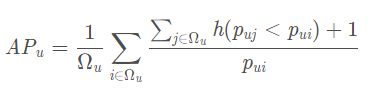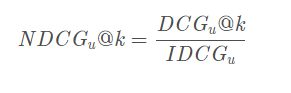推荐 | 微软SAR近邻协同过滤算法拆解(二)
推荐 | 微软SAR近邻协同过滤算法解析(一)前面这篇介绍了整个SAR算法,算法本身比较容易理解。本篇主要对一下里面有趣的小函数。
文章目录
- 1 对角方阵求jaccard / lift
- 2 矩阵取top-k函数
- 3 sparse稀疏矩阵构造
- 4 一些评价指标:NDCG、MAP、MRR、HR、ILS、ROC、AUC、F1等
-
- 4.1 Hit Ratio(HR)
- 4.2 Mean Average Precision(MAP)
- 4.3 Normalized Discounted Cummulative Gain(NDCG)
- 5 时间计数函数
- 参考文献:
1 对角方阵求jaccard / lift
这个发生在 C C C矩阵co-occurence matrix变成 S S S矩阵item similarity matrix,探究的是相互之间的相关性。
一旦我们具有共生矩阵,就可以通过根据给定度量重新缩放共现来获得项目相似性矩阵 :Jaccard, lift, and counts (就是计数,其实等于没改变,没压缩/缩放).
如果 c i i c_{ii} cii 和 c j j c_{jj} cjj 是 矩阵 C C C的第 i i i个 和 第 j j j个对角元素 , 则重新缩放选项为:
Jaccard: s i j = c i j ( c i i + c j j − c i j ) s_{ij}=\frac{c_{ij}}{(c_{ii}+c_{jj}-c_{ij})} sij=(cii+cjj−cij)cijlift: s i j = c i j ( c i i × c j j ) s_{ij}=\frac{c_{ij}}{(c_{ii} \times c_{jj})} sij=(cii×cjj)cijcounts: s i j = c i j s_{ij}=c_{ij} sij=cij
公式如下:
import numpy as np
def jaccard(cooccurrence):
"""Helper method to calculate the Jaccard similarity of a matrix of co-occurrences.
Args:
cooccurrence (np.array): the symmetric matrix of co-occurrences of items.
Returns:
np.array: The matrix of Jaccard similarities between any two items.
"""
diag = cooccurrence.diagonal()
diag_rows = np.expand_dims(diag, axis=0)
diag_cols = np.expand_dims(diag, axis=1)
with np.errstate(invalid="ignore", divide="ignore"):
result = cooccurrence / (diag_rows + diag_cols - cooccurrence)
return np.array(result)
def lift(cooccurrence):
"""Helper method to calculate the Lift of a matrix of co-occurrences.
Args:
cooccurrence (np.array): the symmetric matrix of co-occurrences of items.
Returns:
np.array: The matrix of Lifts between any two items.
"""
diag = cooccurrence.diagonal()
diag_rows = np.expand_dims(diag, axis=0)
diag_cols = np.expand_dims(diag, axis=1)
with np.errstate(invalid="ignore", divide="ignore"):
result = cooccurrence / (diag_rows * diag_cols)
return np.array(result)
这里一定是两个对角方阵的计算,
import numpy as np
from scipy import sparse
data = [[1,3,5],[3,1,6],[5,6,1]]
x = np.array(data)
x
# 求对角方阵的jaccard 、 lift
jaccard(x) # 必须是方阵
lift(x)
其中jaccard的输出:
jaccard(x) # 必须是方阵
Out[63]:
array([[ 1. , -3. , -1.66666667],
[-3. , 1. , -1.5 ],
[-1.66666667, -1.5 , 1. ]])
2 矩阵取top-k函数
def get_top_k_scored_items(scores, top_k, sort_top_k=False):
"""Extract top K items from a matrix of scores for each user-item pair,
{optionally sort results per user.
Args:
scores (np.array): score matrix (users x items).
top_k (int): number of top items to recommend.
sort_top_k (bool): flag to sort top k results.
Returns:
np.array, np.array: indices into score matrix for each users top items, scores corresponding to top items.
"""
# ensure we're working with a dense ndarray
if isinstance(scores, sparse.spmatrix):
scores = scores.todense()
if scores.shape[1] < top_k:
logger.warning(
"Number of items is less than top_k, limiting top_k to number of items"
)
k = min(top_k, scores.shape[1])
test_user_idx = np.arange(scores.shape[0])[:, None]
# get top K items and scores
# this determines the un-ordered top-k item indices for each user
top_items = np.argpartition(scores, -k, axis=1)[:, -k:]
top_scores = scores[test_user_idx, top_items]
if sort_top_k:
sort_ind = np.argsort(-top_scores)
top_items = top_items[test_user_idx, sort_ind]
top_scores = top_scores[test_user_idx, sort_ind]
return np.array(top_items), np.array(top_scores)
在一个user-item的矩阵里面,按行取出最重要的top-k的item。
示例:
import numpy as np
from scipy import sparse
data = [[1,3,5],[3,1,6],[5,6,1]]
x = np.array(data)
get_top_k_scored_items(x, 1, sort_top_k=False) # 按行抽取最大值
结果如下:
(array([[2],
[2],
[1]], dtype=int64),
array([[5],
[6],
[6]]))
第一行(第一个)用户最大值序号为2(矩阵一),值为5(矩阵二)。
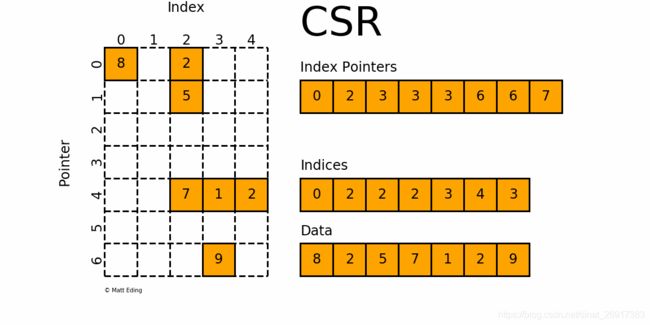
3 sparse稀疏矩阵构造
之前笔者也在研究稀疏矩阵,scipy.sparse、pandas.sparse、sklearn稀疏矩阵的使用,就顺便看一下SAR如何使用:
利用coo_matrix形成矩阵 -> 转化为csr进行计算
截取sar_singlenode.py 中的代码:
# generate pseudo user affinity using seed items
pseudo_affinity = sparse.coo_matrix(
(ratings, (user_ids, item_ids)), shape=(n_users, self.n_items)
).tocsr()
# calculate raw scores with a matrix multiplication
test_scores = pseudo_affinity.dot(self.item_similarity)
# remove items in the seed set so recommended items are novel
test_scores[user_ids, item_ids] = -np.inf
top_items, top_scores = get_top_k_scored_items(
scores=test_scores, top_k=top_k, sort_top_k=sort_top_k
)
get_top_k_scored_items(pseudo_affinity, 1, sort_top_k=False)
这里简单写一个生成的例子:
# 稀疏矩阵
ratings = [5,4,3]
user_ids = [0,1,2]
item_ids = [1,2,1]
n_users = len(user_ids)# 乱写,反正要比max(user_ids)大
n_items = 10 # 乱写,反正要比max(item_ids)大
pseudo_affinity = sparse.coo_matrix(
(ratings, (user_ids, item_ids)), shape=(n_users, n_items)
).tocsr()
pseudo_affinity.todense()
pseudo_affinity.toarray()
生成的结果为:
array([[0, 5, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 4, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 3, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0]], dtype=int32)
csr_matrix可用于各种算术运算:它支持加法,减法,乘法,除法和矩阵幂等操作。其有五种实例化方法,其中前四种初始化方法类似coo_matrix,即通过密集矩阵构建、通过其他类型稀疏矩阵转化、构建一定shape的空矩阵、通过(row, col, data)构建矩阵。其第五种初始化方式这是直接体现csr_matrix的存储特征:csr_matrix((data, indices, indptr), [shape=(M, N)]),意思是,矩阵中第i行非零元素的列号为indices[indptr[i]:indptr[i+1]],相应的值为data[indptr[i]:indptr[i+1]]
>>> import numpy as np
>>> from scipy.sparse import csr_matrix
>>> indptr = np.array([0, 2, 3, 6])
>>> indices = np.array([0, 2, 2, 0, 1, 2])
>>> data = np.array([1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6])
>>> csr = csr_matrix((data, indices, indptr), shape=(3, 3)).toarray()
array([[1, 0, 2],
[0, 0, 3],
[4, 5, 6]])
csr_matrix同样有很多方法,其中tobytes(),tolist(), tofile(),tostring()值得注意,其他具体参考官方文档,csr_matrix对象属性前五个同coo_matrix,另外还有属性如下:
-
indices
与属性data一一对应,元素值代表在某一行的列号
-
indptr
csr_matrix各行的起始值,length(csr_object.indptr) == csr_object.shape[0] + 1
-
has_sorted_indices
判断每一行的indices是否是有序的,返回bool值
-
csr_matrix的优点:
- 高效的算术运算CSR + CSR,CSR * CSR等
- 高效的行切片
- 快速矩阵运算
-
csr_matrix的缺点:
- 列切片操作比较慢(考虑csc_matrix)
- 稀疏结构的转换比较慢(考虑lil_matrix或doc_matrix)
4 一些评价指标:NDCG、MAP、MRR、HR、ILS、ROC、AUC、F1等
4.1 Hit Ratio(HR)
在top-K推荐中,HR是一种常用的衡量召回率的指标,计算公式为:

分母是所有的测试集合,分子表示每个用户top-K列表中属于测试集合的个数的总和。
举个简单的例子,三个用户在测试集中的商品个数分别是10,12,8,模型得到的top-10推荐列表中,分别有6个,5个,4个在测试集中,那么此时HR的值是
(6+5+4)/(10+12+8) = 0.5。
相关定义:
def hit(gt_items, pred_items):
count = 0
for item in pred_items:
if item in gt_items:
count += 1
return count
4.2 Mean Average Precision(MAP)
均准确率AP,假使当我们使用google搜索某个关键词,返回了10个结果。当然最好的情况是这10个结果都是我们想要的相关信息。但是假如只有部分是相关的,比如5个,那么这5个结果如果被显示的比较靠前也是一个相对不错的结果。但是如果这个5个相关信息从第6个返回结果才开始出现,那么这种情况便是比较差的。这便是AP所反映的指标,与recall的概念有些类似,不过是“顺序敏感的recall。
def AP(ranked_list, ground_truth):
"""Compute the average precision (AP) of a list of ranked items
"""
hits = 0
sum_precs = 0
for n in range(len(ranked_list)):
if ranked_list[n] in ground_truth:
hits += 1
sum_precs += hits / (n + 1.0)
if hits > 0:
return sum_precs / len(ground_truth)
else:
return 0
4.3 Normalized Discounted Cummulative Gain(NDCG)
累积增益CG,推荐系统中CG表示将每个推荐结果相关性的分值累加后作为整个推荐列表的得分:

其中,rel表示位置i的推荐结果的相关性,k表示推荐列表的大小。
CG没有考虑每个推荐结果处于不同位置对整个推荐结果的影响,例如,我们总是希望相关性大大的结果排在前面,相关性低的排在前面会影响用户体验。
假设搜索“篮球”结果,最理想的结果是:B1, B2, B3;而出现的结果是B3, B1,
B2的话,CG的值是没有变化的,因此需要下面的DCG。
DCG在CG的基础上引入了位置影响因素,计算公式如下:
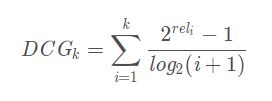
从上面的式子可以得出:1)推荐结果的相关性越大,DCG越大。2)相关性好的排在推荐列表前面的话,推荐效果越好,DCG越大。
DCG针对不同的推荐列表之间很难进行横向评估,而我们评估一个推荐系统不可能仅使用一个用户的推荐列表及相应结果进行评估,而是对整个测试集中的用户及其推荐列表结果进行评估。那么,不同用户的推荐列表的评估分数就需要进行归一化,也就是NDCG。
IDCG表示推荐系统某一用户返回的最好推荐结果列表, 即假设返回结果按照相关性排序, 最相关的结果放在最前面, 此序列的DCG为IDCG。因此DCG的值介于 (0,IDCG] ,故NDCG的值介于(0,1],那么用户u的NDCG@K定义为:
参考例子:
假设搜索回来的5个结果,其相关性分数分别是 3、2、3、0、1、2
那么CG = 3+2+3+0+1+2
可以看到只是对相关的分数进行了一个关联的打分,并没有召回的所在位置对排序结果评分对影响。而我们看DCG:

所以 DCG = 3+1.26+1.5+0+0.38+0.71 = 6.86
接下来我们归一化,归一化需要先结算 IDCG,假如我们实际召回了8个物品,除了上面的6个,还有两个结果,假设第7个相关性为3,第8个相关性为0。那么在理想情况下的相关性分数排序应该是:3、3、3、2、2、1、0、0。计算IDCG@6:
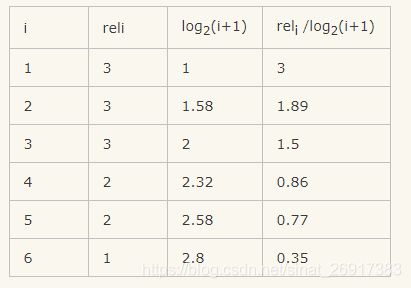
所以IDCG = 3+1.89+1.5+0.86+0.77+0.35 = 8.37
so 最终 NDCG@6 = 6.86/8.37 = 81.96%
5 时间计数函数
之前可以通过%time来计时,这边提供了一个:
from timeit import default_timer
from datetime import timedelta
import time
class Timer(object):
"""Timer class.
`Original code `_.
Examples:
>>> import time
>>> t = Timer()
>>> t.start()
>>> time.sleep(1)
>>> t.stop()
>>> t.interval < 1
True
>>> with Timer() as t:
... time.sleep(1)
>>> t.interval < 1
True
>>> "Time elapsed {}".format(t) #doctest: +ELLIPSIS
'Time elapsed 1...'
"""
def __init__(self):
self._timer = default_timer
self._interval = 0
self.running = False
def __enter__(self):
self.start()
return self
def __exit__(self, *args):
self.stop()
def __str__(self):
return "{:0.4f}".format(self.interval)
def start(self):
"""Start the timer."""
self.init = self._timer()
self.running = True
def stop(self):
"""Stop the timer. Calculate the interval in seconds."""
self.end = self._timer()
try:
self._interval = self.end - self.init
self.running = False
except AttributeError:
raise ValueError(
"Timer has not been initialized: use start() or the contextual form with Timer() as t:"
)
@property
def interval(self):
"""Get time interval in seconds.
Returns:
float: Seconds.
"""
if self.running:
raise ValueError("Timer has not been stopped, please use stop().")
else:
return self._interval
这边执行之后可知:
# 执行
with Timer() as t:
time.sleep(1)
# 运行时间
t.interval
结构来看满方面,可以后续自己用用
参考文献:
推荐算法常用评价指标:NDCG、MAP、MRR、HR、ILS、ROC、AUC、F1等
搜索评价指标——NDCG