ToLua案例学习1-7
学习网址:https://github.com/topameng/tolua
一、下载ToLua工具:http://www.ulua.org/index.html
我用的UGUI比较多,所以下载这个
解压后,直接拷贝文件到项目里面。
二、ToLua自带的案例目录:
运行的demo报错,
打开LuaConst.cs脚本,修改
public static string luaDir = Application.dataPath + "/Scripts/LuaScripts"; //lua逻辑代码目录
游戏中的自己lua代码都在这个文件夹下面:
重新跑demo项目可以正常执行。
三、学习toLua自带的demo:
不想每个案例开一篇博客,就干脆都放在一个脚本里面学习吧。
using UnityEngine;
using System.Collections;
using LuaInterface;
using System;
public class StudytoLua : MonoBehaviour {
LuaState lua = null;
LuaFunction curLuaFunction = null;
void Awake() {
//Example_01();
//Example_02();
Example_03();
}
///
/// 案例一:调用lua代码,学习如何在c#脚本里面运行lua字符串代码
/// DoString
///
private void Example_01() {
//创建一个lua的虚拟机
lua = new LuaState();
//必须先启动虚拟机,否则会报错
lua.Start();
string hello = @"print('hello toLua#')";
//运行lua代码
lua.DoString(hello, "hello");
//销毁虚拟机栈
lua.CheckTop();
lua.Dispose();
lua = null;
}
///
/// 案例二:如何添加lua脚本目录,运行lua脚本
/// DoFile:Dofile则是每次调用都会重新加载使用,相对来说对性能等的消耗都会大一些,而且感觉不利于一些后面代码的书写
/// Require:Require 读取文件是会检查该文件是否被加载过,如果被加载过,则直接返回一个索引,否则则加载并返回一个索引
///
private void Example_02() {
lua = new LuaState();
lua.Start();
string fullPath = Application.dataPath + "/Scripts/LuaScripts";
lua.AddSearchPath(fullPath);
}
///
/// 案例三:调用lua脚本
/// 获取lua文件中的函数对象 LuaState.GetFunction()
/// 调用lua文件中函数:
/// 1)LuaFunction.PCall
/// 2)LuaFunction.Invoke<传入参数类型, 传出参数类型>(传入参数) 这个其实就是执行了PCall,和1)是一致的
/// 3)声明一个委托事件 LuaFunction func = LuaFunction.ToDelegate>(); result = func(1);
///
private void Example_03(){
string scripts = @"
function luaFunc(num)
return num + 1
end
test = {}
test.luaFunc = luaFunc
";
lua = new LuaState();
lua.Start();
lua.DoString(scripts);
curLuaFunction = lua.GetFunction("test.luaFunc"); //获取到lua文件中的函数对象
if (curLuaFunction != null) {
int num = curLuaFunction.Invoke(123456);
Debugger.Log("result0: {0}", num);
num = CallFunc();
Debugger.Log("result1: {0}", num);
DelegateFactory.Init(); //这句话是初始化委托工厂
Func func = curLuaFunction.ToDelegate>();
num = func(123456);
Debugger.Log("result2: {0}", num);
num = lua.Invoke("test.luaFunc", 123456, true);
Debugger.Log("result3: {0}", num);
}
curLuaFunction.Dispose();
lua.CheckTop();
lua.Dispose();
lua = null;
}
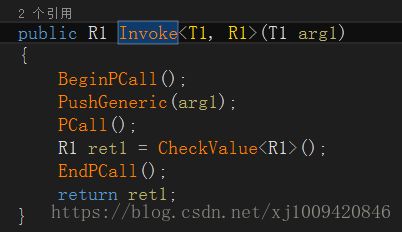
int CallFunc() {
curLuaFunction.BeginPCall(); //开始
curLuaFunction.Push(123456); //传入参数
curLuaFunction.PCall(); //执行参数
int num = (int)curLuaFunction.CheckNumber(); //获取返回值
curLuaFunction.EndPCall(); //结束
return num;
}
void OnGUI() {
if (GUI.Button(new Rect(50, 50, 120, 45), "DoFile")) {
lua.DoFile("ScriptsFromFile.lua");
} else if (GUI.Button(new Rect(50, 150, 120, 45), "Require")) {
lua.Require("ScriptsFromFile");
}
}
} 案例三:LuaFunction.Invoke<传入参数类型, 传出参数类型>(传入参数) 这个方法,进入里面,执行的还是CallFun()的流程,只是包了一层壳,方便使用。
案例四:发现table["map.name"]并没有取出数据,官方案例也有问题,所以想了一下
///
/// 案例四:调用lua的变量
/// LuaState["变量名字"] 取出数据
/// LuaState.GetTable("tablename") 获取table表
///
private void Example_04() {
string script =
@"
print('Objs2Spawn is: '..Objs2Spawn)
var2read = 42
varTable = {1,2,3,4,5}
varTable.default = 1
varTable.map = {}
varTable.map.name = 'map'
meta = {name = 'meta'}
setmetatable(varTable, meta)
function TestFunc(strs)
print('get func by variable')
end
";
lua = new LuaState();
lua.Start();
//创建Objs2Spawn变量,并且赋值
lua["Objs2Spawn"] = 5;
lua.DoString(script);
Debugger.Log("read var from lua: {0}", lua["var2read"]);
Debugger.Log("read table var from lua:{0}", lua["varTable.default"]);
//获取lua的函数
LuaFunction func = lua["TestFunc"] as LuaFunction;
func.Call();
func.Dispose();
LuaTable table = lua.GetTable("varTable");
Debugger.Log("read varTable from lua, default:{0} name:{1}", table["default"], table["map.name"]);
LuaTable curTable = table.GetTable("map");//这个是正确获取map.name的值
Debugger.Log("Read varTable from lua, default: {0} name: {1}", table["default"], curTable["name"]);
table["map.name"] = "new_map01";
Debugger.Log("Modify varTable name:{0}", table["map.name"]);
//添加新的表
table.AddTable("new_map");
LuaTable table1 = (LuaTable)table["new_map"];
table1["name"] = "table1";
Debugger.Log("varTable.new_map name: {0}", table1["name"]);
table1.Dispose();
table1 = table.GetMetaTable();
if (table1 != null) {
Debugger.Log("varTable metatable name: {0}", table1["name"]);
}
object[] list = table.ToArray();
for (int i = 0; i < list.Length; i++) {
Debugger.Log("varTable[{0}], is {1}", i, list[i]);
}
table.Dispose();
lua.CheckTop();
lua.Dispose();
} #region Example_05
///
/// 案例5:tolua封装的协程
/// lua脚本中:
/// 1)协程函数的开启 coDelay = coroutine.start(协程函数名字)
/// 延时 coroutine.wait(单位s,时间)
/// 挂起 coroutine.step()
/// 结束 coroutine.stop(协程对象coDelay) 即结束的参数为开启的返回的对象
/// 下载 coroutine.www(UnityEngine.WWW("http://www.baidu.com"))
/// 注意适用范围,start、stop之外,其他只能在协同函数里面使用
/// 2)collectgarbage('count') 返回当前使用的内存,单位为千字节 http://www.runoob.com/lua/lua-garbage-collection.html
/// 3)a.b 调用静态方法 a:b 调用非静态方法
///
private void Example_05() {
lua = new LuaState();
lua.Start();
//如果执行的lua文件需要使用unity中的类型,需要这个类给luastate绑定
LuaBinder.Bind(lua);
DelegateFactory.Init();
//用于执行协同
LuaLooper looper = gameObject.AddComponent();
looper.luaState = lua;
lua.DoString(luaFile.text, "TestLuaCoroutine.lua");
LuaFunction f = lua.GetFunction("TestCortinue");
f.Call();
f.Dispose();
f = null;
}
void OnGUI() {
if (GUI.Button(new Rect(50, 50, 120, 45), "StartDelay")) {
LuaFunction func = lua.GetFunction("StartDelay");
func.Call();
func.Dispose();
} else if (GUI.Button(new Rect(50, 150, 120, 45), "StopDelay")) {
LuaFunction func = lua.GetFunction("StopDelay");
func.Call();
func.Dispose();
} else if (GUI.Button(new Rect(50, 250, 120, 45), "GC")) {
string garbageCountStr = @"
local result = collectgarbage('count')
print('>>>>>>>>before count:',result)
";
lua.DoString(garbageCountStr);
lua.DoString("collectgarbage('collect')", "StudytoLua.cs");
lua.DoString(garbageCountStr);
Resources.UnloadUnusedAssets();
}
}
#endregion 对应的lua代码:
function fib(n)
local a, b = 0, 1
while n > 0 do
a, b = b, a + b
n = n - 1
end
return a
end
function CoFunc()
print('Coroutine started')
for i = 0, 10, 1 do
print(fib(i))
coroutine.wait(0.1)
end
print("current frameCount: "..Time.frameCount)
coroutine.step()
print("yield frameCount: "..Time.frameCount)
local www = UnityEngine.WWW("http://www.baidu.com")
coroutine.www(www)
local s = tolua.tolstring(www.bytes)
print(s:sub(1, 128))
print('Coroutine ended')
end
function TestCortinue()
coroutine.start(CoFunc)
end
local coDelay = nil
function Delay()
local c = 1
while true do
coroutine.wait(1)
print("Count: "..c)
c = c + 1
end
end
function StartDelay()
coDelay = coroutine.start(Delay)
end
function StopDelay()
coroutine.stop(coDelay)
end案例六:协同的另一种实现方法,用类unity原生,但是效率低,不推荐使用,就不说了。
案例七:Lua原生的协同
#region Example_07
///
/// 案例7:lua的原生的协同:https://www.runoob.com/lua/lua-coroutine.html
///
private void Example_07() {
string script = @"
function fib(n)
local a, b = 0, 1
while n > 0 do
a, b = b, a + b
n = n - 1
end
return a
end
function CoFunc(len)
print('Coroutine started')
local i = 0
for i = 0, len, 1 do
local flag = coroutine.yield(fib(i))
if not flag then
break
end
end
print('Coroutine ended')
end
function Test()
local co = coroutine.create(CoFunc)
return co
end
";
lua = new LuaState();
lua.Start();
lua.LogGC = true;
lua.DoString(script);
//获取到Test方法
LuaFunction func = lua.GetFunction("Test");
func.BeginPCall();
func.PCall();
luaThread = func.CheckLuaThread();
luaThread.name = "LuaTestThread";
func.EndPCall();
func.Dispose();
func = null;
luaThread.Resume(10);
}
void OnGUI() {
if (GUI.Button(new Rect(50, 50, 120, 45), "Resume Thead")) {
int ret = -1;
if (luaThread != null && luaThread.Resume(true, out ret) == (int)LuaThreadStatus.LUA_YIELD) {
Debugger.Log("lua yield: " + ret);
}
} else if (GUI.Button(new Rect(50, 150, 120, 45), "Close Thread")) {
if (luaThread != null) {
luaThread.Dispose();
luaThread = null;
}
}
}
#endregion