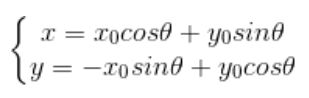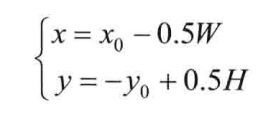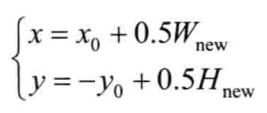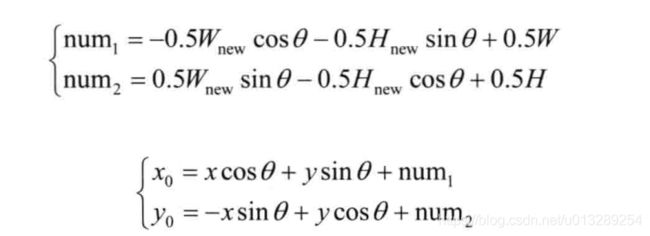图像的旋转之c++实现(qt + 不调包)
1.基本原理
本章所讲的图像旋转算法就是让图像按照其中心点旋转指定角度。图像在旋转之后,其内容不会变形,只是角度改变了,但图像的大小会变化(图像一般会变大,能包含住原先的内容)。图像的旋转变化,比较复杂,涉及到多次矩阵变换。
1.旋转公式
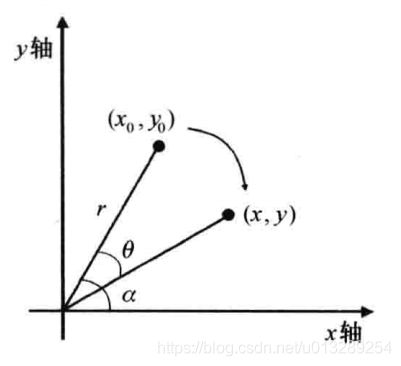
在下图中将坐标为(x0, y0)的像素点顺时针旋转![]() 角度后,其坐标变成(x, y),其中r表示像素坐标距离原点的距离,
角度后,其坐标变成(x, y),其中r表示像素坐标距离原点的距离,![]() 表示旋转前像素点与原点连线的度数。
表示旋转前像素点与原点连线的度数。
可推导出公式:
2.坐标变换
图像坐标系与数学坐标系是不相同,所以在旋转过程中需要进行两次坐标变换。
1)旋转操作前
将图像坐标系转到数学坐标系,公式中,W和H为原始图像的宽高。
2)旋转操作后
将旋转后图像的数学坐标系转到图像坐标系(相当于转回来),公式中,Wnew和Hnew分别表示输出图像的宽高。
3.旋转公式
有了前面的铺垫,我们知道图像的旋转要经过如下三步才能完成:
1.输入图像的坐标系转数学坐标系
2.通过旋转关系计算出旋转后的坐标
3.旋转坐标系(数学坐标系)转图像坐标系
总的公式可见下面(输出坐标映射到原坐标):
2.代码实现(代码是我以前自学图像处理时写的,代码很粗糙没做任何优化,但很好理解)
/*图像的旋转函数(最临近插值法) angle为旋转度数,以弧度表示*/
QImage* MainWindow::RotateNormal(QImage* image,double angle)
{
int srcX1, srcX2, srcX3, srcX4;
int srcY1, srcY2, srcY3, srcY4;
srcX1 = 0;
srcY1 = 0;
srcX2 = image->width() - 1;
srcY2 = 0;
srcX3 = 0;
srcY3 = image->height() - 1;
srcX4 = image->width() - 1;
srcY4 = image->height() - 1;
double fSin = sin(angle);
double fCos = cos(angle);
double tranX1, tranX2, tranX3, tranX4;
double tranY1, tranY2, tranY3, tranY4;
tranX1 = fCos * srcX1 + fSin * srcY1;
tranY1 = -fSin * srcX1 + fCos * srcY1;
tranX2 = fCos * srcX2 + fSin * srcY2;
tranY2 = -fSin * srcX2 + fCos * srcY2;
tranX3 = fCos * srcX3 + fSin * srcY3;
tranY3 = -fSin * srcX3 + fCos * srcY3;
tranX4 = fCos * srcX4 + fSin * srcY4;
tranY4 = -fSin * srcX4 + fCos * srcY4;
unsigned int outWidth = (unsigned int)(max(fabs(tranX4 - tranX1), fabs(tranX3 - tranX2)) + 1.5);
unsigned int outHeight = (unsigned int)(max(fabs(tranY4 - tranY1), fabs(tranY3 - tranY2)) + 1.5);
QImage* newImage = new QImage(outWidth,outHeight,QImage::Format_ARGB32);
double num1 = -0.5 * outWidth * fCos - 0.5 * outHeight * fSin + 0.5 * image->width();
double num2 = 0.5 * outWidth * fSin - 0.5 * outHeight * fCos + 0.5 * image->height();
unsigned char* copyPixel = NULL;
unsigned char* objPixel = NULL;
int x = 0;
int y = 0;
for(long j = 0; j < (long)outHeight; j++)
{
for(long i = 0; i <(long)outWidth; i++)
{
x = (int)(i * fCos + j * fSin + num1 + 0.5);
y = (int)(-i * fSin + j * fCos + num2 + 0.5);
if(x == image->width())
{
x--;
}
if(y == image->height())
{
y--;
}
copyPixel = image->bits() + y * image->width() * 4 + x * 4;
objPixel = newImage->bits() + j * outWidth * 4 + i * 4;
if(x >= 0 && x < image->width() && y >=0 && y < image->height())
{
memcpy(objPixel, copyPixel, 4);
}
}
}
return newImage;
}
/*图像的旋转函数(双线性插值法) angle为旋转度数,以弧度表示*/
QImage* MainWindow::RotateInterpolation(QImage* image,double angle)
{
int srcX1, srcX2, srcX3, srcX4;
int srcY1, srcY2, srcY3, srcY4;
srcX1 = 0;
srcY1 = 0;
srcX2 = image->width() - 1;
srcY2 = 0;
srcX3 = 0;
srcY3 = image->height() - 1;
srcX4 = image->width() - 1;
srcY4 = image->height() - 1;
double fSin = sin(angle);
double fCos = cos(angle);
double tranX1, tranX2, tranX3, tranX4;
double tranY1, tranY2, tranY3, tranY4;
tranX1 = fCos * srcX1 + fSin * srcY1;
tranY1 = -fSin * srcX1 + fCos * srcY1;
tranX2 = fCos * srcX2 + fSin * srcY2;
tranY2 = -fSin * srcX2 + fCos * srcY2;
tranX3 = fCos * srcX3 + fSin * srcY3;
tranY3 = -fSin * srcX3 + fCos * srcY3;
tranX4 = fCos * srcX4 + fSin * srcY4;
tranY4 = -fSin * srcX4 + fCos * srcY4;
long outWidth = (unsigned int)(max(fabs(tranX4 - tranX1), fabs(tranX3 - tranX2)) + 1.5);
long outHeight = (unsigned int)(max(fabs(tranY4 - tranY1), fabs(tranY3 - tranY2)) + 1.5);
QImage* newImage = new QImage(outWidth,outHeight,QImage::Format_ARGB32);
double num1 = -0.5 * outWidth * fCos - 0.5 * outHeight * fSin + 0.5 * image->width();
double num2 = 0.5 * outWidth * fSin - 0.5 * outHeight * fCos + 0.5 * image->height();
double x = 0.0;
double y = 0.0;
int r,g,b;
for (long j = 0; j < outHeight; j++)
{
for(long i =0; i < outWidth; i++)
{
x = (i * fCos + j * fSin + num1 + 0.5);
y = (-i * fSin + j * fCos + num2 + 0.5);
if (x > image->width() || x < 0 || y > image->height() || y < 0)
continue;
int x1, x2, y1, y2;
x1= ( int)x;
x2 = x1 + 1;
y1 = ( int)y;
y2 = y1 + 1;
QColor oldcolor1;
QColor oldcolor2;
QColor oldcolor3;
QColor oldcolor4;
double u, v;
u = x - x1;
v = y - y1;
if ((x >= image->width() - 1 ) && (y >= image->height() - 1 ))
{
oldcolor1 = QColor(image->pixel(x1,y1));
r = oldcolor1.red();
g = oldcolor1.green();
b = oldcolor1.blue();
}
else if (x >= image->width() - 1)
{
oldcolor1 = QColor(image->pixel(x1,y1));
oldcolor3 = QColor(image->pixel(x1,y2));
r = oldcolor1.red() * (1 - v) + oldcolor3.red() * v;
g = oldcolor1.green() * (1 - v) + oldcolor3.green() * v;
b = oldcolor1.blue() * (1 - v) + oldcolor3.blue() * v;
}
else if (x > image->height() - 1)
{
oldcolor1 = QColor(image->pixel(x1,y1));
oldcolor2 = QColor(image->pixel(x2,y1));
r = oldcolor1.red() * (1 - u) + oldcolor2.red() * u;
g = oldcolor1.green() * (1 - u) + oldcolor2.green() * u;
b = oldcolor1.blue() * (1 - u) + oldcolor2.blue() * u;
}
else
{
oldcolor1 = QColor(image->pixel(x1,y1));
oldcolor2 = QColor(image->pixel(x2,y1));
oldcolor3 = QColor(image->pixel(x1,y2));
oldcolor4 = QColor(image->pixel(x2,y2));
int r1,g1,b1;
r = oldcolor1.red() * (1 - u) + oldcolor2.red() * u;
g = oldcolor1.green() * (1 - u) + oldcolor2.green() * u;
b = oldcolor1.blue() * (1 - u) + oldcolor2.blue() * u;
r1 = oldcolor3.red() * (1 - u) + oldcolor4.red() * u;
g1 = oldcolor3.green() * (1 - u) + oldcolor4.green() * u;
b1 = oldcolor3.blue() * (1 - u) + oldcolor4.blue() * u;
r = r * (1 - v) + r1 * v;
g = g * (1 - v) + g1 * v;
b = b * (1 - v) + b1 * v;
}
newImage->setPixel(i, j, qRgb(r, g, b));
}
}
return newImage;
}3.参考资料:
数字图像处理——技术详解与Visual C++实践(左飞等著),写代码与写博客的时间相差两年,至于还参考其他的资料不,我已经忘记了,如若需要,我可以补上去