
System.out.println(Integer.toString(100, -7));
System.out.println(Integer.toString(100, 70));
System.out.println(Integer.toString(100, 1));
System.out.println(Integer.toString(100, 17));
System.out.println(Integer.toString(100, 32));
System.out.println(Integer.toString(100, 37));
System.out.println(Integer.toString(100, 36));
System.out.println("-------------------------");
//其他进制到十进制
System.out.println(Integer.parseInt("100", 10));
System.out.println(Integer.parseInt("100", 2));
System.out.println(Integer.parseInt("100", 8));
System.out.println(Integer.parseInt("100", 16));
System.out.println(Integer.parseInt("100", 23));
//NumberFormatException
//System.out.println(Integer.parseInt("123", 2));
}
}
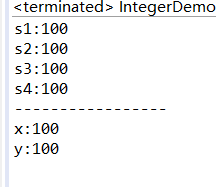
int类型和String类型的相互转换
public class IntegerDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// int -- String
int number = 100;
// 方式1
String s1 = "" + number;
System.out.println("s1:" + s1);
// 方式2
String s2 = String.valueOf(number);
System.out.println("s2:" + s2);
// 方式3
// int -- Integer -- String
Integer i = new Integer(number);
String s3 = i.toString();
System.out.println("s3:" + s3);
// 方式4
// public static String toString(int i)
String s4 = Integer.toString(number);
System.out.println("s4:" + s4);
System.out.println("-----------------");
// String -- int
String s = "100";
// 方式1
// String -- Integer -- int
Integer ii = new Integer(s);
// public int intValue()
int x = ii.intValue();
System.out.println("x:" + x);
//方式2
//public static int parseInt(String s)
int y = Integer.parseInt(s);
System.out.println("y:"+y);
}
}
装箱案例,注意在使用时,Integer x = null;代码就会出现NullPointerException
建议先判断是否为null,然后再使用。
public class IntegerDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 定义了一个int类型的包装类类型变量i
// Integer i = new Integer(100);
Integer ii = 100;
ii += 200;
System.out.println("ii:" + ii);
// 通过反编译后的代码
// Integer ii = Integer.valueOf(100); //自动装箱
// ii = Integer.valueOf(ii.intValue() + 200); //自动拆箱,再自动装箱
// System.out.println((new StringBuilder("ii:")).append(ii).toString());
Integer iii =new Integer("123");
// NullPointerException
if (iii != null) {
iii += 1000;
System.out.println(iii);
}
}
}
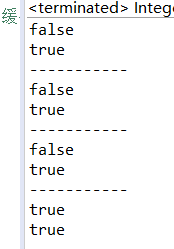
public class IntegerDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Integer i1 = new Integer(127);
Integer i2 = new Integer(127);
System.out.println(i1 == i2);
System.out.println(i1.equals(i2));
System.out.println("-----------");
Integer i3 = new Integer(128);
Integer i4 = new Integer(128);
System.out.println(i3 == i4);
System.out.println(i3.equals(i4));
System.out.println("-----------");
Integer i5 = 128;
Integer i6 = 128;
System.out.println(i5 == i6);
System.out.println(i5.equals(i6));
System.out.println("-----------");
Integer i7 = 127;
Integer i8 = 127;
System.out.println(i7 == i8);
System.out.println(i7.equals(i8));
}
}
*注意:针对-128到127之间的数据,做了一个数据缓冲池,如果数据是该范围内的,
每次并不创建新的空间,Integer的数据直接赋值,如果在-128到127之间,
会直接从缓冲池里获取数据。
统计一个字符串中大写字母字符,小写字母字符,数字字符出现的次数。(不考虑其他字符)
public class CharacterTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 定义三个统计变量。
int bigCount = 0;
int smallCount = 0;
int numberCount = 0;
// 键盘录入一个字符串。
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入一个字符串:");
String line = sc.nextLine();
// 把字符串转换为字符数组。
char[] chs = line.toCharArray();
// 历字符数组获取到每一个字符
for (int x = 0; x < chs.length; x++) {
char ch = chs[x];
// 判断该字符
if (Character.isUpperCase(ch)) {
bigCount++;
} else if (Character.isLowerCase(ch)) {
smallCount++;
} else if (Character.isDigit(ch)) {
numberCount++;
}
}
// 输出结果即可
System.out.println("大写字母:" + bigCount + "个");
System.out.println("小写字母:" + smallCount + "个");
System.out.println("数字字符:" + numberCount + "个");
}
}

java入门基础学习(一)
java入门基础学习(二)
java入门基础学习(三)
java进阶之常见对象(一)
java进阶之冒泡排序
java进阶之选择排序