Linux Ansible自动化运维 loop循环以及过滤器
在2.5版本之前的ansible中,大多数人习惯使用"with_X"风格的关键字操作循环,从2.6版本开始,官方开始推荐使用"loop"关键字代替"with_X"风格的关键字,我们先来看一个小示例,使用loop关键字进行最简单的列表循环,示例如下:
[root@server4 ~]# vim loopxh1.yml
[root@server4 ~]# cat loopxh1.yml
---
- hosts: testB
remote_user: root
gather_facts: no
tasks:
- debug:
msg: "{
{ item }}"
loop:
- teststr1
- teststr2
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
上例使用"loop"关键字,替换了之前总结的"with_list"这种"with_X"风格的关键字,它们的效果是完全相同的。
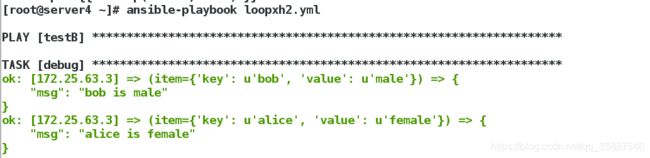
在总结lookup插件的用法时,已经详细的描述过,我们可以使用"loop"关键字配合对应的"lookup"插件,替换更多的、具有更复杂功能的"with_X"风格的关键字,比如,使用loop关键字和dict插件替换"with_dict"关键字,示例如下
[root@server4 ~]# vim loopxh2.yml
[root@server4 ~]# cat loopxh2.yml
---
- hosts: testB
remote_user: root
gather_facts: no
vars:
users:
alice: female
bob: male
tasks:
- debug:
msg: "{
{item.key}} is {
{item.value}}"
loop: "{
{ lookup('dict',users) }}"
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
上例使用了**“loop加lookup"的方式,完成了循环操作,而在2.6版本的官网手册中,官方开始推荐使用"loop加filter”**的方式来替代"loop加lookup"的方式,什么意思呢?我们来看一个小例子,如下:
[root@server4 ~]# vim loopxh3.yml
[root@server4 ~]# cat loopxh3.yml
---
- hosts: testB
remote_user: root
gather_facts: no
vars:
users:
alice: female
bob: male
tasks:
- debug:
msg: "{
{item.key}} is {
{item.value}}"
loop: "{
{ users | dict2items }}"
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
如上例所示,在使用loop关键字操作对应的字典变量users时,并没有借助dict插件,而是借助了一个名为dict2items的过滤器,前文已经总结了过滤器的使用方法,但是并没有介绍dict2items过滤器的用法,那么此处正好介绍一下dict2items过滤器的使用方法,dict2items过滤器是在2.6版本中新加入的过滤器,它可以把一个字典格式的数据进行转换处理,具体会进行怎样的转换处理:
users是一个字典格式的变量,它的结构是这样的
users:
alice: female
bob: male
当users字典被dict2items转换处理以后,会变成如下模样
users:
- key: alice
value: female
- key: bob
value: male
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
这就是dict2items过滤器的作用,看到上述转换后的数据格式,我们可以发现,字典数据经过"dict2items"处理后,与字典数据经过"with_dict"处理后的格式完全相同(可以参考前文的"with_dict"总结),
经过上述描述,我们可以发现,无论是**“with_X”、“loop加lookup"还是"loop加filter”**,都是使用不同的方式,实现相同的功能而已,只是在2.6版本的ansible中,官方开始推荐使用"loop加filter"的方式操作循环。
那么我们就来总结一下这种新的使用方式,由于之前已经总结过各种"with_X"关键字的使用方法,所以此处直接列出各种"with_x"关键字对应的新的使用方式。
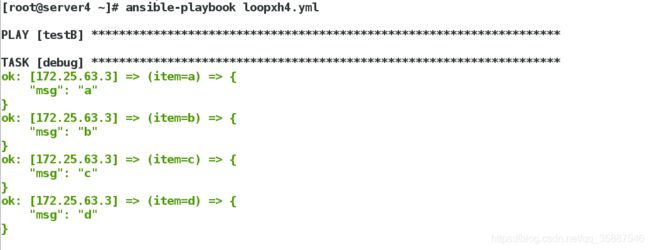
loop替代with_list
loop可以替代with_list,当处理嵌套的列表时,列表不会被拉平
[root@server4 ~]# vim loopxh4.yml
[root@server4 ~]# cat loopxh4.yml
---
- hosts: testB
remote_user: root
gather_facts: no
vars:
testlist:
- a
- [b,c]
- d
tasks:
- debug:
msg: "{
{item}}"
loop: "{
{testlist}}"
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
loop+flatten过滤器代替with_flattened
flatten过滤器可以替代with_flattened,当处理多层嵌套的列表时,列表中所有的嵌套层级都会被拉平
示例如下,flatten过滤器的用法在前文中已经总结过,此处不再赘述
[root@server4 ~]# vim loopxh4.yml
[root@server4 ~]# cat loopxh4.yml
---
- hosts: testB
remote_user: root
gather_facts: no
vars:
testlist:
- a
- [b,c]
- d
tasks:
- debug:
msg: "{
{item}}"
loop: "{
{testlist | flatten}}"
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
loop+flatten过滤器(加参数)替代with_items
flatten过滤器(加参数)可以替代with_items,当处理多层嵌套的列表时,只有列表中的第一层会被拉平
[root@server4 ~]# vim loopxh4.yml
[root@server4 ~]# cat loopxh4.yml
---
- hosts: testB
remote_user: root
gather_facts: no
vars:
testlist:
- a
- [b,c,[e,f]]
- d
tasks:
- debug:
msg: "{
{item}}"
loop: "{
{testlist | flatten(levels=1)}}"
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
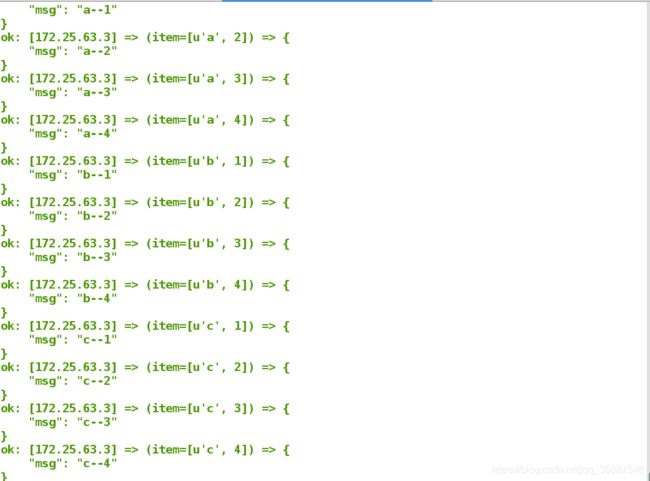
zip_longest过滤器+list过滤器代替with_together
zip_longest过滤器配合list过滤器,可以替代with_together
---
- hosts: testB
remote_user: root
gather_facts: no
vars:
testlist1: [ a, b ]
testlist2: [ 1, 2, 3 ]
testlist3: [ A, B, C, D ]
tasks:
- debug:
msg: "{
{ item.0 }} - {
{ item.1 }} - {
{item.2}}"
with_together:
- "{
{testlist1}}"
- "{
{testlist2}}"
- "{
{testlist3}}"
- debug:
msg: "{
{ item.0 }} - {
{ item.1 }} - {
{item.2}}"
loop: "{
{ testlist1 | zip_longest(testlist2,testlist3) | list }}"
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
上例同时写出了"with_together"和对应的新方式的使用方法,以便进行对比。
当多个列表使用"with_together"进行对齐合并时,如果多个列表的长度不同,则使用最长的列表长度进行对齐,由于短列表中的元素数量不够,所以使用"空值"与长列表中的元素进行对齐,zip_longest过滤器也会像"with_together"一样,对列表进行组合,但是还需要借助list过滤器,将组合后的数据列表化,list过滤器的用法已经总结过,如果你忘了,可以回顾前文,当使用zip_longest过滤器代替with_together关键字时,默认也是使用"空值"与长列表中的元素进行对齐,但是也可以指定其他字符串代替"空值",示例如下,表示使用"NoEle"代替"空值",与长列表中的更多的元素进行对齐。
- debug:
msg: "{
{ item.0 }} - {
{ item.1 }} - {
{item.2}}"
loop: "{
{ testlist1 | zip_longest(testlist2,testlist3,fillvalue='NoEle') | list }}"
- 1
- 2
- 3
从zip_longest过滤器的名字就可以看出,这个过滤器也是使用最长的列表长度进行对齐的,当多个列表的长度不同时,能不能使用最短的列表长度进行对齐呢?没问题,我们只需要借助另一个过滤器即可,这个过滤器的名字是"zip",示例如下
- debug:
msg: "{
{ item.0 }} - {
{ item.1 }} - {
{item.2}}"
loop: "{
{ testlist1 | zip(testlist2,testlist3) | list }}"
- 1
- 2
- 3

zip_longest和zip过滤器在2.3以及以后的版本中可用。
product过滤器配合list过滤器代替with_nested/with_cartesian
product过滤器配合list过滤器,可以替代with_nested和with_cartesian
---
- hosts: testB
remote_user: root
gather_facts: no
vars:
testlist1: [ a, b, c ]
testlist2: [ 1, 2, 3, 4 ]
tasks:
- debug:
msg: "{
{ item.0 }}--{
{ item.1 }}"
loop: "{
{ testlist1 | product(testlist2) | list }}"
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
product过滤器也需要将组合后的数据进行列表化,所以需要借助list过滤器
range过滤器配合list过滤器with_sequence
range过滤器配合list过滤器可以代替with_sequence:
---
- hosts: testB
remote_user: root
gather_facts: no
tasks:
- debug:
msg: "{
{item}}"
loop: "{
{ range(0, 6, 2) | list }}"
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
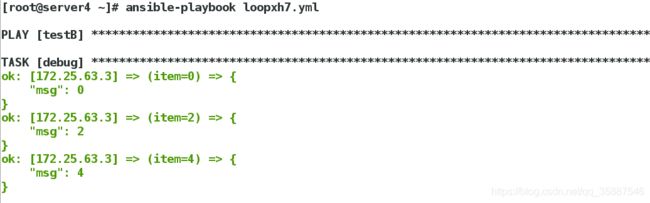
上例表示生成数字,数字从0开始,到6结束,步长为2,但是rangge函数的操作范围不会包含结束范围,也就是说不会包含6,换句话说就是,上例会生成0、2、4三个数字,而不会包含6,在总结with_sequence时我们提到过,with_sequence还有格式化的功能,比如如下示例
- debug:
msg: "{
{item}}"
with_sequence: start=2 end=6 stride=2 format="number is %0.2f"
- 1
- 2
- 3
如果你想要使用新的方式实现上例的效果,还需要配合format过滤器一起使用,示例如下
- debug:
msg: "{
{ 'number is %0.2f' | format(item) }}"
loop: "{
{ range(2, 7, 2) | list }}"
- 1
- 2
- 3
random函数 替代 with_random_choice
使用random函数可以替代with_random_choice,由于random函数是随机取出列表中的一个值,并不涉及循环操作,所以并不用使用loop关键字。
---
- hosts: testB
remote_user: root
gather_facts: no
vars:
testlist: [ a, b, c ]
tasks:
- debug:
msg: "{
{ testlist | random }}"
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
dictsort过滤器也可以替代with_dict
除了上文总结的dict2items过滤器,dictsort过滤器也可以替代with_dict
---
- hosts: testB
remote_user: root
gather_facts: no
vars:
users:
d: daisy
c: carol
a: alice
b: bob
e: ella
tasks:
- debug:
msg: "{
{item.key}} -- {
{item.value}}"
loop: "{
{ users | dict2items }}"
- debug:
msg: "{
{item.0}} -- {
{item.1}}"
loop: "{
{ users | dictsort }}"
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
正如dictsort的名字一样,dictsort具有排序功能,dictsort会根据键名的字母顺序进行排序
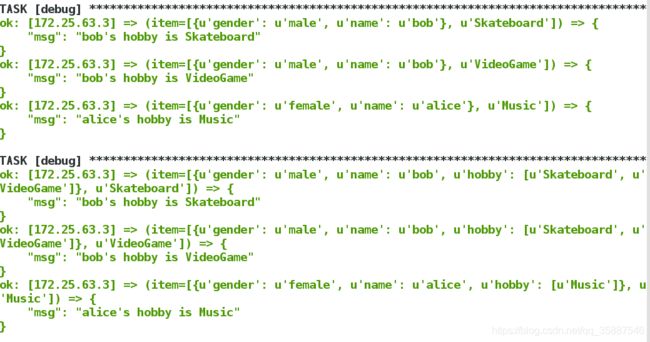
subelements过滤器with_subelements
subelements过滤器可以替代with_subelements
---
- hosts: testB
remote_user: root
gather_facts: no
vars:
users:
- name: bob
gender: male
hobby:
- Skateboard
- VideoGame
- name: alice
gender: female
hobby:
- Music
tasks:
- debug:
msg: "{
{item.0.name}}'s hobby is {
{item.1}}"
with_subelements:
- "{
{users}}"
- hobby
- debug:
msg: "{
{item.0.name}}'s hobby is {
{item.1}}"
loop: "{
{users | subelements('hobby')}}"
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
loop_control
loop_control关键字可以用于控制循环的行为,比如,使用loop_control的index_var选项,就能在遍历列表时,将元素对应的索引写入到指定的变量中,除了index_var选项,loop_control还有一些其他的选项可用,此处我们就来总结一下这些选项。
pause选项
pause选项能够让我们设置每次循环之后的暂停时间,以秒为单位,换句话说就是设置每次循环之间的间隔时间,示例如下
[root@server4 ~]# vim loopxh5.yml
[root@server4 ~]# cat loopxh5.yml
---
- hosts: testB
remote_user: root
gather_facts: no
tasks:
- debug:
msg: "{
{item}}"
loop:
- 1
- 2
- 3
loop_control:
pause: 3
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
上述示例表示每次执行循环时均会停顿3s。
label选项
可以先看一个示例:
[root@server4 ~]# vim loopxh6.yml
[root@server4 ~]# cat loopxh6.yml
---
- hosts: testB
remote_user: root
gather_facts: no
vars:
users:
alice:
name: Alice Appleworth
gender: female
telephone: 123-456-7890
bob:
name: Bob Bananarama
gender: male
telephone: 987-654-3210
tasks:
- debug:
msg: "{
{item.key}}"
loop: "{
{users | dict2items}}"
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
上述示例的执行结果如下:
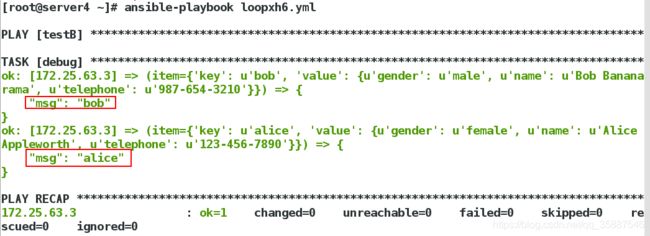 上图所显示的结果中我们只需要红框里的结果,item里的结果我们不是很关注,我们使用label选项可以使运行的结果简化:
上图所显示的结果中我们只需要红框里的结果,item里的结果我们不是很关注,我们使用label选项可以使运行的结果简化:
[root@server4 ~]# vim loopxh6.yml
[root@server4 ~]# cat loopxh6.yml
---
- hosts: testB
remote_user: root
gather_facts: no
vars:
users:
alice:
name: Alice Appleworth
gender: female
telephone: 123-456-7890
bob:
name: Bob Bananarama
gender: male
telephone: 987-654-3210
tasks:
- debug:
msg: "{
{item.key}}"
loop: "{
{users | dict2items}}"
loop_control:
label: "{
{item.key}}"
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
上述示例与之前示例不同之处在于使用了loop_controol关键字,并且使用了label选项,label的值为item.key,与msg的值完全相同,执行上述示例,结果如下:
 可以看出,输出信息变简洁了,这就时label选项的作用,在输出信息时简化输出item的信息。
可以看出,输出信息变简洁了,这就时label选项的作用,在输出信息时简化输出item的信息。