SpringBoot + Vue (axios)实现 Restful API 交互
SpringBoot + Vue 实现 RestFul API 交互
- 一、SpringBoot 编写后端 API
-
-
- 1.1 编写一个最简单 API 服务
- 1.2 常见接收参数的方式
-
- 二、使用 axios 完成 ajax 请求
-
-
- 2.1 axios 基本配置
- 2.2 axios 实例
-
- 2.2.1 GET 请求
-
- 一、不带参数的 get 请求
- 二、带参数的 get 请求
- 三、请求路径中带参数
- 2.2.2 POST 请求
-
- 一、以实体类的形式接收参数
- 2.2.3 PUT 请求
- 2.2.4 DELETE 请求
-
在 RestFul API 中,前后端是分离的,后端不在负责视图的渲染,只负责返回指定的前端请求后端 Rest 风格的 API,后端接收到前端的请求之后,会根据请求方法类型,参数执行一些对应的操作。然后返回 JSON 格式的数据给前端。前端使用 ajax 技术发送 http 请求,可以使用原生的 API,比如 xhr、fetch、Promise API。Jquery 中的 $.ajax,以及现在常用的第三方 http 库 axios
一、SpringBoot 编写后端 API
1.1 编写一个最简单 API 服务
我在 application.yml 中定义的端口是 3030,所以之后的请求都会以 http://localhost:3030 作为根路径,在下面我写好了一个最简单的 API,然后我们启动项目
@CrossOrigin
@RestController
public class StartController {
@RequestMapping("/")
public String Test() {
return "hello";
}
}
如果你看到这个页面,说明项目启动成功了。
接下来给大家解释一下这个项目的注解
- @CrossOrigin 前后端分离的项目一定会遇到这个问题,使用这个注解解决跨域请求
- @RestController 使用这个注解,我们返回的数据会以 JSON 格式自动返回给前端
- @RequestMapping("/") 这个注解表示配置请求的路径,我们没有指定请求方法,所以任何方法都可以接受
1.2 常见接收参数的方式
其他的请求方式都是一样的,这里我们以 GET 请求为示例
// 不带参数,一般获取参数所有数据
@GetMapping("/get")
public String testGet() {
return "我是 GET 请求";
}
// 携带请求参数,携带参数获取数据
@GetMapping("/get/params")
public String test (@RequestParam("name") String name) {
return "名称" + name;
}
// RestAPI,获取请求路径中的数据。 一般用来请求单条数据
@GetMapping("/get/{id}")
public String testGet1(@PathVariable("id") Integer id) {
return "id:" + id;
}
// 接收实体参数,只要与实体的属性一一对应,就可以接收。 以实体类的形式接受参数
@GetMapping("/get/model")
public Map<String,Object> testGet2(@ModelAttribute User user) {
Map<String,Object> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("user",user);
map.put("code",200);
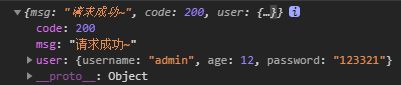
map.put("msg","请求成功~");
return map;
}
// 接受 JSON格式的实体类
@GetMapping("/get/json/data")
public Map<String,Object> testGet3(@RequestBody User user) {
Map<String,Object> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("user",user);
map.put("code",200);
map.put("msg","请求成功~");
return map;
}
二、使用 axios 完成 ajax 请求
axios 基本使用
2.1 axios 基本配置
我们看下官网的使用说明
实例方法
以下是可用的实例方法。指定的配置将与实例的配置合并。
axios#request(config)
axios#get(url[, config])
axios#delete(url[, config])
axios#head(url[, config])
axios#options(url[, config])
axios#post(url[, data[, config]])
axios#put(url[, data[, config]])
axios#patch(url[, data[, config]])
实例配置
{
url: '/user',
methods: 'GET',
data: {
"username": "abc",
"password": "123321"
}
...
}
示例:
// 直接请求 GET
axios.get('/user')
// 请求参数会在 url 中显示: /user?username=admin&password=123456
axios.get("/user",{
params: {
"username" : "admin",
"password": "123456"
}
})
// 使用配置的方式配置请求参数, 请求参数会以 JSON 字符串的形式传递,如果 header 中设置了 Content-Type 为 form 表单,就可以使用普通的参数接收
axios({
url: '/user',
methods: 'post',
data: {
"username": "admin",
"password": "123321"
},
},{
headers: {
"token": "123321"
}
})
2.2 axios 实例
2.2.1 GET 请求
一、不带参数的 get 请求
后端代码接收不带参数的 get 请求
// 不带参数
@GetMapping("/get")
public String testGet() {
return "我是 GET 请求";
}
前端编写 ajax
async function testGetAsync() {
// GET 请求,不带参数
const {
data: res} = await this.axios.get("http://localhost:3030/get")
console.log(res)
}
运行结果
![]()
二、带参数的 get 请求
- SpringBoot 中 RequestParam 注解就是用来接收 url 中 键值对中的数据
后端代码:
// 携带请求参数
@GetMapping("/get/params")
public String test (@RequestParam("name") String name) {
return "名称" + name;
}
前端 ajax 代码
// GET 请求,携带参数
const {
data: res1} = await this.axios.get('http://localhost:3030/get/params',{
params: {
name: 'coco'
}
})
console.log(res1)
get 请求携带参数,我们可以发现请求路径的变化,请求参数是可以看得到的

响应结果
![]()
三、请求路径中带参数
补充说明,这种请求路径携带参数的方式是标准的 Restful API 格式,一般在 get 请求中获取 单个数据,或者 delete 方法中删除 一条记录使用的比较多
后端代码
// RestAPI,获取请求路径中的数据
@GetMapping("/get/{id}")
public String testGet1(@PathVariable("id") Integer id) {
return "id:" + id;
}
前端 ajax 代码
// 路径携带参数,请求路径我使用 ES6 中的新语法编写的
const {
data: res2} = await this.axios.get(`http://localhost:3030/get/3`)
console.log(res2)
响应结果
![]()
以上便是 GET 请求使用比较多的地方
2.2.2 POST 请求
在 RestFul API 中,一般用来提交 FORM 表单用到的会比较多。并且使用 post 请求携带的参数也比 get 请求更多。我在写项目当中,post 请求常常会用来做登录表单提交,数据添加等等
为了测试方便,我编写了一个如下的实体类。为了避免不必要的麻烦,在这里我一般不会去写构造函数
public class User {
private String username;
private Integer age;
private String password;
//getter、setter,toString 方法省略
}
一、以实体类的形式接收参数
- SpringBoot 中 ModelAttribute 注解,是用来接收对象的(前端发送的数据必须和实体的属性一一对应。如果有一个不对应,后端就无法把前端发送的数据注入到实体内)
后端代码
// 接收实体参数,只要与实体的属性一一对应,就可以接收
@PostMapping("/post/model")
public Map<String,Object> testPost(@RequestBody User user) {
System.out.println("实体:"+user.toString());
Map<String,Object> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("user",user);
map.put("code",200);
map.put("msg","请求成功~");
return map;
}
前端 ajax 代码
// 接收实体类
const {
data: res3} = await this.axios.post('http://localhost:3030/post/model',{
age: 12,
username: "admin",
password: "123321"
})
补充说明
- 在 axios 中使用 POST 提交数据时,数据会以 application/json 发送到后端,这是和传统的 form 表达那不同的地方。
- 所以在后端使用 @ModelAttribute 是使用不了的。如果时使用其它方式发送 post 请求,我们可以设置 header 中的 Content-Type 的值为
application/x-www-form-urlencoded;charset=UTF-8 - 因此所有在 SpringBoot 中接收数据必须使用 @RequestBody 注解,讲前端的数据以 JSON 的格式接收
2.2.3 PUT 请求
PUT 请求在 Restful API 中常用来更新数据,使用这个我们就能区别开 POST 请求了,使用方式和 POST 请求几乎是一致的
后端代码
@PutMapping("/put/data")
public Map<String,Object> testGet3(@RequestBody User user) {
Map<String,Object> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("user",user);
map.put("code",200);
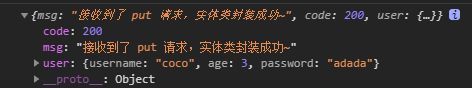
map.put("msg","接收到了 put 请求,实体类封装成功~");
return map;
}
前端代码
const {
data: res4} = await this.axios.put('http://localhost:3030/put/data',{
age: 3,
username: "coco",
password: "adada"
},{
headers: {
"token": "123123131231dadawdw"
}
})
console.log(res4)
2.2.4 DELETE 请求
DELETE 请求用来删除一条记录中的数据, 和 GET 请求一样用于获取 url 中的参数
后端代码
@DeleteMapping("/delete/{id}")
public String testDelete(@PathVariable("id") Integer id) {
return "delete:" + id;
}
前端代码
const {
data: result} = await this.axios.delete(`http://localhost:3030/delete/${
5}`)
console.log(result)
运行效果
![]()
好了,今天的内容到这里就结束了~
如果大家有想知道的都可以提出来哦