react 笔记
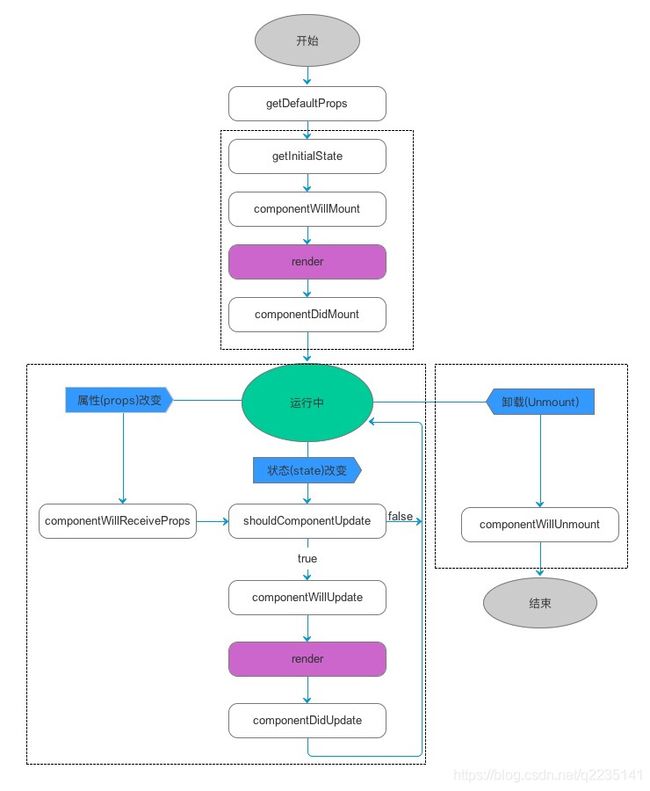
一、生命周期:
-
初始化
getDefaultProps() getIniterStates() componentwillmount() render() componentdidmount() -
运行中
componentWillReceiveProps() shouldComponentUpdate() componentwillUpdate() render() componentdidUpdate() -
卸载
compoentwillUnmount()
二、特性
-
声明式
-
虚拟DOM
-
支持服务端渲染
-
单向数据绑定 flux
-
状态机组件
三、渲染流程
四、shouldComponentUpdate
接受参数后,生成新的虚拟Dom对象树,使用Diff算法比较新旧对象树,找出有差异的节点,以打补丁的形式更新到真实Dom上
五、虚拟Dom存在的原因
真实Dom树有231个元素属性,大部分与渲染无关,渲染真实Dom非常耗性能
虚拟Dom以对象树的形式模拟真实Dom,只添加与渲染有关的属性,利用Diff算法
找出更新的部分,然后更新到真是Dom上,提升了渲染效率
六、Diff算法
jsx最终都会被转换成createClass()的形式,每个元素及组件都是一个对象,最终形成一个虚拟Dom对象树的结构。
Diff算法是从外而内开始比较,会比较节点的类型、属性、子元素等,如果根节点类型不一致,会重新渲染整个对象树。
Diff会借助列表元素的key值进行比较,key最好不是循环的index,有助于提升Diff算法的效率
七、JSX语法规则
-
元素渲染:所有组件最终编译为 React.createElement(type, {props}, …children)
-
组件命名:首字母大写
-
组件嵌套:只能有一个根节点,并用()包含
-
props:只读,父组件传递 constructor(props){ … },至上而下数据流
-
state:不能直接修改this.state,通过this.setState() 修改
setState不会立刻改变React组件中state的值; setState通过引发一次组件的更新过程来引发重新绘制; - shouldComponentUpdate - componentWillUpdate - render - componentDidUpdate 多次setState函数调用产生的效果会合并 this.setState({name: 'newName'}) this.setState((preState,props)=>{ return preState + newState }) -
事件处理:
class Demo extends React.component { constructor(props){ this.state.name = props.name this.handEvent = this.handEvent.bind(this) } handEvent (e) { console.log(e.target.name) } render () { return { } } } -
条件渲染:
class Demo extends React.component { constructor(props){ super(props) this.state.flag = true this.state.name = props.name this.handEvent = this.handEvent.bind(this) this.handCommit = this.handCommit.bind(this) } handEvent (e) { console.log(e.target.name) } handCommit (e) { console.log(e.target.name) } render () { return { if (this.state.flag) { } else { } // or {this.state.flag ? : } } } } -
列表&keys:
class Demo extends React.component { constructor(props){ super(props) this.state.items = props.array } render () { const items = this.state.items.map((item) =>- {item.name}
) return {- {items}
-
表单:
import React form 'react' class Demo extends React.component { constructor (props) { super(props) this.state = {name: ''} this.handInput = this.handInput.bind(this) this.handCommit = this.handCommit.bind(this) } handInput (e) { this.setState({name: e.target.value}) /* this.setState((preState,props) => { name:preState.name + e.targer.value }) */ } handCommit (e) { e.preventDefault() console.log({this.state.name}) } render () { return { } } } -
状态提升:兄弟之间共享状态的情况,将状态提升至最近父组件进行管理(至上而下)
-
组合:
// 组合 function Dialog(props) { return ({props.title}
{props.message}
{props.children} -
深入JSX:
-
React 与 引用组件类型必须在当前作用域
组件编译后:React.createElement(component,props, ...children) -
运行时选择类型
class Demo extends React.component { constructor (props) { super(props) this.state.types = ['Button','Input'] } render () { const componentType = this.state.types[0] return {} } } -
JSX中的子代:可以为任何对象(常量,变量,表达式,函数,引入组件),最终返回为JSX标签即可
-
使用PropTypes检查类型:
import 'PropTypes' from 'prop-types' class Demo extends React.component { constructor (props) { super(props) this.state.name = props.name this.state.number = props.number } render () { return {} } } Demo.PropTypes = { name: PropTypes.string, number: ProTypes.number }{this.state.name} {this.state.number} -
受控组件&木偶组件:
受控组件:React负责渲染表单的组件仍然控制用户后续输入时所发生的变化。相应的,其值由React控制的输入表单元素称为“受控组件”
木偶组件:只用作渲染数据,没有状态管理的组件
由于该标签的value属性是只读的, 所以它是 React 中的一个非受控组件
// 受控 import React form 'react' class Demo extends React.component { constructor (props) { super(props) this.state = {name: '默认值'} this.handInput = this.handInput.bind(this) this.handCommit = this.handCommit.bind(this) } handInput (e) { this.setState({name: e.target.value}) } handCommit (e) { e.preventDefault() console.log({this.state.name}) } render () { return {
-