Spring控制反转(IOC)/依赖注入(DI)的初步使用
一、Spring概述
Spring是一个开放源代码的设计层面框架,他解决的是业务逻辑层和其他各层的松耦合问题,因此它将面向接口的编程思想贯穿整个系统应用。
Spring是于2003 年兴起的一个轻量级的Java 开发框架,由Rod Johnson创建。简单来说,Spring是一个分层的JavaSE/EE full-stack(一站式) 轻量级开源框架。
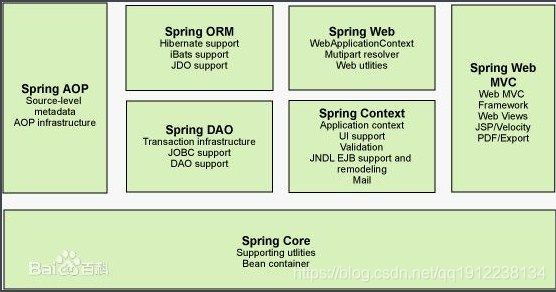
Spring技术其实已经能够囊括所有的JavaEE开发领域,比如对象管理、数据库管理、页面管理以及一些细小技术的整合,可以这么说,Spring除了不能帮你写代码之外,剩下的它都能帮你做,所以我们把这么强大的一个框架引入到项目中,这样带来的好处就可以节省很多时间去干自己想干的事情。
二、Spring的优势
1、轻量
从大小与开销两方面而言Spring都是轻量的。完整的Spring框架可以在一个大小只有1MB多的JAR文件里发布。并且Spring所需的处理开销也是微不足道的。此外,Spring是非侵入式的:典型地,Spring应用中的对象不依赖于Spring的特定类。
2、控制反转
Spring通过一种称作控制反转(IoC)的技术促进了低耦合。当应用了IoC,一个对象依赖的其它对象会通过被动的方式传递进来,而不是这个对象自己创建或者查找依赖对象。你可以认为IoC与JNDI相反——不是对象从容器中查找依赖,而是容器在对象初始化时不等对象请求就主动将依赖传递给它。
3、面向切面
Spring提供了面向切面编程的丰富支持,允许通过分离应用的业务逻辑与系统级服务(例如审计(auditing)和事务(transaction)管理)进行内聚性的开发。应用对象只实现它们应该做的——完成业务逻辑——仅此而已。它们并不负责(甚至是意识)其它的系统级关注点,例如日志或事务支持。
4、容器
Spring包含并管理应用对象的配置和生命周期,在这个意义上它是一种容器,你可以配置你的每个bean如何被创建——基于一个可配置原型(prototype),你的bean可以创建一个单独的实例或者每次需要时都生成一个新的实例——以及它们是如何相互关联的。然而,Spring不应该被混同于传统的重量级的EJB容器,它们经常是庞大与笨重的,难以使用。
5、框架
Spring可以将简单的组件配置、组合成为复杂的应用。在Spring中,应用对象被声明式地组合,典型地是在一个XML文件里。Spring也提供了很多基础功能(事务管理、持久化框架集成等等),将应用逻辑的开发留给了你。
6、MVC
Spring的作用是整合,但不仅仅限于整合,Spring 框架可以被看做是一个企业解决方案级别的框架。客户端发送请求,服务器控制器(由DispatcherServlet实现的)完成请求的转发,控制器调用一个用于映射的类HandlerMapping,该类用于将请求映射到对应的处理器来处理请求。HandlerMapping 将请求映射到对应的处理器Controller(相当于Action)在Spring 当中如果写一些处理器组件,一般实现Controller 接口,在Controller 中就可以调用一些Service 或DAO 来进行数据操作 ModelAndView 用于存放从DAO 中取出的数据,还可以存放响应视图的一些数据。 如果想将处理结果返回给用户,那么在Spring 框架中还提供一个视图组件ViewResolver,该组件根据Controller 返回的标示,找到对应的视图,将响应response 返回给用户。
三、控制反转IOC
1、控制反转概述
控制反转(Inversion of DControl,缩写为IOC),是面向对象编程中的一种设计原则,可以用来减少计算机代码之间的耦合度。
控制反转可以帮助我们创建一个类的对象
2、Spring相关jar包
- spring-core : spring的核心包,只要用spring这个是必须要有的
- spring-beans : spring的核心包,我们刚才配置的XML根目录就是beans,所以spring用它管理bean
- spring-aop : spring的重要包,主要完成spring的另一大核心功能AOP的
- spring-expression : spring的重要包,里面定义了一些表达式语言和AOP包一起用完成AOP功能的
- spring-context : spring的核心包,spring的大部分容器功能都是由它来完成的,就像咱今天用的IOC容器就是其中之一
- spring-jcl : spring的日志管理包,spring进行日志管理的重要jar包
3、Spring的xml配置文件
applicationContext.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="..." class="...">
<!-- collaborators and configuration for this bean go here -->
</bean>
<bean id="..." class="...">
<!-- collaborators and configuration for this bean go here -->
</bean>
<!-- more bean definitions go here -->
</beans>
- spring的配置文件用的XML因为要完成很多的功能,所以它把它的功能都拆分成小的XSD文件,放在同一的schema目录下,开发者需要用什么功能,就引入什么功能即可,这个叫做命名空间引入功能。例如:在spring的初始的时候只用到spring的对象管理功能,引入了一个beans的XSD即可
- XSD就是spring的配置文件可以配置的功能都放在一个一个的XSD文件中,这种方式叫做命名空间引入功能,此处的命名空间指的就是schema这个统一的XSD存放位置
- spring把每个类都当做JavaBean来封装功能,所以在创建对象的时候都是以bean标签进行数据操作的;
- bean标签可以通过属性的指定来创建不同类的对象,其中class属性配置类的权限定名称用于反射生成对象,id用于区分bean与bean之间的唯一标识
4、小例子
实体类UserInfo.java
package com.gaj.entity;
/**
* Java实体类
* @author Jan
*
*/
public class UserInfo {
private Integer id;
private String name;
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "UserInfo [id=" + id + ", name=" + name + "]";
}
}
dao层接口
package com.gaj.dao;
import com.gaj.entity.UserInfo;
public interface UserInfoDAO {
public UserInfo findUserById(Integer id);
}
dao层实现类
package com.gaj.dao.Impl;
import com.gaj.dao.UserInfoDAO;
import com.gaj.entity.UserInfo;
/**
* 模拟获得对象及属性
* @author Jan
*
*/
public class UserInfoDAOImplement implements UserInfoDAO{
@Override
public UserInfo findUserById(Integer id){
// 创建方法返回值
UserInfo user = new UserInfo();
// 设置属性
user.setId(1);
user.setName("张三");
//返回
return user;
}
}
service层接口
package com.gaj.service;
import com.gaj.entity.UserInfo;
public interface UserInfoService {
public UserInfo findUserById(Integer id);
}
service层实现类
package com.gaj.service.impl;
import com.gaj.dao.UserInfoDAO;
import com.gaj.entity.UserInfo;
import com.gaj.service.UserInfoService;
public class UserInfoServiceImplement implements UserInfoService {
private UserInfoDAO userDao;
public UserInfo findUserById(Integer id){
return userDao.findUserById(id);
}
}
配置文件 applicationContext.xml
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="userDao" class="com.gaj.dao.Impl.UserInfoDAOImplement" />
<bean id="service" class="com.gaj.service.impl.UserInfoServiceImplement" />
beans>
JUnit测试类
package com.gaj.test;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanFactory;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.xml.XmlBeanFactory;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.core.io.ClassPathResource;
import org.springframework.core.io.Resource;
import com.gaj.dao.UserInfoDAO;
import com.gaj.entity.UserInfo;
import com.gaj.service.UserInfoService;
import com.gaj.service.impl.UserInfoServiceImplement;
@SuppressWarnings("deprecation")
public class MyTest {
@Test
public void findUserById(){
// spring方式1
// 获取配置文件中的对象
Resource resource = new ClassPathResource("applicationContext.xml");
// 获取工厂类
BeanFactory factory = new XmlBeanFactory(resource);
// 获取我们需要的对象信息
UserInfoDAO dao = (UserInfoDAO)factory.getBean("userDao");
UserInfoService service = (UserInfoService)factory.getBean("service");
// 打印查看是否有该对象
System.out.println(dao);
System.out.println(service);
}
@Test
public void findUserById2(){
// spring方式2
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
// 按id属性取值 需要强转
UserInfoDAO dao = (UserInfoDAO) context.getBean("userDao");
// 按id属性和class属性取值
UserInfoService service = context.getBean("service",UserInfoServiceImplement.class);
// 简写为按class属性取值,也可以直接写类名,但如果xml配置了多个不同名的id属性并且相同的class属性时则报错找不到类
// UserInfoService service = context.getBean(UserInfoServiceImplement.class);
System.out.println(dao);
System.out.println(service);
}
}
注:在spring配置文件中不能出现两个类型相同的bean,如果出现了两个类型相同的bean,Spring就无法判定该使用哪个Bean来创建对象,从而引发报错!
四、依赖注入DI
1、依赖注入概述
依赖注入(Dependency Injection,简称DI),还有一种方式叫“依赖查找”(Dependency Lookup)。通过控制反转,对象在被创建的时候,由一个调控系统内所有对象的外界实体,将其所依赖的对象的引用传递给它。也可以说,依赖被注入到对象中。
依赖注入可以在IOC创建对象的时候帮助IOC给这个对象的属性赋值
2、小例子
- 通过实体类的set方法赋值
实体类UserInfo.java
package com.gaj.entity;
/**
* Java实体类
* @author Jan
*
*/
public class UserInfo {
private Integer id;
private String name;
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "UserInfo [id=" + id + ", name=" + name + "]";
}
}
利用spring创建UserInfo对象
配置applicationContext.xml
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="user1" class="com.gaj.entity.UserInfo" >
<property name="id" value="1" />
<property name="name" value="张三" />
bean>
beans>
测试类
@Test
public void entityTest(){
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
UserInfo user1 = context.getBean("user1",UserInfo.class);
System.out.println(user1);
}
赋值原理:根据提供的属性名称找到对应的set方法,然后把值赋予这个属性完成操作。
- 通过实体类的有参构造赋值
实体类
package com.gaj.entity;
public class UserInfo2 {
private Integer id;
private String name;
// 无参构造
public UserInfo2() {
}
// 有参构造
public UserInfo2(Integer id, String name) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "UserInfo2 [id=" + id + ", name=" + name + "]";
}
}
xml配置文件
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="user2" class="com.gaj.entity.UserInfo2">
<constructor-arg name="id" value="2" />
<constructor-arg index="1" value="李四" />
bean>
beans>
测试类
@Test
public void entityTest(){
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
UserInfo2 user2 = context.getBean("user2", UserInfo2.class);
System.out.println(user2);
}
总结:set方式给属性赋值我们称之为值注入,优点一个属性对应一个set方法,非常直接。缺点是set方法要写一堆。
构造函数的赋值的方式我们称之为构造注入,优点一个构造函数可以给多个属性赋值,缺点是编写起来不太容易。
- 注入日期格式属性的值
实体类
package com.gaj.entity;
import java.util.Date;
public class UserInfo3 {
private Integer id;
private String name;
private Date birthday;
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Date getBirthday() {
return birthday;
}
public void setBirthday(Date birthday) {
this.birthday = birthday;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "UserInfo3 [id=" + id + ", name=" + name + ", birthday=" + birthday + "]";
}
}
xml配置文件
解决方案:创建一个时间对象把时间对象赋值给birthday属性
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="date" class="java.util.Date" />
<bean id="user3" class="com.gaj.entity.UserInfo3">
<property name="id" value="3" />
<property name="name" value="王五" />
<property name="birthday" ref="date" />
bean>
beans>
测试类
@Test
public void entityTest(){
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
UserInfo3 user3 = context.getBean("user3", UserInfo3.class);
System.out.println(user3);
}
3、DI赋值总结*
- 直接赋值
<property name="属性名称" value="属性值" />
- 调用其他bean的对象给属性赋值
<property name="属性名称" ref="其他bean的ID" />