初试PyOpenGL二 (Python+OpenGL)基本地形生成与高度检测
在上文中,讲述了PyOpenGL的基本配置,以及网格,球形的生成,以及基本的漫游。现在利用上一篇的内容,来利用高程图实现一个基本的地形,并且,利用上文中的第三人称漫游,以小球为视角,来在地形上前后左右漫游,能实时检测高度。下面先看下效果图:
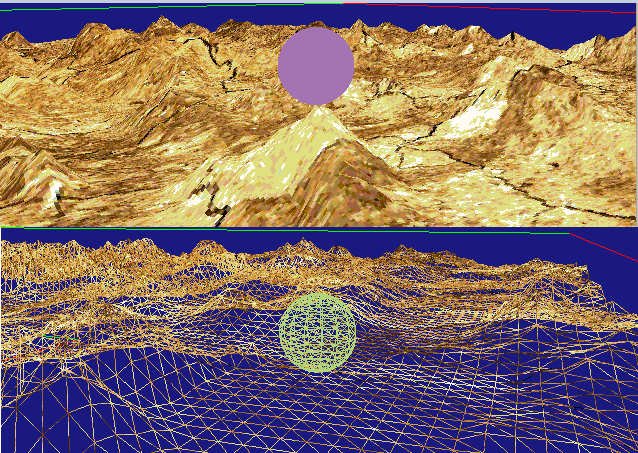
二张图,球分别在不同的地方,不同的显示模型,一个是全填充的,一个是线连,可以从中看到一些基本的思路。大致过程分别如下,首先拿到一张高度图,检索其中的高度对应的通道的值,然后用来改变网格的高度。这个过程只需要在初始化时生成就行了,所以我们可以简单的用CPU来完成这个。然后是球体的漫游,这部分在上文中已经讲了第一与第三人称漫游,用的就是其中的第三人称作漫游,在这里,我们主要是要检索球下面的地形的高度,因为需要实时计算,这部分用GPU来完成。
我们先看下,根据高度图来改变网格高度的相关代码(请对照前文中的网格类Plane来看,下面的setHeight为其中的一个方法):

1 def setHeight(this,image): 2 ix = image.size[0] 3 iy = image.size[1] 4 this.heightImage = image 5 print ix,iy 6 #print "xr,yr",this.xr,this.yr 7 lerp = lambda a,b,d:a * d + b * (1.0 - d) 8 fade = lambda t : t*t*(3.0-2.0*t) #t*t*t*(t*(t*6.0-15.0)+10.0) 9 for y in range(this.yr): 10 for x in range(this.xr): 11 index = 5 * (this.xr * y + x) + 3 12 #print index 13 fx = float(x) / float(this.xr - 1) * float(ix - 1) 14 fy = float(y) / float(this.yr - 1) * float(iy - 1) 15 #print float(x) / float(this.xr - 1),fx,float(y) / float(this.yr - 1),fy 16 xl,xr,yu,yd = int(math.floor(fx)),int(math.ceil(fx)),int(math.floor(fy)),int(math.ceil(fy)) 17 dx,dy = fade(fx - xl),fade(fy - yu) 18 #print "loc:",xl,xr,yu,yd,dx,dy 19 #left up,right up,left down,right down 20 lu,ru,ld,rd = image.im[ix * yu + xl],image.im[ix * yu + xr],image.im[ix * yd + xl],image.im[ix * yd + xr] 21 #print ix * yu + xl,lu,ru,ld,rd 22 hight = lerp(lerp(lu,ru,dx),lerp(ld,rd,dx),dy) 23 this.data[index] = hight / 255.0 24 #print "setHeight:",hight / 255.0
当初完成这段代码后,我有时后悔在前面学习noise时,没有自己先完成一个根据高度图生成地形,不然理解柏林噪声函数会是一件非常简单的事,这段代码很简单,得到image的信息,然后把原来的地形网格他们二个做一个映射关系,就好像二个大小不同的矩阵,根据其中一个在本矩阵里的位置,找出在另一个矩阵中对应的位置。首先index得到的是当初位置网络数据里的高度索引,第前面文章中,这个值是0,然后根据线性关系,就如上面后说,找到当前位置对应在image的位置,fx,fy.为什么我说很后悔先看了noise,大家可以看下,这里的代码的逻辑和noise里的就是一样,但是这里我可以自己推出来,而看noise里的过程花费太多不必要的时间。在这里,我们可以想象的到,fx,fy是整数的机会不大,那么无论取floor(fx)或ceil(fx),都有较大的偏差,正确的方法应该是根据fx的小数位来做floor(fx)或ceil(fx)权重进行计算。简单来说,就是根据fx,fy来取在它周围的四个像素点,然后根据他们的小数位来对四个小数点进行混合计算。其中小数部分需要的fade可以用lerp,也可以用二阶平滑来至三阶平滑的映射关系,而像素值根据简单线性关系求就可以了。理解这里的以后,再去看柏林噪声实践(一) 海波等就容易理解多了。
这个是初始化地形的高度值,下面就是重点,如果根据球所在的位置,来得到当前位置里的高度,然后用来设定球的高度(简化问题,只求球心下的高度,二片卡住球的问题就没考虑)。有了前面的基础,在CPU中进行得到高度值也很容易,但是现在是漫游过程中,当前位置每时都在计算,CPU应该用来进行更复杂的逻辑运算,这部分交给GPU了,先给出相关着色器代码:

1 update_v = """ 2 //#version 330 compatibility 3 #version 130 4 uniform sampler2D tex0; 5 uniform float xw; 6 uniform float yw; 7 uniform float height; 8 //the location of center of the sphere 9 uniform vec2 xz; 10 uniform float sphereRadius; 11 uniform mat4 mMatrix; 12 uniform mat4 vMatrix; 13 uniform mat4 pMatrix; 14 out vec4 o_color; 15 void main() { 16 vec4 pos = vec4(gl_Vertex); 17 vec2 uv = vec2(xz/vec2(xw,yw) + vec2(0.5,0.5)); 18 uv.y = 1.0 - uv.y; 19 vec3 rgb = texture2D(tex0, uv).rgb; 20 pos.y = pos.y + sphereRadius + rgb.r;//height;// 21 o_color = vec4(uv.x, uv.y, rgb.r, 1); 22 gl_Position = pMatrix * vMatrix * mMatrix * pos; 23 24 //vec4 v = vec4(gl_Vertex); 25 //vec2 uv = vec2(xz/vec2(xw,yw) + vec2(0.5,0.5)).xy; 26 //uv.y = 1.0 - uv.y; 27 //v.x = v.x + xz.x; 28 //v.z = v.z + xz.y; 29 //v.y = v.y + texture2D(tex0, uv).r+ sphereRadius; 30 //o_color = vec4(uv.x,uv.y, 0, 1 ); 31 //gl_Position = gl_ModelViewProjectionMatrix * v; 32 }""" 33 34 update_f = """ 35 //#version 330 compatibility 36 #version 130 37 in vec4 o_color; 38 void main() { 39 //vec4 color = texture2D(tex1, gl_TexCoord[0].st); 40 gl_FragColor = o_color;// vec4( 0, 1, 0, 1 ); 41 }"""
这段代码大致思想和前面一样,不过纹理坐标需要映射到0-1之前,不过,也少了混合周围定点的计算,因为我们在设定纹理时(glTexParameterf),已经告诉着色器,自动线性混合了。在这里,需要说明的是,因为130后,已经废弃了固定管线的相关功能与API,虽然还能用,但是毕竟要向前看,所以主体的部分有二部分,一部分是用的是着色器版本120固定管线提供的gl_ModelViewProjectionMatrix,以及120后的,自己提供MVP,也顺便练习下如何在PyOpenGL里进行矩阵的基本操作。其中height是CPU计算的高度,这个就放附件里,不拿出来说了,至于为什么还拿出一个CPU版,前面不是说了不交给CPU吗,主要是我发现,有些旧的显卡对于这段逻辑处理还是有些问题(有一问题浪费大量时间才发现是旧显卡的问题),代码就不放了,大家有兴趣可以去附件里看。
嗯,还有必要说下绘制部分,地形网络用到一个颜色纹理,而球需要用到高度纹理,在glsl中,多纹理,多着色器如何设定以及完成。

1 class allshader: 2 def __init__(this): 3 this.planeProgram = shaders.compileProgram(shaders.compileShader(plane_v, GL_VERTEX_SHADER), 4 shaders.compileShader(plane_f, GL_FRAGMENT_SHADER)) 5 #the parameter tex0 must be use in shaders,otherwise the 6 #glGetUniformLocation get -1 7 this.planeProgram.tex0 = glGetUniformLocation(this.planeProgram,"tex0") 8 this.planeProgram.tex1 = glGetUniformLocation(this.planeProgram,"tex1") 9 print this.planeProgram.tex0,this.planeProgram.tex1 10 11 this.updateProgram = shaders.compileProgram(shaders.compileShader(update_v, GL_VERTEX_SHADER), 12 shaders.compileShader(update_f, GL_FRAGMENT_SHADER)) 13 this.updateProgram.xl = glGetUniformLocation(this.updateProgram,"xw") 14 this.updateProgram.yl = glGetUniformLocation(this.updateProgram,"yw") 15 this.updateProgram.height = glGetUniformLocation(this.updateProgram,"height") 16 this.updateProgram.sphereRadius = glGetUniformLocation(this.updateProgram,"sphereRadius") 17 this.updateProgram.tex0 = glGetUniformLocation(this.updateProgram,"tex0") 18 this.updateProgram.xz = glGetUniformLocation(this.updateProgram,"xz") 19 this.updateProgram.hight = glGetUniformLocation(this.updateProgram,"hight") 20 this.updateProgram.mMatrix = glGetUniformLocation(this.updateProgram,"mMatrix") 21 this.updateProgram.vMatrix = glGetUniformLocation(this.updateProgram,"vMatrix") 22 this.updateProgram.pMatrix = glGetUniformLocation(this.updateProgram,"pMatrix") 23 24 25 def DrawGLScene(): 26 glClear(GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT | GL_DEPTH_BUFFER_BIT) 27 glMatrixMode(GL_MODELVIEW) 28 camera.setLookat() 29 #texture set 30 glActiveTexture(GL_TEXTURE0) 31 glBindTexture(GL_TEXTURE_2D, colorMap) 32 glActiveTexture(GL_TEXTURE1) 33 glBindTexture(GL_TEXTURE_2D, hightMap) 34 #plane 35 glUseProgram(shaderall.planeProgram) 36 glUniform1i(shaderall.planeProgram.tex0, 0) 37 plane.draw() 38 glUseProgram(0) 39 #sphare 40 eyeLoc = camera.origin 41 uv = eyeLoc[0] / plane.xl + 0.5,eyeLoc[2] / plane.yl + 0.5 42 glUseProgram(shaderall.updateProgram) 43 glUniform1f(shaderall.updateProgram.xl, plane.xl) 44 glUniform1f(shaderall.updateProgram.yl, plane.yl) 45 #CPU compute height 46 #glUniform1f(shaderall.updateProgram.height, plane.getHeight(eyeLoc[0],eyeLoc[2])) 47 glUniform1f(shaderall.updateProgram.sphereRadius, sph.radius) 48 glUniform1i(shaderall.updateProgram.tex0, 1) 49 #print uv 50 glUniform2f(shaderall.updateProgram.xz,eyeLoc[0],eyeLoc[2]) 51 #print "eye:",eyeLoc,eyeLoc[0],eyeLoc[2] 52 getMVP(eyeLoc) 53 sph.draw() 54 glUseProgram(0) 55 glActiveTexture(GL_TEXTURE0) 56 glBindTexture(GL_TEXTURE_2D, 0) 57 glDisable(GL_TEXTURE_2D) 58 glActiveTexture(GL_TEXTURE1) 59 glBindTexture(GL_TEXTURE_2D, 0) 60 glDisable(GL_TEXTURE_2D) 61 62 glBegin(GL_LINES) 63 glColor(1.0,0.0,0.0) 64 glVertex3f(-plane.xl / 2.0, 1.0, -plane.yl / 2.0) 65 glVertex3f(100.0, 1.0, -plane.yl / 2.0) 66 glColor(0.0,1.0,0.0) 67 glVertex3f(-plane.xl / 2.0, 1.0, -plane.yl / 2.0) 68 glVertex3f(-plane.xl / 2.0, 1.0, 100.0) 69 70 glColor(1.0,0.0,0.0) 71 glVertex3f(0.0, 0.0,0.0) 72 glVertex3f(100.0, 0.0, 0.0) 73 glColor(0.0,1.0,0.0) 74 glVertex3f(0.0, 0.0, 0.0) 75 glVertex3f(0.0, 1.0, 100.0) 76 glEnd() 77 78 glutSwapBuffers()
嗯,python好像对中文注解支持不友好,故采用我的鬼哭神嚎的英语,大家就不要笑了。说一下,后面给出二个坐标系,用来确定当家位置的,一个是左下角,一个是中心,分别向X,Z正轴发射出去。
下面这段是设定球MVP的代码:

1 def getMVP(eye): 2 v = ny.array(glGetFloatv(GL_MODELVIEW_MATRIX), ny.float32) 3 p = ny.array(glGetFloatv(GL_PROJECTION_MATRIX), ny.float32) 4 m = ny.array([[1, 0, 0, 0],[0, 1, 0, 0], [0, 0, 1, 0],[eye[0],0,eye[2],1]],ny.float32) 5 #print m 6 glUniformMatrix4fv(shaderall.updateProgram.pMatrix,1,GL_FALSE,p) 7 glUniformMatrix4fv(shaderall.updateProgram.vMatrix,1,GL_FALSE,v) 8 glUniformMatrix4fv(shaderall.updateProgram.mMatrix,1,GL_FALSE,m) 9 #glgeffloat
附件:Python地形.zip 和上方的漫游模式一样,其中EDSF前后左右移动,WR分别向上与向下,鼠标右键加移动鼠标控制方向,V切换第一人称与第三人称。UP与DOWN切换前面操作的移动幅度。在第三人称下,因为球中着色器限定了Y轴,故那时模式看起来如2.5D的那种游戏视角,能左右转动视角,不能看到天,不知2.5D游戏里的那种是不是也是这样被限制住了。
