Hibernate入门之数据库连接的增删改查
Hibernate快速入门
这里不再重复介绍Hibernate的理论和优势,具体的可以向度娘了解
之前学过Hibernate,但是对于其原理和操作还是很模糊,用这篇博客记录一个增删改查的小实验,来更好地理解Hibernate
首先下载Hibernate
可去官网下载Hibernate,我下载的是
![]()
官网下载比较慢,并且还有可能中间网速过低时下载的文件解压出错,附上一个下载链接
https://download.csdn.net/download/linmengmeng_1314/10367114
下载解压缩之后,可以看到如下目录结构:

- documentation:存放Hibernate相关的文件和API
- lib:存放Hibernate编译和运行所依赖的包,其中子目录require下的jar是Hibernate运行项目所必需的包
project:存放Hibernate相关的源代码和资源,其中project下的stc目录及其重要,里面包含了Hibernate的配置信息
首先导入Hibernate框架相关依赖jar包
将下面的包全部复制到hibernate_demo1项目的webContent下面的WEB-INF下面的lib文件里,或者添加一个名为Hibernate的UserLibrary,将包都导入,然后右键项目buildPath导入Hibernate库
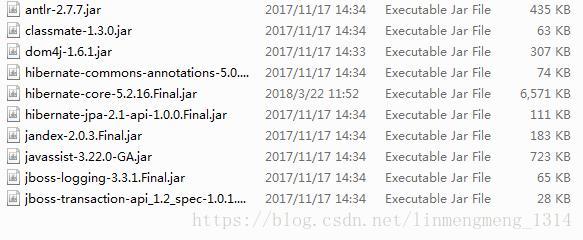
首先导入lib/required目录下所有的jar包:
再导入mysql数据库的驱动jar包:
![]()
最后导入日志相关的jar包,其中这里使用的日至相关的包是指slf4j的包,我用的是slf4j-1.7.25
MySQL驱动包和slf4j下载链接:
链接: https://pan.baidu.com/s/1gGtN0fo86vRyh7KvZlrPtA 密码: 7rhy
导入完日志相关的jar包之后,我们还须将project/etc/log4j.properties文件导入到工程hibernate_demo1的src目录下,这样工程的整个结构就为:

其中的JUnit库也是需要引入的,因为后面要用到单元测试
引入方法:右键项目,buildPath,addLIbrary,选择Junit,然后选择JUnit4或者Junit5都可以
创建数据库与表
正如前面所说,Hibernate是一个轻量级的JDBC封装,也就是说,我们可以使用Hibernate来完成原来我们使用JDBC完成的操作,也就是与数据库的交互操作。所以我们首先要创建数据库与表,这里我使用的数据库是mysql。
create database hibernateTest;
use hibernateTest;
create table t_customer(
id int primary key auto_increment,
name varchar(20),
address varchar(50)
);创建实体类
首先在Eclipse上创建一个Dynamic Web Project,比如我创建的是hibernate_demo1,然后再切到Java透视图。这儿我们在com.lmm.customer包中创建一个实体类——Customer.java。
package com.lmm.customer;
public class Customer {
private int id;
private String name;
private String address;
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getAddress() {
return address;
}
public void setAddress(String adress) {
this.address = adress;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Customer: [id = " + id + ", name = " + name + ", address = " + address + "]\n";
}
}Hibernate的相关配置文件
准备好以上工作之后,我们终于要踏入Hibernate的学习中了。首先我们要编写Hibernate的相关配置文件,Hibernate的相关配置文件分为两种:
- xxx.hbm.xml:它主要是用于描述类与数据库中的表的映射关系。
- hibernate.cfg.xml:它是Hibernate框架的核心配置文件。
有关这两个配置文件的详细介绍,我们后面会给大家讲解,如果就在这里弄的话,违背了我的初衷了,本文只是怎样快速入门Hibernate。
映射配置文件
首先我们要学会如何编写映射配置文件,大家要知道编写完的映射配置文件应与实体类在同一个包下,并且名称应是类名.hbm.xml,所以我们要在com.lmm.customer包下创建一个Customer.hbm.xml文件,但是它的约束应该怎么写呢?可以在Hibernate的核心jar包——hibernate-core-5.2.16.Final.jar的org.hibernate包下查找到hibernate-mapping-3.0.dtd文件,打开该文件,找到如下内容:
然后复制黏贴到Customer.hbm.xml文件中。
这里我先给出Customer.hbm.xml文件的内容,但内容不做过多介绍:
<hibernate-mapping package="com.lmm.customer">
<class name="Customer" table="t_customer" catalog="hibernateTest">
<id name="id" column="id">
<generator class="native">generator>
id>
<property name="name" column="name" length="20">property>
<property name="address" column="address" length="50">property>
class>
hibernate-mapping>
核心配置文件
核心配置文件主要是Hibernate框架所使用的,它主要包含了连接数据库的相关信息和Hibernate的相关配置等。
现在我们要学会如何编写Hibernate核心配置文件,大家也要知道编写完的核心配置文件应在src目录下,并且名称应是hibernate.cfg.xml,所以我们要在src目录下创建一个hibernate.cfg.xml文件,但是它的约束应该怎么写呢?可以在Hibernate的核心jar包——hibernate-core-5.2.16.Final.jar的org.hibernate包下查找到hibernate-configuration-3.0.dtd文件,打开该文件,找到如下内容:
然后复制黏贴到hibernate.cfg.xml文件中。
在这个文件中到底如何配置昵?我们可以参考hibernate-release-5.2.16.Final\project\etc\hibernate.properties文件。这里我先给出hibernate.cfg.xml文件的内容,但内容不做过多介绍:
<hibernate-configuration>
<session-factory>
<property name="hibernate.connection.driver_class">com.mysql.jdbc.Driverproperty>
<property name="hibernate.connection.url">jdbc:mysql:///hibernateTestproperty>
<property name="hibernate.connection.username">rootproperty>
<property name="hibernate.connection.password">linmengproperty>
<property name="hibernate.show_sql">trueproperty>
<property name="hibernate.format_sql">trueproperty>
<property name="hibernate.dialect">org.hibernate.dialect.MySQLDialectproperty>
<mapping resource="com/lmm/customer/Customer.hbm.xml"/>
session-factory>
hibernate-configuration>Hibernate快速入门开发测试
在com.lmm.test包下创建一个单元测试类——HibernateTest1.java。
package com.lmm.test;
import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.*;
import java.util.List;
import org.hibernate.Query;
import org.hibernate.Session;
import org.hibernate.SessionFactory;
import org.hibernate.cfg.Configuration;
import org.hibernate.query.spi.QueryParameterBindingTypeResolver;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import com.lmm.customer.Customer;
class HibernateTest1 {
//保存一个Customer
//@Test
public void saveCustomerTest() {
Customer customer = new Customer();
customer.setName("小明");
customer.setAddress("航院");
//使用Hibernate的API来完成将Customer信息保存到mysql数据库中的操作
Configuration configuration = new Configuration().configure(); //Hibernate框架加载hibernate
SessionFactory sessionFactory = configuration.buildSessionFactory();
Session session = sessionFactory.openSession(); //相当于得到一个Connection
//开启事务
session.beginTransaction();
//操作
//session.save(customer);
//事务提交
session.getTransaction().commit();
session.close();
sessionFactory.close();
}
//@Test
public void findCustomerByIdTest(){
Configuration configuration = new Configuration().configure(); //Hibernate框架加载hibernate
SessionFactory sessionFactory = configuration.buildSessionFactory();
Session session = sessionFactory.openSession(); //相当于得到一个Connection
//开启事务
session.beginTransaction();
//根据业务来编写代码
Customer customer = session.load(Customer.class, 1);
System.out.println(customer.getName());
//事务提交
session.getTransaction().commit();
session.close();
sessionFactory.close();
}
//修改操作
//@Test
public void updateCustomerTest() {
//Hibernate框架直接加载hibernate.cfg.xml,没有hibernate.properties测试也可以通过
//如果new Configuration后面不加.configure的话,默认加载hibernate.properties,没有的话会报错,无法运行
Configuration configuration = new Configuration().configure();
SessionFactory sessionFactory = configuration.buildSessionFactory();
Session session = sessionFactory.openSession(); //相当于得到一个Connection
//开启事务
session.beginTransaction();
//根据业务来编写代码
Customer customer = session.get(Customer.class, 1);
customer.setName("郑敏");
customer.setAddress("武汉");
session.update(customer);
//事务提交
session.getTransaction().commit();
session.close();
sessionFactory.close();
}
//删除操作
@Test
public void deletCustomerTest() {
Configuration configuration = new Configuration().configure(); //Hibernate框架加载hibernate
SessionFactory sessionFactory = configuration.buildSessionFactory();
Session session = sessionFactory.openSession(); //相当于得到一个Connection
//开启事务
session.beginTransaction();
//根据业务来编写代码
Customer customer = session.get(Customer.class, 2);
session.delete(customer);
//事务提交
session.getTransaction().commit();
session.close();
sessionFactory.close();
}
//查询所有的customer
@Test
public void deletCustomerTest() {
Configuration configuration = new Configuration().configure(); //Hibernate框架加载hibernate
SessionFactory sessionFactory = configuration.buildSessionFactory();
Session session = sessionFactory.openSession(); //相当于得到一个Connection
//开启事务
session.beginTransaction();
//根据业务来编写代码
Query query = session.createQuery("from Customer");
List list = query.list();
System.out.println(list);
//事务提交
session.getTransaction().commit();
session.close();
sessionFactory.close();
}
} 可以单独测试一个小方法,右键CustomerTest.java代码,RunAs选择JUnit即可,测试完毕之后,如下图证明测试成功,这里我测试的是delete方法

测试通过之后记得查看数据库里面的数据,这样会更加有兴趣接着实验
全部测试如若都无任何问题,则我们就算入门Hibernate了。
Hibernate执行原理总结
可从度娘上摘抄到如下文字:
通过Configuration().configure();读取并解析hibernate.cfg.xml配置文件。
由hibernate.cfg.xml中的读取解析映射信息。
通过config.buildSessionFactory();得到sessionFactory。
sessionFactory.openSession();得到session。
session.beginTransaction();开启事务
persistent operate; 执行你自己的操作。
session.getTransaction().commit();提交事务。
关闭session
关闭sessionFactory。