RocketMQ——与Netty的结合
RocketMQ作为一个高效的分布式消息队列,通信质量是必须保证的,而Netty是一个高效的网络应用框架,因此RocketMQ选择Netty来实现底层的通信功能。
-
Netty介绍
Netty是一个高效的JAVA网络应用框架,它提供异步事件驱动的方式,使用Netty可以快速开发出高性能的网络应用程序。
Netty从很多协议实现中吸取了丰富的经验,比如SMTP、HTTP等基于二进制和文本的传统协议。借助Netty可以开发出高质量的通信程序。 -
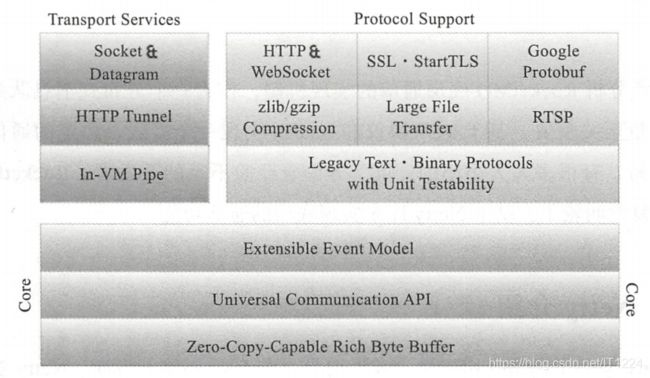
Netty模型
如图所示,Netty主要分成三大部分:第一部分包括零拷贝技术、统一的通讯API和可扩展的事件模型;第 二部分是传输层;第三部分就是协议支持。
-
ByteBuffer的重新设计
CPU的处理速度比网络传输数据的速度要快得多,因此会引入缓冲区,让网络传输的数据先积压在缓冲区,等到有一定数量后再交给CPU做处理。Netty并没有使用原生的ByteBuffer,原生的ByteBuffer使用起来会复杂一些,像复位flip这样的操作都必须手动完成,Netty使用了自己重新实现的buffer API,功能上还包括允许自定义缓存类型,透明的零拷贝实现等等,使用上也更简单,更适合开发。
ByteBuffer实现的是一个轻量级的字节数组包装器,它有读写操作,相应的维护readerIndex和writerIndex,有了这两个索引可以很清晰的计算出可读部分(writerIndex - readerIndex)、可写部分(capacity - writerIndex)、废弃部分(readerIndex)。用户也能使用discardReadBytes主动清理掉废弃部分,增加更多的可写空间。和原生的ByteBuffer相比,Netty封装的ByteBuffer更简单、扩展性更大。 -
统一的I/O接口和拦截链的事件模型
Netty 提供了统一的异步I/O编程接口Channel,它抽象了所有点对点的操作。
public interface Channel extends AttributeMap, Comparable<Channel> {
EventLoop eventLoop();
Channel parent();
ChannelConfig config();
boolean isOpen();
boolean isRegistered();
Channel read();
ChannelFuture write(Object var1);
ChannelFuture write(Object var1, ChannelPromise var2);
Channel flush();
ChannelFuture writeAndFlush(Object var1, ChannelPromise var2);
ChannelFuture writeAndFlush(Object var1);
...
}
那我们再谈基于拦截链的事件模型。Netty具有良好的I/O事件模型,整体的层次结构是严格定义的,允许在不破坏现有代码的结构上自定义事件类型,扩散性很好。在Netty中,ChannelPipeline在初始化时可以定义一系列的Handler,那么ChannelPipeline 内部的channelEvent就会被这一组Handler处理,也就是说对于事件的处理过程以及管道内部处理器的交互过程,用户会具有绝对的控制力。
-
RocketMQ基于Netty的通信实现
RemotingServer、RemotingClient分别对应通信的服务端和客户端。下面将介绍RemotingServer这个顶层通信类,RemotingClient过程类似。
- RemotingServer
public interface RemotingService {
void start();// 客户端服务端都需要启动程序,下面同理
void shutdown();
void registerRPCHook(RPCHook rpcHook);
}
public interface RemotingServer extends RemotingService {
void registerProcessor(final int requestCode, final NettyRequestProcessor processor,
final ExecutorService executor);
// 设置接收到消息后的处理方法
void registerDefaultProcessor(final NettyRequestProcessor processor, final ExecutorService executor);
int localListenPort();
Pair<NettyRequestProcessor, ExecutorService> getProcessorPair(final int requestCode);
RemotingCommand invokeSync(final Channel channel, final RemotingCommand request,
final long timeoutMillis) throws InterruptedException, RemotingSendRequestException,
RemotingTimeoutException;
void invokeAsync(final Channel channel, final RemotingCommand request, final long timeoutMillis,
final InvokeCallback invokeCallback) throws InterruptedException,
RemotingTooMuchRequestException, RemotingTimeoutException, RemotingSendRequestException;
void invokeOneway(final Channel channel, final RemotingCommand request, final long timeoutMillis)
throws InterruptedException, RemotingTooMuchRequestException, RemotingTimeoutException,
RemotingSendRequestException;
}
NettyRemotingServer是RemotingServer的一个实现,下面将详细分析NettyRemotingServer类。
public NettyRemotingServer(final NettyServerConfig nettyServerConfig) {
this(nettyServerConfig, null);
}
public NettyRemotingServer(final NettyServerConfig nettyServerConfig,
final ChannelEventListener channelEventListener) {
super(nettyServerConfig.getServerOnewaySemaphoreValue(), nettyServerConfig.getServerAsyncSemaphoreValue());
this.serverBootstrap = new ServerBootstrap();// 从这里开始就已经有Netty的影子了
this.nettyServerConfig = nettyServerConfig;
this.channelEventListener = channelEventListener;
int publicThreadNums = nettyServerConfig.getServerCallbackExecutorThreads();
if (publicThreadNums <= 0) {
publicThreadNums = 4;
}
// 在构造函数中给NettyRemotingServer中的各个属性进行初始化,包括线程池、channelEventListener、ServerBootstrap等等
this.publicExecutor = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(publicThreadNums, new ThreadFactory() {
private AtomicInteger threadIndex = new AtomicInteger(0);
// 保证并发情况下的线程安全
@Override
public Thread newThread(Runnable r) {
return new Thread(r, "NettyServerPublicExecutor_" + this.threadIndex.incrementAndGet());
}
});
if (useEpoll()) {
// 采用epoll IO模型,对线程池组进行初始化
this.eventLoopGroupBoss = new EpollEventLoopGroup(1, new ThreadFactory() {
private AtomicInteger threadIndex = new AtomicInteger(0);
@Override
public Thread newThread(Runnable r) {
return new Thread(r, String.format("NettyEPOLLBoss_%d", this.threadIndex.incrementAndGet()));
}
});
// selector线程组初始化,默认serverSelectorThreads = 3
this.eventLoopGroupSelector = new EpollEventLoopGroup(nettyServerConfig.getServerSelectorThreads(), new ThreadFactory() {
private AtomicInteger threadIndex = new AtomicInteger(0);
private int threadTotal = nettyServerConfig.getServerSelectorThreads();
@Override
public Thread newThread(Runnable r) {
return new Thread(r, String.format("NettyServerEPOLLSelector_%d_%d", threadTotal, this.threadIndex.incrementAndGet()));
}
});
} else {
// 不使用Epoll机制
this.eventLoopGroupBoss = new NioEventLoopGroup(1, new ThreadFactory() {
private AtomicInteger threadIndex = new AtomicInteger(0);
@Override
public Thread newThread(Runnable r) {
return new Thread(r, String.format("NettyNIOBoss_%d", this.threadIndex.incrementAndGet()));
}
});
this.eventLoopGroupSelector = new NioEventLoopGroup(nettyServerConfig.getServerSelectorThreads(), new ThreadFactory() {
private AtomicInteger threadIndex = new AtomicInteger(0);
private int threadTotal = nettyServerConfig.getServerSelectorThreads();
@Override
public Thread newThread(Runnable r) {
return new Thread(r, String.format("NettyServerNIOSelector_%d_%d", threadTotal, this.threadIndex.incrementAndGet()));
}
});
}
...
}
//实现顶层接口RemotingService的start方法,做程序启动
//defaultEventExecutorGroup 应用场景:当需要提交多个任务给defaultEventExecutor执行。可以从EventExecutorGroup中选择一个EventExecutor,向EventExecutor中添加要执行的任务。在Netty中要避免I/O线程阻塞,因此用defaultEventExecutorGroup的方式,将任务交给EventExecutor去做
@Override
public void start() {
this.defaultEventExecutorGroup = new DefaultEventExecutorGroup(
nettyServerConfig.getServerWorkerThreads(),
new ThreadFactory() {
private AtomicInteger threadIndex = new AtomicInteger(0);
@Override
public Thread newThread(Runnable r) {
return new Thread(r, "NettyServerCodecThread_" + this.threadIndex.incrementAndGet());
}
});
prepareSharableHandlers();
// 在Netty中有两个线程组,第一个是boss,一个是worker,官方上建议的说法是parent,一个是child,也就是说,前一个线程组生产的线程循环接受客户端的连接,一旦有新的连接,就会为这个新的连接分配资源,然后从worker线程组中选择一个线程(EventLoop)绑定到此连接中,此后客户端和服务端的交互由这个线程去完成。由此可以看出,一个EventLoop可以处理多个channel,一个channel在生命周期只会和一个EventLoop进行绑定,一旦一个channel上有耗时handler需要EventLoop处理,那么就会阻塞其他channel上的handler执行。
ServerBootstrap childHandler =
this.serverBootstrap.group(this.eventLoopGroupBoss, this.eventLoopGroupSelector)
.channel(useEpoll() ? EpollServerSocketChannel.class : NioServerSocketChannel.class)
.option(ChannelOption.SO_BACKLOG, 1024)
.option(ChannelOption.SO_REUSEADDR, true)
.option(ChannelOption.SO_KEEPALIVE, false)
.childOption(ChannelOption.TCP_NODELAY, true)
.childOption(ChannelOption.SO_SNDBUF, nettyServerConfig.getServerSocketSndBufSize())
.childOption(ChannelOption.SO_RCVBUF, nettyServerConfig.getServerSocketRcvBufSize())
.localAddress(new InetSocketAddress(this.nettyServerConfig.getListenPort()))
.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
public void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
// 指定EventExecutorGroup,尤其是处理耗时的handler,都要使用EventExecutorGroup,若不指定,默认处理handler的是IO线程
ch.pipeline()
.addLast(defaultEventExecutorGroup, HANDSHAKE_HANDLER_NAME, handshakeHandler)
// 给channel 添加一系列的handler,给defaultEventExecutorGroup执行
.addLast(defaultEventExecutorGroup,
encoder, //Sharable编码器(MessageToByte),接受的请求对象是一个RemotingCommand,后面详细介绍它的格式定义。在这里就是解析RemotingCommand,把其中有效的header和body的信息读取出来,写入到byteBuf中,发送出去
new NettyDecoder(),//解码器,基于LengthFieldBasedFrameDecoder,也就是有长度标识的decoder
/**
public NettyDecoder() {
super(FRAME_MAX_LENGTH, 0, 4, 0, 4);前4个字节代表长度,那么后面的字节就是实际传输的数据,将ByteBuf转换成原生的NIO ByteBuffer并解析转换成RemotingCommand
}
*/
new IdleStateHandler(0, 0, nettyServerConfig.getServerChannelMaxIdleTimeSeconds()),
connectionManageHandler,
serverHandler
);
}
});
if (nettyServerConfig.isServerPooledByteBufAllocatorEnable()) {
childHandler.childOption(ChannelOption.ALLOCATOR, PooledByteBufAllocator.DEFAULT);
}
try {
ChannelFuture sync = this.serverBootstrap.bind().sync();
InetSocketAddress addr = (InetSocketAddress) sync.channel().localAddress();
this.port = addr.getPort();
} catch (InterruptedException e1) {
throw new RuntimeException("this.serverBootstrap.bind().sync() InterruptedException", e1);
}
if (this.channelEventListener != null) {
this.nettyEventExecutor.start();
}
this.timer.scheduleAtFixedRate(new TimerTask() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
NettyRemotingServer.this.scanResponseTable();
} catch (Throwable e) {
log.error("scanResponseTable exception", e);
}
}
}, 1000 * 3, 1000);//周期性的扫描,将过期的request删掉而且触发callback方法,即executeInvokeCallback。(有一个map记录着所有的运行过的请求,只需要遍历这个map即可)
/**
public void executeInvokeCallback() {
if (invokeCallback != null) {
// 用原子类的CAS机制去保障只运行一次callback
if (this.executeCallbackOnlyOnce.compareAndSet(false, true)) {
invokeCallback.operationComplete(this);//回调operationComplete
}
}
}
**/
}
// 将原生的NIO byteBuffer 解析成RemotingCommand
public static RemotingCommand decode(final ByteBuffer byteBuffer) {
int length = byteBuffer.limit();
int oriHeaderLen = byteBuffer.getInt();
int headerLength = getHeaderLength(oriHeaderLen);
byte[] headerData = new byte[headerLength];
byteBuffer.get(headerData);
RemotingCommand cmd = headerDecode(headerData, getProtocolType(oriHeaderLen));
int bodyLength = length - 4 - headerLength;
byte[] bodyData = null;
if (bodyLength > 0) {
bodyData = new byte[bodyLength];
byteBuffer.get(bodyData);
}
cmd.body = bodyData;
return cmd;
}
- 补充RemotingCommand
RemotingCommand 是RocketMQ 自定义的协议, 具体格式如图所示。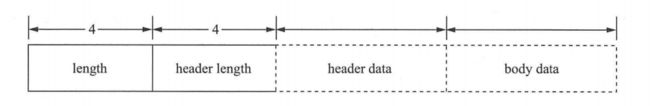
RocketMQ各个组件间的通信需要频繁在字节码和RemotingCommand之间转换,那么只需要调用RemotingCommand中封装好的操作就可以完成,比如decode、headerDecode等等。
private int code;
private LanguageCode language = LanguageCode.JAVA;
private int version = 0;
private int opaque = requestId.getAndIncrement();
private int flag = 0;
private String remark;
private HashMap<String, String> extFields;
private transient CommandCustomHeader customHeader;
public static RemotingCommand decode(final byte[] array) {
ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.wrap(array);
return decode(byteBuffer);
}
public static RemotingCommand decode(final ByteBuffer byteBuffer) {
int length = byteBuffer.limit();
int oriHeaderLen = byteBuffer.getInt();
int headerLength = getHeaderLength(oriHeaderLen);
byte[] headerData = new byte[headerLength];
byteBuffer.get(headerData);
RemotingCommand cmd = headerDecode(headerData, getProtocolType(oriHeaderLen));
int bodyLength = length - 4 - headerLength;
byte[] bodyData = null;
if (bodyLength > 0) {
bodyData = new byte[bodyLength];
byteBuffer.get(bodyData);
}
cmd.body = bodyData;
return cmd;
}
public static int getHeaderLength(int length) {
return length & 0xFFFFFF;
}