JavaScript中的内置对象
JavaScript中的内置对象
一、概述
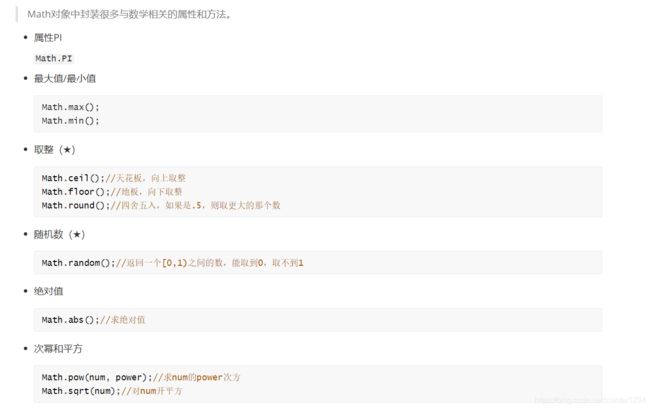
二、Math对象
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
// Math对象是js直接给我提供好的一个对象
// Math中提供了很多和数学运算相关的方法
// Math提供了一个属性 PI
// console.log(Math.PI);
// Math提供的方法:
// 求最大值和最小值
// 1,2, 3
// 作用: 求最大值
// 参数: 需要比较的数字,可以有很多个
// 返回值:最大的那个数
// var result = Math.max(1, 22, -4, 6)
// console.log(result);
// // var arr = [1, 2, 3]
// // 求最小值
// var min = Math.min(1, 4);
// console.log(min);
// 取整
// parseInt() 直接把小数部分删掉
// Math.ceil() // 天花板 向上取整
// Math.floor() // 地板 向下取整
// Math.round() 四舍五入
// Math.ceil() 向上取整 取得是大的那个数
console.log(Math.ceil(1.1));
console.log(Math.ceil(1.9));
console.log(Math.ceil(-1.1));
console.log(Math.ceil(-1.9));
// Math.floor() 向下取整 取的小的那个数
console.log(Math.floor(1.1));
console.log(Math.floor(1.9));
console.log(Math.floor(-1.1));
console.log(Math.floor(-1.9));
console.log(Math.round(1.1)); //1
console.log(Math.round(1.9)); //2
console.log(Math.round(-1.1)); // -1
console.log(Math.round(-1.9)); // -2
// 3. 求绝对值
// -1 1
// 1 1
// absolute
console.log(Math.abs(-1));
console.log(Math.abs(1));
// 4. 2 的 10 1024
// 求次幂 Math.pow(a, b) a的b次幂
// 求开方 Math.sqrt(9)
console.log(Math.pow(2, 10));
console.log(Math.pow(2, 3));
console.log(Math.sqrt(9));
/*
max: 最大值
min: 最小值
ceil: 向上取整
floor: 向下去程
round: 四舍五入
abs: 绝对值
pow: 次幂
sqrt: 开方
*/
</script>
</body>
</html>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
// Math.random() 随机生成一个小数 [0,1) 包含0,不包含1
console.log(Math.random());
// 随机0-2这几个数 0 1 2
// 0 ------2 0----1.99999999
// 问题1: 到不了2
// 问题2: 小数 ---- > 整数
// 0-----------1.99999999999
// 0----------0.999999999
// 1----------1.999999999
// 0 和 1 概率
// console.log(parseInt(Math.random() * 2))
// 公平的随机 0, 1 ,2
// 0-0.999999999999999999
// 0-2.999999999999999999
//0-0.9999999
//1-1.9999999
//2-2.999999
var result = parseInt(Math.random() * 3)
console.log(result);
// floor
// 结论 0-N的随机 parseInt(Math.random() * (N+1))
</script>
</body>
</html>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
// 随机 0-5
// console.log(parseInt(Math.random() * 6));
// // 2-4 0-2 + 2 策略: 随机数 都是从0开始随机
// console.log(parseInt(Math.random() * 3) + 2 )
// // -1 0 1
// // 0 - 2 -1
// console.log(parseInt(Math.random() * 3) - 1 )
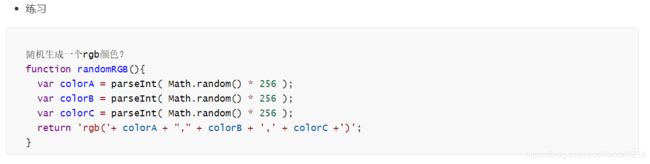
// 随机一个颜色 rgb的颜色 封装成一个函数
// rgb(255, 255, 255)
function randomColor() {
var red = parseInt(Math.random() * 256);
var green = parseInt(Math.random() * 256);
var blue = parseInt(Math.random() * 256);
// rgb(255, 255, 255)
return 'rgb(' + red + ',' + green + ',' + blue + ')';
}
console.log(randomColor())
document.body.style.backgroundColor = randomColor()
</script>
</body>
</html>
三、Date对象
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
// Date是js内置的一个构造函数 ,日期还需要创建
// 如何创建一个日期对象
// 用法1: new Date() 创建一个当前的时间
var date = new Date();
console.log(date);
// 用法2:参数:指定的时间的字符串 创建一个指定的时间
// new Date('2018-12-12 12:00:00')
var date1 = new Date('2018-12-12 12:00:00');
console.log(date1);
// 用法3: 参数可以是年月日时分秒 月份从0开始
// var date2 = new Date(2018, 1, 2);
// console.log(date2);
// 用法4: 参数可以是时间戳 1970年1月1日0时 距离现在过去的毫秒数
var date3 = new Date(1498099000356);
console.log(date3);
/*
1. new Date() 创建当前时间
2. new Date('2018-12-12') 指定的时间
3. new Date(2018, 11, 12) 指定的时间
3. new Date(时间戳) 指定时间
*/
</script>
</body>
</html>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
var date = new Date();
console.log(date);
// 让时间按照一定的格式进行打印
// toString() 把日期转换成字符串
// 格式定死了
// toLocaleString()
console.log(date.toString());
// toLocaleString 把日期转换成字符串,符合当地的习惯
console.log(date.toLocaleString());
console.log(date.toLocaleDateString())
console.log(date.toLocaleTimeString())
// 2019-01-12 17:45:00
// 2019年01月12日
</script>
</body>
</html>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
var date = new Date();
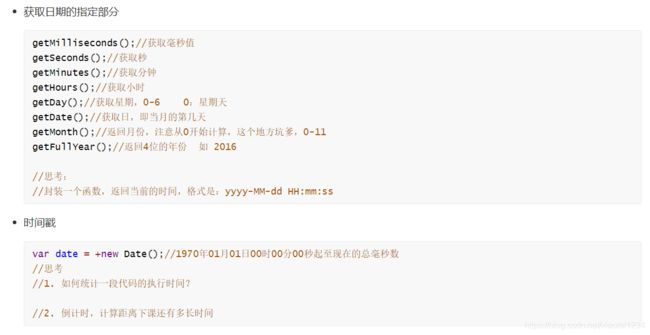
// 如何获取时间的年份
var year = date.getFullYear();
console.log(year);
// 注意:日期对象中,获取到的月份从0开始
var month = date.getMonth() + 1
console.log(month);
// 日期
// 注意: getDay: 获取的是星期
// getDate(): 获取的是日期
var day = date.getDate();
console.log(day);
// 获取小时
var hour = date.getHours();
console.log(hour);
// 获取分钟 minute
var minute = date.getMinutes();
console.log(minute);
// 获取秒 second
var second = date.getSeconds();
console.log(second);
</script>
</body>
</html>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
// 需求:把当前时间显示到页面中
// yyyy-mm-dd hh:mm:ss
// document.write()
var date = new Date();
var year = date.getFullYear();
var month = date.getMonth() + 1;
var day = date.getDate();
var hour = date.getHours();
var minute = date.getMinutes();
var second = date.getSeconds();
var millisSecond = date.getMilliseconds();
// yyyy-mm-dd hh:mm:ss
// 对于月份 日期 小时 分钟 秒钟如果小于10 就应该在前面+0
var str = year + '-' + addZero(month) + '-' + addZero(day) + ' ' + addZero(hour) + ':' + addZero(minute) + ':' + addZero(second) + ":" + millisSecond;
document.write(str);
function addZero(n) {
return n < 10 ? '0' + n : n;
}
</script>
</body>
</html>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
// 时间戳: 指的是一个日期的数字表示形式
// 任何一个日期其实都可以用数字来表示
// var date = new Date();
// 1547287516587 表示1970年1月1日距离现在所过去的毫秒
// 1547287516587 --- >时间 new Date(時間戳)
// console.log(+date);
// 1. 时间戳就表示一个时间 是一个时间的数字的表示
// 2. 时间戳作用:计算两个时间的差
// 2.1 计算一段代码的执行时间
// date是开始的时间
// var start = new Date()
// var sum = 0;
// for(var i = 1; i <= 100000000; i++) {
// sum += i;
// }
// console.log(sum);
// // end是结束的时间
// var end = new Date();
// console.log(end - start);
// 2.2 倒计时
// 计算下载距离过年还有多久 过年那天: 2019年2月5日 0时 0分 0秒
var now = new Date();
var future = new Date('2019-02-05 00:00:00');
// 距离过年还有的秒数
var time = parseInt((future - now)/1000);
// 1天
var day = parseInt(time/3600/24);
console.log(day);
// 小时 1小时 = 60分钟 = 3600
var hour = parseInt(time/3600) % 24;
console.log(hour);
// 分钟 = 60秒钟 只显示不足60的部分
var minute = parseInt(time / 60 ) % 60;
console.log(minute);
// 秒钟 不足60
var second = time % 60;
console.log(second);
document.write(''
);
document.write('距离过年还有:'+ day+'天' + hour + '小时' + minute + '分钟' + second + '秒钟')
document.write('');
</script>
</body>
</html>
四、Array对象
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge" />
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
// Array: 构造函数
// 数组对象需要自己创建
// var arr = new Array();
// var arr = []; // 内部也相当于 new Array()
// var arr = new Array(1,2,3);
// var arr = [1,2,3];
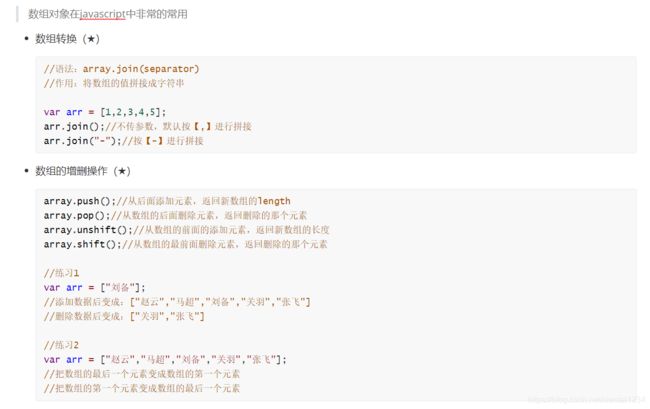
// 数组的方法 join:
// join的作用: 把一个数组 中所有的元素 拼接成一个字符串, 并且返回字符串
// 参数: 分隔符 默认是 ,
// 返回值: 字符串
// 错误的理解: arr数组变成了字符串, 数组还是原来的数组
// 需求 张飞赵云张辽
var arr = ["张飞", "赵云", "张辽"]
var result = arr.join("")
console.log(result)
console.log(arr)
</script>
</body>
</html>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge" />
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
// 如何给数组增加元素
// 数组的push方法
// var arr = ["孙权", "周瑜", "大乔"]
// 需求:给数组最后面添加一个小巧
// push:
// 作用: 给数组最后面添加一个或者多个元素
// 参数:1个或者多个值
// 返回值:添加后数组的长度
// var result = arr.push("小乔", "吕蒙", "孙策")
// console.log(result)
// console.log(arr)
// 需求: 给数组前面添加咋办?
// unshift:
// 作用:在数组的最前面添加一个值或者多个值
// 参数: 一个值或者多个值
// 返回值:添加后新数组的长度
// var arr = ["孙权", "周瑜", "大乔"]
// // arr.unshift("孙坚", "甘宁")
// arr.unshift("孙坚")
// var result = arr.unshift("甘宁")
// console.log(arr, result)
// 注意点:只能删除最后面的一个元素
// 在数组的后面删除一个元素
// pop
// 功能: 删除数组最后一个元素
// 参数:无
// 返回值: 删除的那个元素
// var arr = ["司马懿", "曹操", "典韦"]
// var result = arr.pop()
// console.log(arr, result)
// shift()
// 作用:在数组的最前面删除一个元素
// 参数:无
// 返回值:删除的元素
var arr = ["司马懿", "曹操", "典韦"]
var result = arr.shift()
console.log(arr)
console.log(result)
// push: 最后面添加
// pop: 最后面删除
// unshift: 在最前面添加
// shift() 在最前面删除
</script>
</body>
</html>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge" />
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
//练习1
// var arr = ["刘备"]
// //添加数据后变成:["赵云","马超","刘备","关羽","张飞"]
// arr.unshift("马超")
// arr.unshift("赵云")
// arr.push("关羽", "张飞")
// // console.log(arr)
// //删除数据后变成:["关羽","张飞"]
// arr.shift()
// arr.shift()
// arr.shift()
// console.log(arr)
//练习2
var arr = ["赵云", "马超", "刘备", "关羽", "张飞"]
//把数组的最后一个元素变成数组的第一个元素
// var last = arr.pop()
// arr.unshift(last)
// arr.unshift(arr.pop())
// console.log(arr)
//把数组的第一个元素变成数组的最后一个元素
arr.push(arr.shift())
console.log(arr)
</script>
</body>
</html>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge" />
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
// var arr = [1, 2, 3, 4]
// reverse()
// 翻转一个数组
// 翻转一个数组, 返回这个翻转后的数组
// arr.reverse()
// console.log(arr)
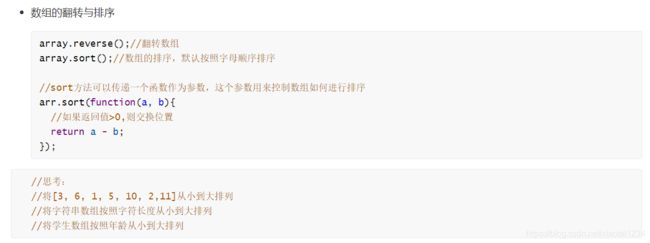
// 数组的排序
// sort : 默认按照 unicode码点 abcdefg
// 如果想要自己指定排序的规则, 需要传递参数
// var arr = [1, 3, 5, 11, 7, 4, 9]
// a 默认在 b的前面
// 如果整个函数返回值 <0 ab不换位置
// 如果整个函数返回等于0 ab不换位置
// 如果整个函数返回大于0 ab换位置
// arr.sort(function(a, b) {
// // a 和 b给我们进行比较
// // 需要指定排序的规则
// if (a > b) {
// return -1
// }
// if (a === b) {
// return 0
// }
// if (a < b) {
// return 1
// }
// // 从大到小
// // a > b -1
// // a < b
// // return b - a
// })
// console.log(arr)
// 需求:从大到小
// 如果 a 大于 b 不交换位置
var arr = [1, 3, 5, 7, 9, 2, 4, 8, 10]
// 要求:大家会用
arr.sort(function(a, b) {
// if (a < b) {
// return 1
// } else {
// return -1
// }
return b - a
})
console.log(arr)
</script>
</body>
</html>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge" />
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
//思考:
//将[3, 6, 1, 5, 10, 2,11]从小到大排列
//将字符串数组按照字符长度从小到大排列
//将学生数组按照年龄从小到大排列
// var arr = [3, 6, 1, 5, 10, 2, 11]
// arr.sort(function(a, b) {
// if (a < b) {
// return -1
// }
// if (a > b) {
// return 1
// }
// return 0
// })
// console.log(arr)
// var arr = ["bb", "a", "dddd", "ccc"] // ['a', 'bb', 'ccc', 'dddd']
// arr.sort(function(a, b) {
// if (a.length < b.length) {
// return -1
// }
// if (a.length > b.length) {
// return 1
// }
// return 0
// })
// console.log(arr)
// [1,2,3] ['a', 'b', 'c'] [{}, {}, {}]
// [[], [], []]
var arr = [
{
name: "zs", age: 18, score: 100 },
{
name: "ls", age: 38, score: 120 },
{
name: "ww", age: 88, score: 20 },
{
name: "zl", age: 8, score: 10 }
]
arr.sort(function(a, b) {
return a.age - b.age
})
console.log(arr)
</script>
</body>
</html>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge" />
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
// var arr1 = [1, 2, 3]
// var arr2 = [4, 5, 6]
// var arr3 = [7, 8, 9]
// 需求:把两个数组合并成一个数组 [1,2,3,4,5,6]
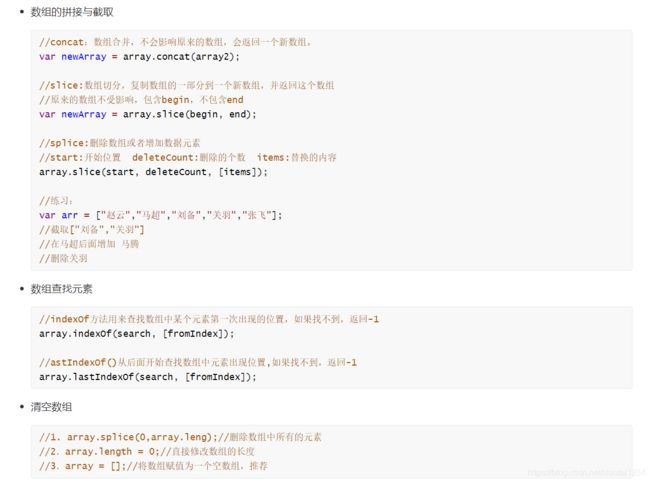
// concat()
// 作用:用于合并两个数组,原数组不会发生改变, 返回合并后的这个数组
// 参数1: 需要合并的数组
// 返回值:合并后的数组
// var newArr = arr1.concat(arr2).concat(arr3)
// console.log(newArr)
// 截取数组, 从数组中截取某个部分,原数组不会发生改变,截取到的结果就是返回值
var arr = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6]
// slice: 截取数组
// 用法1: 不传参数
// var newArr = arr.slice()
// console.log(newArr)
// 用法2: 传递一个begin slice(begin) 从哪个下标开始截取
// var newArr = arr.slice(1)
// console.log(newArr)
// 用法3: slice(begin, end) 从begin下标开始截取,截取到end
var newArr = arr.slice(2, 4)
console.log(newArr)
// slice() : 截取整个数组
// slice(begin) 从begin开始截取到最后,包含begin
// slice(begin, end) 从begin开始截取到end, 不包含end
/*
join()
push
pop
unshift
shift
reverse
sort
concat
slice
*/
</script>
</body>
</html>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge" />
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
// 可以在数组的任意位置增加或者删除元素
// 用法一:arr.splice(start) : 从start开始删除元素
// 参数1: start 从谁开始删除元素
// 参数2: deleteCount: 删除的个数, 如果不传,表示删除start后所有的
// 参数3: 表示需要添加的元素,可以添加多个
// 返回值: 删除的那部分元素
var arr = ["张飞", "赵云", "马超", "黄忠", "关羽"]
// var newArr = arr.splice(2)
// console.log(arr)
// console.log(newArr)
// var newArr = arr.splice(1, 1)
// console.log(newArr)
// console.log(arr)
// arr.splice(2, 1, "魏延", "张苞")
// console.log(arr)
// arr.splice(2, 0, "魏延")
arr.splice(5, 0, "你好")
console.log(arr)
// splice(start) 从start开始删除所有的元素 '
// splice(start, deleteCount) // 从start开始删除指定的个数
// splice(start, deleteCount, item1, item2)// 从start开始删除指定个数,并且添加item1和item2
</script>
</body>
</html>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge" />
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
//练习:
var arr = ["赵云", "马超", "刘备", "关羽", "张飞"]
//1. ["刘备","关羽"]
// var newArr = arr.slice(2, 4)
// console.log(newArr)
//在马超后面增加 马腾
// arr.splice(2, 0, "马腾")
// console.log(arr)
//删除关羽
arr.splice(3, 1)
console.log(arr)
</script>
</body>
</html>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge" />
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
// indexOf
// arr.indexOf(value)
// 功能: 获取value在数组中第一次出现的下标
var arr = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 10, 2, 3, 4, 5]
// 2在数组中第一次出现的下标
// 返回值: value第一次出现的位置,如果数组中没有,返回-1
// indexOf的作用: 判断数组中是否包含某个值
// 如果返回的下标的是-1说明没有,, 如果是其他值,说明是存在的
// var result = arr.indexOf(10)
// console.log(result)
// 判断10是否在数组中
// if (arr.indexOf(10) === -1) {
// console.log("不存在")
// } else {
// console.log("存在")
// }
// lastIndexOf : 从后往前查找,第一次出现的位置
var result = arr.lastIndexOf(4)
console.log(result)
/*
join
push
pop
unshift
shift
reverse
sort
concat
slice
splice
indexOf
lastIndexOf
*/
</script>
</body>
</html>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge" />
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
var arr = [1, 2, 3, 4]
//1.
// arr.splice(0)
// 2.
// arr = []
// 3.
arr.length = 0
console.log(arr)
</script>
</body>
</html>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge" />
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
// var arr = ["c", "a", "z", "a", "x", "a", "a", "z", "c", "x", "a", "x"]
//1. 找到数组中第一个a出现的位置
// console.log(arr.indexOf("a"))
//2. 找到数组中最后一个a出现的位置
// console.log(arr.lastIndexOf("a"))
//3. 找到数组中每一个a出现的位置
// for (var i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
// if (arr[i] === "a") {
// console.log(i)
// }
// }
//4. 数组去重,返回一个新数组
// 思路: 有一个新数组, 遍历老数组,判断新数组中是否存在元素 如果不存在,添加到新数组中
// var newArr = []
// for (var i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
// // 判断newArr中是否存在arr[i]
// if (newArr.indexOf(arr[i]) === -1) {
// newArr.push(arr[i])
// }
// }
// console.log(newArr)
// ... Set
// console.log([...new Set(arr)])
//5. 获取数组中每个元素出现的次数
var arr = ["c", "a", "z", "a", "x", "a", "a", "z", "c", "x", "a", "x"]
// 思路:
// a:1 b:2 c:3
//1. 有一个空对象
//2. 遍历数组 arr[i] a, b, c
//3. 判断对象中是否存在 arr[i]
//4. 如果存在, 值+1 如果不存在,增加这个属性 值=1
var obj = new Object()
for (var i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
// 判断 obj中是否有 arr[i]
if (arr[i] in obj) {
// 有
obj[arr[i]]++
} else {
// 没有
obj[arr[i]] = 1
}
}
console.log(obj)
</script>
</body>
</html>
五、基本包装类型
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge" />
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
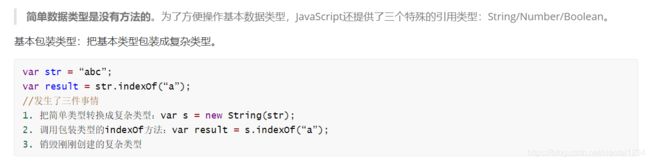
// 1. 简单类型(值类型) number string boolean null undefind
// 因为简单类型只有一个值,没有任何的属性和方法
// 2. 复杂类型(引用类型) object array function 自定义的对象
// 复杂类型可以有属性和方法,复杂类型
// 问题
// 简单类型的字符串 没有属性和方法
// var str = "abc"
// js给我们提供的字符串对象
// 创建的字符串对象, 他是有属性和方法的
// var str = new String("abc")
// console.log(str)
// js为了方便我们操作简单类型,允许我们直接调用对应的复杂类型的方法
// js中字符串可以直接调用方法
// var str = "abc"
// js内部 把简单类型给我们包装成复杂类型
// 1. var str = new String(str)
// 2. var length = str.length
// 3. str = 'abc'
// console.log(str.length)
// 字符串为什么可以调用length属性
// 1. 字符串是简单类型,没有属性和方法
// 2. 但是呢,js给简单类型提供了对应的复杂类型 number Number string String boolean Boolean
// 3. 我们直接调用简单类型的属性和方法的时候,js内部会自动帮我们把简单类型变成复杂类型。
</script>
</body>
</html>
1.Number对象
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge" />
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
// var num = 11
// 这个num能调用什么方法???
// console.log(num.toString())
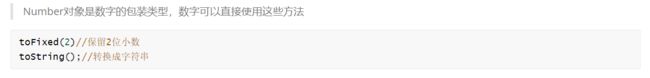
//toFixed: 保留小数的位数
var num = 1.1111111
console.log(num.toFixed(2))
</script>
</body>
</html>
2.Boolean对象
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge" />
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
var flag = true
console.log(flag.toString())
</script>
</body>
</html>
3.String对象
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge" />
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
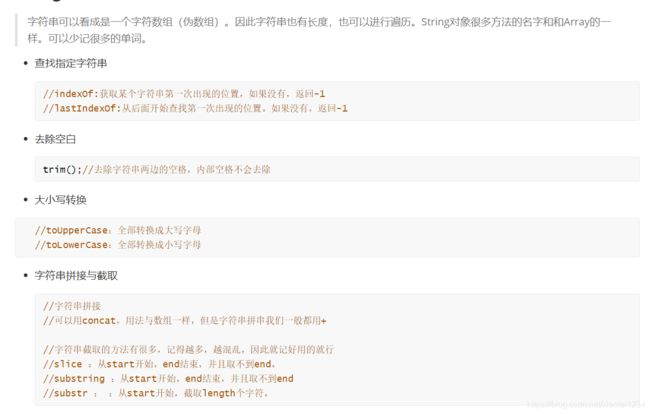
// 1. 字符串可以很数组一样进行遍历, 字符串虽然可以很数组一样遍历,它不是数组
// var str = "abcdefg"
// for (var i = 0; i < str.length; i++) {
// console.log(str[i])
// }
// 2. indexOf 和 lastIndexOf str.indexOf('a') 获取a这个字符串在字符串中第一次出现的位置
// var str = "abcdefg"
// console.log(str.indexOf("dd"))
// 3. trim() : 作用: 去除字符串两边的空格的
// trim的作用: 表单的处理
// var str = " aaa bbb "
// console.log("------" + str.trim() + "------")
//4. 大小写转换 toUpperCase() toLowerCase()
// var str = "Hello World"
// console.log(str.toUpperCase())
// console.log(str.toLowerCase())
// 5. 字符串的拼接 和 截取
// var str = "abc"
// var str1 = "bcd"
// console.log(str.concat(str1))
// console.log(str + str1)
// 字符串截取
var str = "abcdefg"
// slice(begin, end)
// substring (begin, end)
// substr(begin, length) 表是从bigin开始截取,截取length个
// var newStr = str.slice(1, 3)
// var newStr = str.substring(1, 3)
var newStr = str.substr(1, 2)
console.log(newStr)
/*
indexOf
lastIndexOf
trim
toUpperCase
toLowerCase
concat
slice
substring
substr
*/
</script>
</body>
</html>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge" />
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
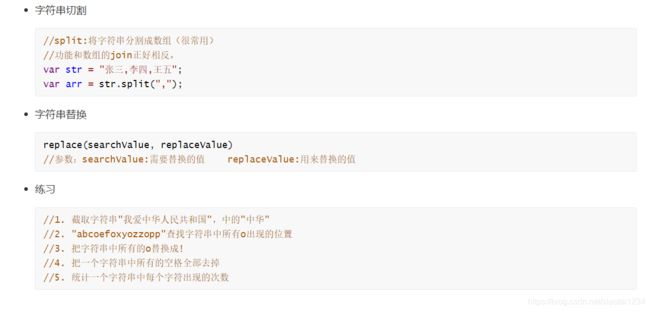
// split可以把一个字符串按照分隔符切割成一个数组
// 字符串的split方法 和数组的join方法正好相反
// 返回值: 一个数组
// var str = "张飞|赵云|马超"
// var arr = str.split("|")
// console.log(arr)
// console.log(arr.join("|"))
// 用法: 翻转一个字符串
// ' ' ''
var str = "abcdefg"
var newStr = str
.split("")
.reverse()
.join("")
console.log(newStr)
</script>
</body>
</html>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge" />
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
// var str = "大家好,我是伟哥,我最帅,我有对象"
// // 需求: 把 最帅 改成 最有钱
// // replace
// // 参数1: 表示要替换的值
// // 参数2: 替换成什么值
// var newStr = str.replace("帅", "有钱")
// // 字符串所有的方法, 不会改变字符串本身,需要结果的话,需要接受返回值
// console.log(newStr)
/*
indexOf
lastIndexOf
trim
toUpperCase()
toLowerCase
concat
slice
substring
substr
split
replace
*/
var str = " abc "
var newStr = str.trim()
console.log(newStr)
</script>
</body>
</html>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge" />
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
//1. 截取字符串"我爱中华人民共和国",中的"中华"
// var str = "我爱中华人民共和国"
// var newStr = str.slice(2, 4)
// console.log(newStr)
//2. "abcoefoxyozzopp"查找字符串中所有o出现的位置
// 字符串是可以遍历的
// var str = "abcoefoxyozzopp"
// for (var i = 0; i < str.length; i++) {
// if (str[i] === "o") {
// console.log(i)
// }
// }
//3. 把字符串中所有的o替换成!
// var str = "abcoefoxyozzopp"
// // 正则表达式
// for (var i = 0; i < str.length; i++) {
// if (str[i] === "o") {
// str = str.replace("o", "!")
// }
// }
// console.log(str)
//4. 把一个字符串中所有的空格全部去掉 ' ' ''
// var str = "a bcoe fo xy oz zopp"
// str = str.replace(/ /g, "")
// console.log(str + "-----")
//5. 统计一个字符串中每个字符出现的次数
// var str = "abcoefoxyozzopp"
// // console.log(str[1])
// var obj = {}
// for (var i = 0; i < str.length; i++) {
// if (str[i] in obj) {
// obj[str[i]]++
// } else {
// obj[str[i]] = 1
// }
// }
// console.log(obj)
</script>
</body>
</html>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge" />
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
// var str = "my_name_is_jim_green"
// 需求: 把他给我变成驼峰命名 MyNameIsJimGreen
// 1. split('_') ['my', 'name', 'is', 'jim', 'green']
// 2. 把数组中所有项的第一个字符串变成大写
// 3. 把数组拼接起来 join('')
// var arr = str.split("_")
// for (var i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
// if (i === 0) {
// continue
// }
// // console.log(arr[i][0].toUpperCase())
// // console.log(arr[i].slice(1))
// arr[i] = arr[i][0].toUpperCase() + arr[i].slice(1)
// }
// console.log(arr.join(""))
var str = "my_name_is_jim_green"
// 1. 把字符串切割成数组
var arr = str.split("_")
for (var i = 1; i < arr.length; i++) {
arr[i] = arr[i].slice(0, 1).toUpperCase() + arr[i].slice(1)
}
console.log(arr.join(""))
</script>
</body>
</html>
六、arguments
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge" />
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
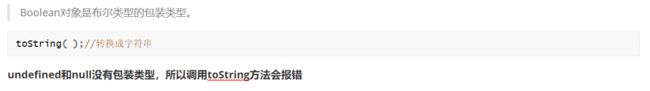
// null 和undefined没有包装类型 Null Undefined
// null 和 undefined不能调用任何属性和方法。,只要调用了就会报错。
// var num = true
// // console.log(num.aa)
// console.log(num.toString())
console.log(undefined + "")
</script>
</body>
</html>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge" />
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
// arguments是js中内置的一个对象,所有的函数中都自带了一个arguments对象
// arguments的作用:收集函数调用时传递的所有参数
// function fn(a, b) {
// console.log(a, b)
// console.log(arguments)
// }
// fn(1, 2, 3)
// arguments的作用: 收集所有的参数,将来如果参数个数不确定的时候,就可以使用
// 获取最大的那个数
// 需求,可以传无限个参数
// max(1,2) 2
// max(1,2,3) //3
// max(1, 2, 3, 4)
function max() {
console.log(arguments)
// 求arguments中最大的数即可
var max = arguments[0]
for (var i = 0; i < arguments.length; i++) {
if (arguments[i] > max) {
max = arguments[i]
}
}
console.log(max)
}
max(1, 2, 3)
max(1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6)
// 确定参数,还是需要使用形参、
function add(n1, n2) {
return arguments[0] + arguments[1]
}
add(1, 2)
</script>
</body>
</html>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge" />
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
var arr = [1, 3, 5, 7, 9, 2, 4, 8, 10]
// 要求:大家会用
// arr.sort(function(a, b) {
// // if (a < b) {
// // return 1
// // } else {
// // return -1
// // }
// return b - a
// })
// console.log(arr)
// var arr = [1, 3, 5, 7, 9, 2, 4, 8, 10]
var arr = [
{
name: "zs", age: 18, score: 100 },
{
name: "ls", age: 38, score: 120 },
{
name: "ww", age: 88, score: 20 },
{
name: "zl", age: 8, score: 10 }
]
function bubbleSort(arr, fn) {
for (var i = 0; i < arr.length - 1; i++) {
for (var j = 0; j < arr.length - 1 - i; j++) {
// arr[j] > arr[j + 1]
// arr[j] - arr[j + 1]
// arr[j].length - arr[j + 1].length
if (fn(arr[j], arr[j + 1]) > 0) {
var temp = arr[j]
arr[j] = arr[j + 1]
arr[j + 1] = temp
}
}
}
}
bubbleSort(arr, function(a, b) {
return b.score - a.score
})
console.log(arr)
</script>
</body>
</html>