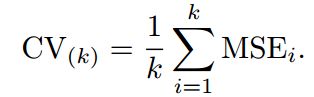K折交叉验证
写在开头:最近参加了DF的数据竞赛,发现了交叉验证的强大之处。计算时间会长很多但是真的可以把准确率提高很多!这里有对交叉验证很好的解释:知乎专栏:Cross-Validation详解
总结 :为什么要使用交叉验证?
- 训练集和测试集的划分方法很大程度上影响最终的模型与参数的值。
- 要尽量使用更多的数据参与到模型的训练中
- 普通的交叉验证方法LOOCV(Leave-one-out cross-validation)每次只用1个数据做测试,用其他n-1个数据作训练,耗费的时间过长。
- KFold Cross Validation 将所有数据集分成K份,每次不重复地取其中一份做测试集,用其他K-1份做训练集训练模型,之后计算该模型在测试集上的 M S E i MSE_i MSEi,将K次的 M S E i MSE_i MSEi取平均得到最后的MSE
常用在比赛中的方法是直接使用sklearn的StratifiedKFold sklearn:StratifiedKFold
from sklearn.model_selection import KFold,StratifiedKFold
class sklearn.model_selection.StratifiedKFold(n_splits=’warn’, shuffle=False, random_state=None)
参数:
-
n_splits : int类型,默认值为3(0.2版本中会改为5)。为折叠的数量(最少为2)。一般来说,根据经验我们一般选择值为5或10。
-
shuffle : boolean类型, 选择是否在分割成批次之前对数据的每个分层进行打乱。
-
random_state : 如果是int,则random_state是随机数生成器使用的种子; 如果是RandomState实例,则random_state是随机数生成器; 如果没有,随机数生成器所使用的RandomState实例np.random。在shuffle== True时使用。
实例:
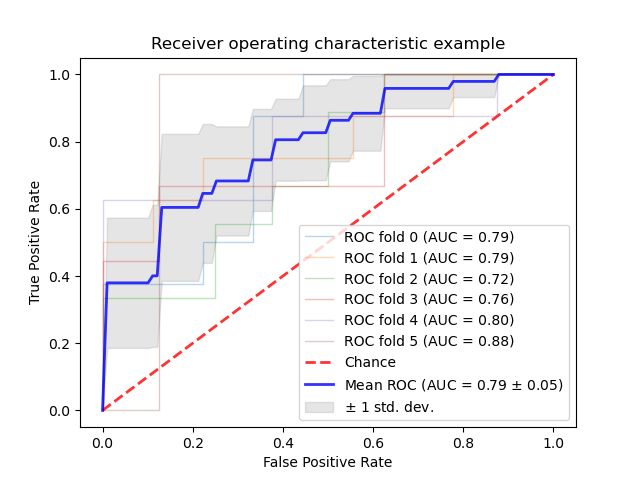
- 这是一个使用K折交叉验证下分类器分类结果的ROC曲线变化实例
- 此示例显示了由K-fold交叉验证创建的不同数据集的ROC响应。采用所有这些曲线,可以计算曲线下的平均面积,并且当训练集被分成不同的子集时,可以看到曲线的方差。这大致显示了分类器输出如何受到训练数据变化的影响,以及K折叠交叉验证产生的分裂彼此之间的差异。
import numpy as np
from scipy import interp
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn import svm, datasets
from sklearn.metrics import roc_curve, auc
from sklearn.model_selection import StratifiedKFold
# #############################################################################
# Data IO and generation
# Import some data to play with
iris = datasets.load_iris()
X = iris.data
y = iris.target
X, y = X[y != 2], y[y != 2]
n_samples, n_features = X.shape
# Add noisy features
random_state = np.random.RandomState(0)
X = np.c_[X, random_state.randn(n_samples, 200 * n_features)]
# #############################################################################
# Classification and ROC analysis
# Run classifier with cross-validation and plot ROC curves
cv = StratifiedKFold(n_splits=6)
classifier = svm.SVC(kernel='linear', probability=True,
random_state=random_state)
tprs = []
aucs = []
mean_fpr = np.linspace(0, 1, 100)
i = 0
for train, test in cv.split(X, y):
probas_ = classifier.fit(X[train], y[train]).predict_proba(X[test])
# Compute ROC curve and area the curve
fpr, tpr, thresholds = roc_curve(y[test], probas_[:, 1])
tprs.append(interp(mean_fpr, fpr, tpr))
tprs[-1][0] = 0.0
roc_auc = auc(fpr, tpr)
aucs.append(roc_auc)
plt.plot(fpr, tpr, lw=1, alpha=0.3,
label='ROC fold %d (AUC = %0.2f)' % (i, roc_auc))
i += 1
plt.plot([0, 1], [0, 1], linestyle='--', lw=2, color='r',
label='Chance', alpha=.8)
mean_tpr = np.mean(tprs, axis=0)
mean_tpr[-1] = 1.0
mean_auc = auc(mean_fpr, mean_tpr)
std_auc = np.std(aucs)
plt.plot(mean_fpr, mean_tpr, color='b',
label=r'Mean ROC (AUC = %0.2f $\pm$ %0.2f)' % (mean_auc, std_auc),
lw=2, alpha=.8)
std_tpr = np.std(tprs, axis=0)
tprs_upper = np.minimum(mean_tpr + std_tpr, 1)
tprs_lower = np.maximum(mean_tpr - std_tpr, 0)
plt.fill_between(mean_fpr, tprs_lower, tprs_upper, color='grey', alpha=.2,
label=r'$\pm$ 1 std. dev.')
plt.xlim([-0.05, 1.05])
plt.ylim([-0.05, 1.05])
plt.xlabel('False Positive Rate')
plt.ylabel('True Positive Rate')
plt.title('Receiver operating characteristic example')
plt.legend(loc="lower right")
plt.show()