左神算法基础class6—题目3拓扑排序
左神算法基础class6—题目3拓扑排序
- 1.题目:拓扑排序
- 2.分析
- 3.核心代码
- 4.完整代码
- 5.输出结果
1.题目:拓扑排序
拓扑排序算法适用范围:要求①有向图②有入度为0的节点③没有环
2.分析
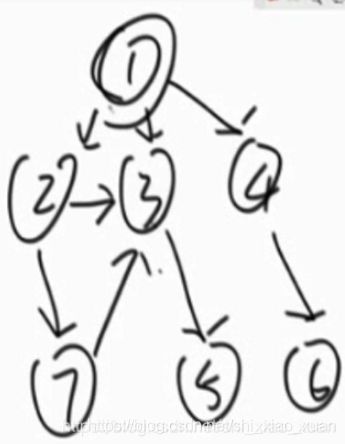
在程序编译时,往往会有头文件互相依赖的情况,在图中箭头被指向的节点可以看做依赖于指向它的节点。如下图a依赖于b,c,d,而b又依赖c,k;d依赖k

那么拓扑排序的输出顺序是不依赖别的点的先输出。先输出k,c,删去k,c这时没有别的节点指向b,d了,输出b,d,最后,节点只剩下a再输出。
在图中可以用入度表示依赖情况,入度为零就是没有别的点指向它,可以先输出。输出后其指向的节点入度减一视为删去输出的点。
过程如下:
①为了方便查找,使用map存储节点与入度方便查找与修改入度(不能反过来),使用queue存储入度为零的节点用于暂存需要输出的点。
②遍历图中的所有节点,把所有入度为零的节点放入队列
③输出入度为零的节点
④把入度为零的节点所指向的节点的入度减一(相当于删去当前节点)若减一后入度为零加入队列
⑤在入度为0的队列不空的情况下重复③④
3.核心代码
list<Node*> sortedTopology(Graph graph)
{
unordered_map<Node*,int> inMap; //存储节点与入度
queue<Node*> zeroInQueue; //存储入度为零的节点
unordered_map<int,Node*>::iterator ite = graph.nodes.begin();
//遍历图中的所有节点,把所有入度为零的节点放入队列
while(ite != graph.nodes.end())
{
inMap.insert(pair<Node*,int>(ite->second,ite->second->in));
if(ite->second->in == 0)
zeroInQueue.push(ite->second);
ite++;
}
//输出入度为零的节点
//把入度为零的节点所指向的节点的入度减一(相当于删去当前节点)
//若又有入度为零的节点加入队列
list<Node*> result;
while(!zeroInQueue.empty())
{
Node* help = zeroInQueue.front();
zeroInQueue.pop();
result.push_back(help);
cout<<help->value<<" ";
for(Node* t : help->nexts)
{
if(--inMap.find(t)->second == 0)
zeroInQueue.push(t);
}
}
return result;
}
4.完整代码
#include
using namespace std;
/* run this program using the console pauser or add your own getch, system("pause") or input loop */
//拓扑排序
list<Node*> sortedTopology(Graph graph)
{
unordered_map<Node*,int> inMap; //存储节点与入度
queue<Node*> zeroInQueue; //存储入度为零的节点
unordered_map<int,Node*>::iterator ite = graph.nodes.begin();
//遍历图中的所有节点,把所有入度为零的节点放入队列
while(ite != graph.nodes.end())
{
inMap.insert(pair<Node*,int>(ite->second,ite->second->in));
if(ite->second->in == 0)
zeroInQueue.push(ite->second);
ite++;
}
//输出入度为零的节点
//把入度为零的节点所指向的节点的入度减一(相当于删去当前节点)
//若又有入度为零的节点加入队列
list<Node*> result;
while(!zeroInQueue.empty())
{
Node* help = zeroInQueue.front();
zeroInQueue.pop();
result.push_back(help);
cout<<help->value<<" ";
for(Node* t : help->nexts)
{
if(--inMap.find(t)->second == 0)
zeroInQueue.push(t);
}
}
return result;
}
int main(int argc, char** argv) {
vector<vector<int> > matrix= {
{
12,1,2},
{
13,1,3},
{
14,1,4},
{
9,2,7},
{
10,7,3},
{
8,3,5},
{
10,4,6}};
GraphGenerator g;
Graph graph = g.createGraph(matrix);
sortedTopology(graph);
return 0;
}
注:图的存储请见图的存储与表达中。