白话HashMap源码(上)
HashMap一句话就可以说个大概:
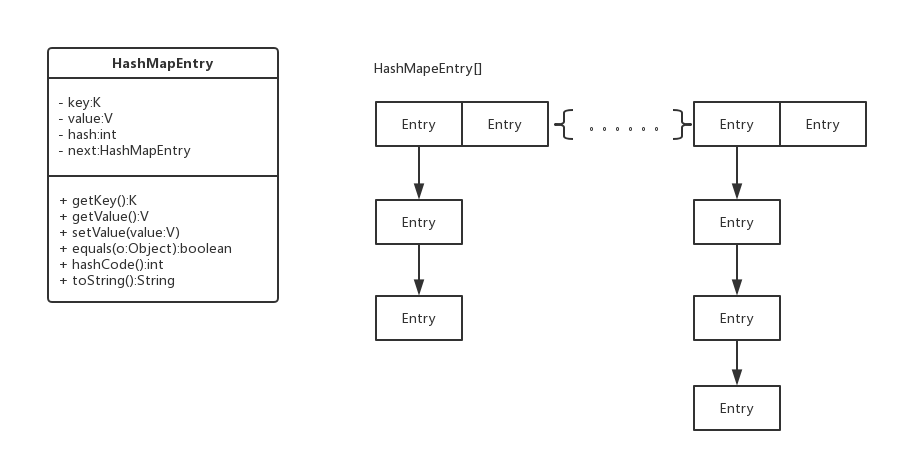
用哈希算法把key计算出索引index,然后将key、value构成的HashMapEntry放入HashMapEntry[index],即完成了put功能,get时将key重计算出index去取HashMapEntry。
以上只是最表层的思想,如果不同key计算出相同的index呢?HashMapEntry里的next就起到作用了。
如上图:横排的Entry为HashMapEntry[],纵向的箭头表示同一index下存在多个Entry,Entry之间采用的是链式存储。
HashMap的大体设计思路就是如此了,接下来看看源码是如何写的(源码是android-23)。
构造函数
无参构造函数:创建空表设置阈值
/**
* Min capacity (other than zero) for a HashMap. Must be a power of two
* greater than 1 (and less than 1 << 30).
*/
//HashMap最小的容量。此容量必须是以2为底的次方数,且大于1小于2的30次方
private static final int MINIMUM_CAPACITY = 4;
/**
* An empty table shared by all zero-capacity maps (typically from default
* constructor). It is never written to, and replaced on first put. Its size
* is set to half the minimum, so that the first resize will create a
* minimum-sized table.
*/
//空表,容量是最小容量的一半
private static final Entry[] EMPTY_TABLE
= new HashMapEntry[MINIMUM_CAPACITY >>> 1];//无符号右移
public HashMap() {
table = (HashMapEntry[]) EMPTY_TABLE;
threshold = -1; // Forces first put invocation to replace EMPTY_TABLE阈值超过阈值时需要扩容
} 带容量的构造参数
对传入的容量值稍作处理,然后创建表
/**
* Max capacity for a HashMap. Must be a power of two >= MINIMUM_CAPACITY.
*/
//吧啦吧啦,容量必须是以2为底的次方数,且大于MINIMUM_CAPACITY
private static final int MAXIMUM_CAPACITY = 1 << 30;
public HashMap(int capacity) {
if (capacity < 0) {//抛异常
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Capacity: " + capacity);
}
if (capacity == 0) {//容量为0时和无参构造函数逻辑一致,我认为可以HashMap()然后return搞定,不需要重复代码
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
HashMapEntry[] tab = (HashMapEntry[]) EMPTY_TABLE;
table = tab;
threshold = -1; // Forces first put() to replace EMPTY_TABLE
return;
}
if (capacity < MINIMUM_CAPACITY) {
capacity = MINIMUM_CAPACITY;
} else if (capacity > MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) {
capacity = MAXIMUM_CAPACITY;
} else {
capacity = Collections.roundUpToPowerOfTwo(capacity);//获取大于等于capacity并且是 2 的次方的整数
}
makeTable(capacity);
}
private HashMapEntry[] makeTable(int newCapacity) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked") HashMapEntry[] newTable
= (HashMapEntry[]) new HashMapEntry[newCapacity];//根据传入的容量创建数组
table = newTable;
threshold = (newCapacity >> 1) + (newCapacity >> 2); // 3/4 capacity
//设置容量阈值,如果大于阈值则扩充数组大小
return newTable;
} 带负载因子的构造方法
什么是负载因子?
HashMap的存储结构是一个数组,数组内的项为链表。
数组的优势是查找迅速,由于分配的内存空间连续,但产生的index不一定连续,所以会产生空间的浪费。
链表的优势是增删快速,但查找速度不如数组,必须一个一个的向下查找。
负载因子的功能就是为了协调数组与链表之间的优劣,负载因子大则链表的长度会大以致查找速度会降低,否则数组的长度大造成空间的浪费。
根据实际的使用情况,设置合适的负载因子。由于源码并未实际设置,所以负载因子的功能只带过。
/**
* Constructs a new {@code HashMap} instance with the specified capacity and
* load factor.
*
* @param capacity
* the initial capacity of this hash map.
* @param loadFactor
* the initial load factor.
* @throws IllegalArgumentException
* when the capacity is less than zero or the load factor is
* less or equal to zero or NaN.
*/
public HashMap(int capacity, float loadFactor) {
this(capacity);
if (loadFactor <= 0 || Float.isNaN(loadFactor)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Load factor: " + loadFactor);
}
/*
* Note that this implementation ignores loadFactor; it always uses
* a load factor of 3/4. This simplifies the code and generally
* improves performance.
*/
}带子集的构造方法
根据子集的大小调整自身的数组大小,将子集数据装填到自身。
public HashMap(Map map) {
//设置数组大小
this(capacityForInitSize(map.size()));
//装填子集
constructorPutAll(map);
}
//返回需要的大小
static int capacityForInitSize(int size) {
int result = (size >> 1) + size; // Multiply by 3/2 to allow for growth
//对传入的size乘以1.5,但是移位的操作快速所以采用了移位代替乘
// boolean expr is equivalent to result >= 0 && result
//返回值要求>= 0 且
//假设MAXIMUM_CAPACITY为1000
//(MAXIMUM_CAPACITY-1)=0111
//~(MAXIMUM_CAPACITY-1)=1000
//所以result & ~(MAXIMUM_CAPACITY-1))的目的是去低位,与0一定为0,除非高位不为0,但高位不为0的话就大于MAXIMUM_CAPACITY了所以就有了如下
return (result & ~(MAXIMUM_CAPACITY-1))==0 ? result : MAXIMUM_CAPACITY;
}
//装填
final void constructorPutAll(Map map) {
if (table == EMPTY_TABLE) {//如果是空表则翻倍空间大小
doubleCapacity(); // Don't do unchecked puts to a shared table.
}
for (Entry e : map.entrySet()) {
//组装key value 进行装填
constructorPut(e.getKey(), e.getValue());
}
} 装填项
private void constructorPut(K key, V value) {
if (key == null) {//key为null时维护entryForNullKey
HashMapEntry entry = entryForNullKey;
if (entry == null) {
entryForNullKey = constructorNewEntry(null, value, 0, null);
size++;
} else {
entry.value = value;
}
return;
}
int hash = Collections.secondaryHash(key);
HashMapEntry[] tab = table;
int index = hash & (tab.length - 1);//计算出index
HashMapEntry first = tab[index];//此项不为空向下搜索链表
for (HashMapEntry e = first; e != null; e = e.next) {
if (e.hash == hash && key.equals(e.key)) {
e.value = value;
return;
}
}
// No entry for (non-null) key is present; create one
tab[index] = constructorNewEntry(key, value, hash, first);
size++;
}
HashMapEntry constructorNewEntry(
K key, V value, int hash, HashMapEntry first) {
return new HashMapEntry(key, value, hash, first);
} PUT
public V put(K key, V value)
传入key、value,计算hash
如果存在key则更新并返回旧值,否则添加新HashMapEntry并返回null
除此以外有一个特例,HashMap内还维护了一个entryForNullKey用于存储key=null时的value
@Override public V put(K key, V value) {
if (key == null) {
return putValueForNullKey(value);
}
int hash = Collections.secondaryHash(key);
HashMapEntry[] tab = table;
int index = hash & (tab.length - 1);
for (HashMapEntry e = tab[index]; e != null; e = e.next) {
if (e.hash == hash && key.equals(e.key)) {
preModify(e);
V oldValue = e.value;
e.value = value;
return oldValue;
}
}
// No entry for (non-null) key is present; create one
modCount++;
if (size++ > threshold) {
tab = doubleCapacity();
index = hash & (tab.length - 1);
}
addNewEntry(key, value, hash, index);
return null;
}
第一步存null的Key
transient int size;
transient int modCount;
//transient 此关键字不参与序列化,存储时不会保存,只存于此对象。
private V putValueForNullKey(V value) {
HashMapEntry entry = entryForNullKey;
if (entry == null) {//不存在旧值
addNewEntryForNullKey(value);
size++;//总存储量
modCount++;//修改次数
return null;
} else {//存在旧值
preModify(entry);//修改前操作
V oldValue = entry.value;
entry.value = value;
return oldValue;
}
}
void addNewEntryForNullKey(V value) {
entryForNullKey = new HashMapEntry(null, value, 0, null);
}
//空实现,可以做一些修改前的预处理
void preModify(HashMapEntry e) { } 第二步更新key
HashMapEntry[] tab = table;
//由hash求得index
int index = hash & (tab.length - 1);
//遍历链表
for (HashMapEntry e = tab[index]; e != null; e = e.next) {
if (e.hash == hash && key.equals(e.key)) {//key存在于HashMap中的条件:hash和key相同
preModify(e);//预处理
V oldValue = e.value;
e.value = value;//更新
return oldValue;
}
} 第三步存新key
能够走到这里说明key不为null,且之前没有存储过此key
modCount++;//修改计数加一
if (size++ > threshold) {//存储空间大于阈值,加倍空间
tab = doubleCapacity();
index = hash & (tab.length - 1);
}
addNewEntry(key, value, hash, index);
return null;增加空间大小
private HashMapEntry[] doubleCapacity() {
HashMapEntry[] oldTable = table;
int oldCapacity = oldTable.length;
//如果已经是最大的则无法增加
if (oldCapacity == MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) {
return oldTable;
}
//容量翻倍
int newCapacity = oldCapacity * 2;
HashMapEntry[] newTable = makeTable(newCapacity);
//表中无数据直接返回
if (size == 0) {
return newTable;
}
//表中有数据,需要将数据转移到新表
for (int j = 0; j < oldCapacity; j++) {
//代码见下
}
return newTable;
} 将数据转移到新表
疑问:在对链表重新分布处理时,如果链表内的entry被放入新index,但源码并未对entry前项的next指针赋null。索引使用时并不会有问题,但同一对象指针被存在了两处。没看懂望高人指点。
for (int j = 0; j < oldCapacity; j++) {
/*
* Rehash the bucket using the minimum number of field writes.
* This is the most subtle and delicate code in the class.
*/
HashMapEntry e = oldTable[j];
if (e == null) {//null不管
continue;
}
int highBit = e.hash & oldCapacity;//旧index
HashMapEntry broken = null;
newTable[j | highBit] = e;//存入新的index
//对链表重新分布,疑问处
for (HashMapEntry n = e.next; n != null; e = n, n = n.next) {
int nextHighBit = n.hash & oldCapacity;
if (nextHighBit != highBit) {
if (broken == null)
newTable[j | nextHighBit] = n;
else
broken.next = n;
broken = e;
highBit = nextHighBit;
}
}
if (broken != null)
broken.next = null;
} 新表处理过后进行put
void addNewEntry(K key, V value, int hash, int index) {
table[index] = new HashMapEntry(key, value, hash, table[index]);
} GET
key为null的处理,否则由key计算hash找出index的项,对列表遍历查找。
列表内查找条件:
key地址相同
或
entry的hash相同且key的值相同
找不到返null
public V get(Object key) {
if (key == null) {
HashMapEntry e = entryForNullKey;
return e == null ? null : e.value;
}
int hash = Collections.secondaryHash(key);
HashMapEntry[] tab = table;
for (HashMapEntry e = tab[hash & (tab.length - 1)];
e != null; e = e.next) {
K eKey = e.key;
if (eKey == key || (e.hash == hash && key.equals(eKey))) {
return e.value;
}
}
return null;
} Remove
@Override public V remove(Object key) {
if (key == null) {//key为空的情况
return removeNullKey();
}
int hash = Collections.secondaryHash(key);
HashMapEntry[] tab = table;
int index = hash & (tab.length - 1);
for (HashMapEntry e = tab[index], prev = null;
e != null; prev = e, e = e.next) {//链表的移除方式
if (e.hash == hash && key.equals(e.key)) {
if (prev == null) {
tab[index] = e.next;
} else {
prev.next = e.next;
}
modCount++;
size--;
postRemove(e);
return e.value;
}
} private V removeNullKey() {
HashMapEntry e = entryForNullKey;
if (e == null) {
return null;
}
entryForNullKey = null;
modCount++;
size--;
postRemove(e);
return e.value;
}
/**
* Subclass overrides this method to unlink entry.
*/
//空实现 移除后操作
void postRemove(HashMapEntry e) { }