java期末复习题目练习
总结一下在复习过程中的知识点:
20181218
**文件操作--列出指定目录下的全部内容
public class Homework {
public static void main(String[] args) {
File f=new File("e:"+File.separator+"科技创新");
print(f);
}
private static void print(File f) {
if(f!=null){
if(f.isDirectory()){
File[]files=f.listFiles();
if(files!=null){
for(File ff:files){
print(ff);
}
}
}else{
System.out.println(f);//1.第一层如果文件为空即没有子文件就输出他自己的名字(路径)2.最后一层文件夹中的最后一个文件输出路径
}
}
}
}**20181220
两种输出数组的方法
1. System.out.println(Arrays.toString(a));
2.for(int aa:a){
System.out.print(aa+" ");
}
**Arrays.binarySearch()
前提是先对数组进行排序,Arrays.sort(a);
System.out.println("3的下标:"+Arrays.binarySearch(a, 3));
数组里的数返回的就是它的下标
它对于非数组中的值的返回是这样的:假设该数据存在于数组中,并按照大小顺序排列,此时的low值是假设该数据在数组中的下标
**
ArrayList对象的输出方式
1.Iterator it=list.iterator();
while(it.hasNext()){
System.out.println(it.next());
}//用迭代器的方法
2.for(int i=0;i
}//用list.get(下标)的方法
**
//ListIterator在Iterator基础上添加了add(),previous()和hasPrevious()方法
ListIterator aIter=a.listIterator();
//普通的Iterator只有三个方法,hasNext(),next()和remove()
Iterator bIter=b.iterator();
********
while(bIter.hasNext())
{
if(aIter.hasNext())
aIter.next();//游标移动下一个元素
aIter.add(bIter.next());游标移动B的元素并写入A的后面
}
*****
一种计算斐波那切数列的方法(封装函数即方法的样式)
private static int getNum(int i) {
int count=0;
if(i==0)count=0;
if(i==1)count=1;
if(i>1)count=getNum(i-1)+getNum(i-2);
return count;
}//得到的就是一个菲波那切数
*********
inti=0;
while(getNum(i)<10000){
System.out.print(getNum(i)+" ");
i++;
}
System.out.print(getNum(i));*****
如果要把列表里的数调出来使用的话,首先先把它转化成String(.tostring)然后转化成相应的类型(parse**)
********20181222
//集合遍历输出方式1.基本的for循环2.for each 3.使用集合的迭代器Iterator 4.直接输出(toString)
/*for(int i=0;i it=set.iterator();
while(it.hasNext()){
System.out.println(it.next());//3.
}
System.out.println(set);//4. *******集合里面存对象元素,排序,输出
public class Homework {
public static void main(String[] args) {
TreeSet mytree=new TreeSet<>();
mytree.add(new Person("Tom",24));
mytree.add(new Person("Jerry",21));
mytree.add(new Person("Brown",26));
mytree.add(new Person("Bob",28));
mytree.add(new Person("Brown",21));
mytree.add(new Person("Brown",21));
Iterator it=mytree.iterator();
while(it.hasNext()){
Person p=(Person) it.next();//需要把它转换成类类型不然输出的是地址
System.out.println(p.name+" "+p.age);
}
}
/* 集合元素是对象,无法自然排序的解决方案
* 1.类要先实现一个接口comparable,然后重写compareTo()方法,有个地方很米的就是
* compareto()没有调用但是还能起到排序的功能
* 2.如果是按年龄排的序,年龄重复德华不会重复添加同理姓名重复的话,也不会重复添加
*
*/
public static class Person implements Comparable{
private String name;
private int age;
public Person(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
@Override
/*重写的比较方法比较两个对象一一对应全部相等:(原来的方法如果指定的数与参数相等返回0。如果指定的数小于参数返回 -1。如果指定的数大于参数返回 1。)
* 把类中的元素挨个的比较*/
public int compareTo(Object o) {
Person p=(Person)o;//转换成相同的类类型
//姓名相同比较年龄
/*int tempt1=this.name.compareTo(p.name);
return tempt1==0?this.age-p.age:tempt1;*/
//return this.age-p.age;//按照年龄排序
//年龄相同比较姓名
int tempt=this.age-p.age;
return tempt==0?this.name.compareTo(p.name):tempt;
}
}
} *******
20181224
今天虽然是平安夜,但是还是要好好复习的呀
今天是总结的学习的map
方法和代码都在下面了
public class Homework {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//map的初始方法
Map map=new HashMap();
//map的添加元素的方法是put
map.put(1, "sunyucui");
map.put(2, "tom");
map.put(6, "jerry");
map.put(5, "tom");
map.put(1, "liyifeng");
System.out.println(map.keySet());//只输出key值
System.out.println(map.values());//只输出value值
//
// 将Map.Entry的对象存入里set集合里,用对象去掉用key和value
//这个是常用的方法
Set> entrys=map.entrySet();
Iterator> it=entrys.iterator();
while(it.hasNext()){
Map.Entry en=it.next();
System.out.println("key:"+en.getKey()+" values:"+en.getValue());
}
//把value放入collection集合里,但是只能调用values
/*Collection c=map.values();
Iterator it=c.iterator();
while(it.hasNext()){
System.out.println("值:"+it.next());
}*/
//把key放在set集合里,输出key值,并通过key输出value
/*Set keys=map.keySet();
Iterator it=keys.iterator();
while(it.hasNext()){
int key=(int)it.next();
System.out.println("键:"+key+"值: "+map.get(key));
}
map.clear();
System.out.println(map);
System.out.println(map.isEmpty());*/
}
} ******
20181215
自定义一个异常类(输入一个大于10的数捕获异常)
public class Homework {
public static void compute(int a) throws MyException{
System.out.println("use the compute("+a+")");
if(a>10){
throw new MyException(a);
}
System.out.println("常规退出");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
compute(1);
compute(10);
compute(20);
} catch (MyException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
System.out.println("catch:"+e.toString());
}
}
//自定义的异常类 ,并继承Exception类
static class MyException extends Exception{
private int content;
public MyException(int content){
this.content=content;
}
public int getContent() {
return content;
}
}
}
1.新建一个异常类MyException
2.定义一个方法,包含什么情况下会抛出异常if(***){throw new MyException(***)},方法的开头加上throws MyException
下学期可能会学到的一个知识
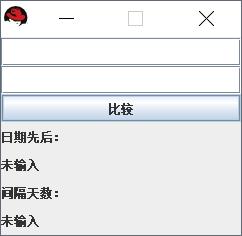
运行效果是这样的:
附上代码:
import java.awt.Container;
import java.awt.GridLayout;
import java.awt.event.ActionEvent;
import java.awt.event.ActionListener;
import javax.swing.JButton;
import javax.swing.JFrame;
import javax.swing.JLabel;
import javax.swing.JPanel;
import javax.swing.JTextField;
public class Homework {
public static class riqi extends JFrame implements ActionListener{
private JPanel p_main = new JPanel();
private JTextField t_text1 = new JTextField(20);
private JTextField t_text2 = new JTextField(20);
private JButton b_bun = new JButton("比较");
private JLabel l_lab1 = new JLabel("日期先后:");
private JLabel l_dateShow = new JLabel("未输入");
private JLabel l_lab2 = new JLabel("间隔天数:");
private JLabel l_subShow = new JLabel("未输入");
public riqi(String title){
setTitle(title);
Container cp = getContentPane();
cp.add(p_main);
p_main.setLayout(new GridLayout(7,1));
p_main.add(t_text1);
p_main.add(t_text2);
p_main.add(b_bun);
b_bun.addActionListener(this);
p_main.add(l_lab1);
p_main.add(l_dateShow);
p_main.add(l_lab2);
p_main.add(l_subShow);
pack();
setResizable(false);
setDefaultCloseOperation( JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE );
}
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e){
String s1 = t_text1.getText();
String s2 = t_text2.getText();
double d1 = Double.parseDouble(s1);
double d2 = Double.parseDouble(s2);
int sub = (int)(d1-d2);
if(sub<0){
l_dateShow.setText(s1+","+s2);
}
else{
l_dateShow.setText(s2+","+s1);
}
l_subShow.setText(Math.abs(sub)+"");
}
}
public static void main(String args[]){
riqi c = new riqi("日期比较");
c.setVisible(true);
}
}
********
明天就要考试啦,虽然听说题目不难但是还是有些小紧张
所以今天就总结一下可能会出道的题目吧
---------------文件输入输出-----------
字节流:
Outputstream out----FileoutputStream(文件对象)
IntputStream in-----FileInputStream(文件对象)
*当文件不存在时会自动创建
*当向文件写入东西的时候,要解析成字节数组,然后out.write(数组)写入文件,write()后加一个flush()清除缓存区
同理当从文件中读数据时要把读到的数据存到字节数组(in.read(数组))中然后转换成String类型输出(new String(数组))
//利用in.read()可以有顺序的读数据当读完的时候返回-1可以用来判断是否读完数据
*File.separator代表分隔符的意思不同的操作系统下分隔符是不一样的
字符流:
Reader-----FileWriter(文件对象)
Writer-----FileReader(文件对象)
可以直接写入字符串,读出的数据先放到字符数组然后转换成String类型,也是write()和read()的方法
**通过Scanner类从文件中获取数据
File f1=new File(文件路径)
Scanner sc=new Scanner(f1);
读到的数据不包含空格
**将信息写到文件中,需要建立通道:
PrintWriter pw=new PrintWriter(文件对象名)
或: PrintWriter pw=new PrintWriter(System.out)
第2种格式是在显示器上显示信息,以下两个语句是等价的:
System.out.println(“AAAAA!”);
pw.println((“AAAAA!”);
1.文件复制:把一个文件的东西复制到另一个文件中
2.文件的写入,写入学生信息//文件的读,输出学生信息及成绩并把总成绩输出来
public class Homework {
//在文件内容未知的情况下文件的复制Scanner 读数据PrintWriter写数据
//缺点是Scanner读不到空格,
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
File f1=new File("e:"+File.separator+"test1.txt");
File f2=new File("e:"+File.separator+"Copytest.txt");
Scanner sc =new Scanner(f1);
PrintWriter pw=new PrintWriter(f2);
while(sc.hasNext()){
String str=sc.next();
pw.write(str);
}
pw.flush();//清除缓存区
pw.close();//一定要关闭资源
sc.close();
}
}
public class Homework {
public static void main(String[] args) throws FileNotFoundException {
File f1=new File("e:"+File.separator+"test1.txt");
File f2=new File("e:"+File.separator+"chengji.txt");
Scanner sc=new Scanner(f1);
PrintWriter pw=new PrintWriter(f2);
String name,s1,s2,s3;
int c1,c2,c3,total;
name=sc.next();s1=sc.next();s2=sc.next();s3=sc.next();
pw.write(name+" "+s1+" "+s2+" "+s3+" "+"总成绩"+"\r\n");
System.out.println(name+" "+s1+" "+s2+" "+s3+" "+"总成绩");
while(sc.hasNext()){
name=sc.next();
c1=sc.nextInt();
c2=sc.nextInt();
c3=sc.nextInt();
total=c1+c2+c3;
pw.write(name+" "+c1+" "+c2+" "+c3+" "+total+"\r\n");
pw.flush();
System.out.println(name+" "+c1+" "+c2+" "+c3+" "+total);
}
sc.close();
pw.close();
}
}
**********************
public class Homework {
//在文件内容未知的情况下文件的复制FileInputStream in读数据 FileOutputStream out写数据
//
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
File f1=new File("e:"+File.separator+"test1.txt");
File f2=new File("e:"+File.separator+"Copytest.txt");
FileOutputStream out=new FileOutputStream(f2);
FileInputStream in=new FileInputStream(f1);
byte[]b=new byte[(int)f1.length()];
int len=0;
while((len=in.read(b))!=-1){//一边读取一遍输出
/*因为是一边读一边写,如果不把in.read()赋值给一个变量就会丢失数据*/
out.write(b, 0, len);
}
}
}
*********************
public class Homework {
//在文件内容未知的情况下文件的复制FileReader in读数据 FileWriter out写数据
//
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
File f1=new File("e:"+File.separator+"test1.txt");
File f2=new File("e:"+File.separator+"Copytest.txt");
FileWriter out=new FileWriter(f2);
FileReader in=new FileReader(f1);
int b=in.read();
while(b!=-1){
out.write(b);
//write(int)方法虽然接收的是int类型参数,但是是按照byte类型来处理的。
b=in.read();
}
out.close();
in.close();
}
}--------------集合类的使用-------------
1.简单的操作系统进行增删改查
Collection(利用迭代器Iterator进行集合的输出)
list(可重复可为空):ArrayList (随机访问速度快) // LinkedList(频繁的插入删除)
Set(不可重复最多一个空):HashSet // TreeSet(有序)
//除了具有Collection接口必备的iterator()方法外,List还提供一个listIterator()方法,返回一个 ListIterator接口,和标准的Iterator接口相比,ListIterator多了一些add()之类的方法,允许添加,删除,设定元素, 还能向前或向后遍历。
Map(键值对): TreeMap (自动排序)// HashMap
对于不能自然排序的对象元素 可以继承comparable并重载CompareTo()方法,或者写一个比较器(一个类继承comparator重写compare()方法)
2.编写一个交错合并列表元素的程序
3.在集合中每隔两个元素删除一个
-------------- 异常处理----------------
1.自定义一个异常处理
2.小的知识点的记忆
--------------接口和抽象类-----------
1.实现多态
--------------常用实用类的使用--------
String Integer Double Character ,,,,,
这些封装类之间的相互转化
小技巧:需要对一个数进行内部的一些处理可以先转化成String类型然后存入 字符数组内 这样就可以将数切割单独处理,利用数组.CharAt(下标)调用
-----------简单的算法-------------
斐波那切数列,素数,水仙花数,其他的一系列数,海伦公式,数组的一些操作,大小写转换,数的四舍五入的一些精度的运算,判断闰年,获得一个随机数,打印一些形式,冒泡排序
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
怕考试的时候系统会出现一些不可描述的情况 所以记录一下会出现的情况
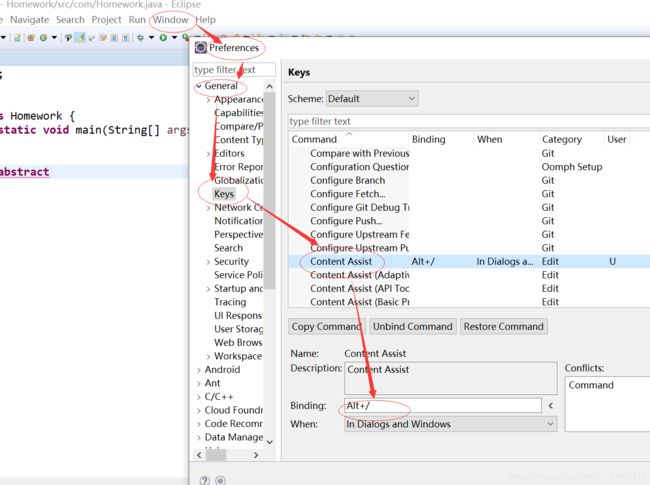
1.Alt+/失效的话
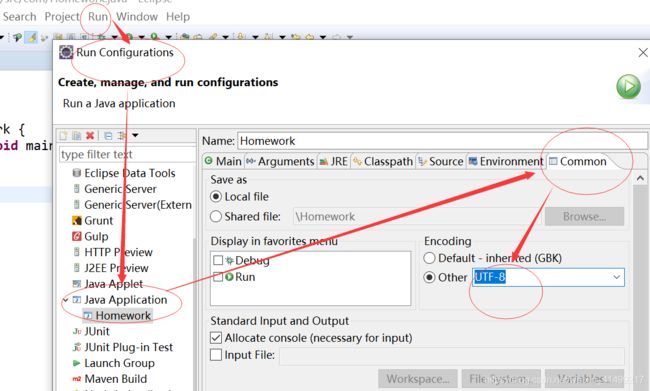
2.从文件里读数据的时候得到乱码
**********
下一个问题
public class Homework {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Random r=new Random();
int a=r.nextInt(10)+10;//输出10~20之间的随机数
/*int a=r.nextInt(a)+b;输出a~(a+b)之间的随机数*/
System.out.println(a);
}
}
************
java期末复习最后一天
public class Homework {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/*输入三角形的三边,判断是否可以构成三角形,然后输出面积,结果保留两位小数并且四舍五入
* **/
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入一个三角形的三边:\na:");
double a=sc.nextDouble();
System.out.println("b:");
double b=sc.nextDouble();
System.out.println("c:");
double c=sc.nextDouble();
System.out.println("是否能够成三角形:"+isSjx(a,b,c));
System.out.println("三角形的面积是:"+getArea(a,b,c));
}
private static double getArea(double a, double b, double c) {
double p=(a+b+c)/2.0;
double s=Math.sqrt(p*(p-a)*(p-b)*(p-c));
s=jingQueDu(s);
return s;
}
private static double jingQueDu(double s) {
BigDecimal bd=new BigDecimal(s);
s=bd.setScale(2, BigDecimal.ROUND_HALF_UP).doubleValue();
return s;
}
private static boolean isSjx(double a, double b, double c) {
if(a+b>c&&a+c>b&&c+b>a){
return true;
}else return false;
}
}public class Homework {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/*输入三角形的三边,判断是否可以构成三角形,然后输出面积,结果保留两位小数并且四舍五入
* 需要注意的是:把输入的整型变量转换成String类型然后转换成字符数组一个一个的判断,判断的时候
* 做求余运算的时候可以自动变成整形运算,但是在判断的时候要用字符
* **/
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入人一个整数:");
int a=sc.nextInt();
String aa=new Integer(a).toString();
System.out.println("奇数个数有"+jiShu(aa)+"个");
System.out.println("偶数个数"+ouShu(aa)+"个");
System.out.println("0有"+ling(aa)+"个");
}
private static int ling(String aa) {
int count=0;
char[]c=aa.toCharArray();
for(int i=0;ipublic class Homework {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/*利用三种方法来计算某个公式
**/
int n=10000;
JiSuan.getJiSuan_for(n);
JiSuan.getJiSuan_while(n);
JiSuan.getJiSuan_dowhile(n);
}
public static class JiSuan{
private static double s1=0;
private static double s2=0;
private static double s3=0;
public static void getJiSuan_for(int n) {
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
s1=s1+(1.0/(i*i))*(int)Math.pow(-1, i+1);
}
System.out.println("for:"+s1);
}
public static void getJiSuan_dowhile(int n) {
int i=1;
do{
s2=s2+(1.0/(i*i))*(int)Math.pow(-1, i+1);
i++;
}while(i<=n);
System.out.println("dowhile:"+s2);
}
public static void getJiSuan_while(int n) {
int i=1;
while(i<=n){
s3=s3+(1.0/(i*i))*(int)Math.pow(-1, i+1);
i++;
}
System.out.println("while:"+s3);
}
}
}public class Homework {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/*直线类含有求交点的方法
**/
Line l1=new Line(1, 6, 2, 12);
Line l2=new Line(1, 12, 4, 24);
Point p=l1.jiaoDian(l2);
p.show();
}
public static class Point{
double x;
double y;
public Point(double x, double y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
public Point() {
}
public double getX() {
return x;
}
public void setX(double x) {
this.x = x;
}
public double getY() {
return y;
}
public void setY(double y) {
this.y = y;
}
public void show(){
System.out.println("["+x+","+y+"]");
}
}
//两点确定一条直线
public static class Line extends Point{
double a, b;
public Line(double x, double y, double a, double b) {
super(x, y);
this.a = a;
this.b = b;
}
public double getK(){//计算斜率
double x=getX();
double y=getY();
double k1=(y-b)/x-a;
return k1;
}
public double getB(){//计算B
return b-getK()*a;
}
public Point jiaoDian(Line l){//计算和另一个直线的交点返回一个点类类型
double k1=getK();
double k2=l.getK();
double b1=getB();
double b2=l.getB();
double jx;
double jy;
if(k1==k2){
jx=0;jy=0;//没有交点
}else{
jx=(b1-b2)/(k1-k2);//利用方程组
jy=k1*jx+b1;//代入其中一条直线
}
Point p=new Point(jx,jy);
return p;
}
}
}