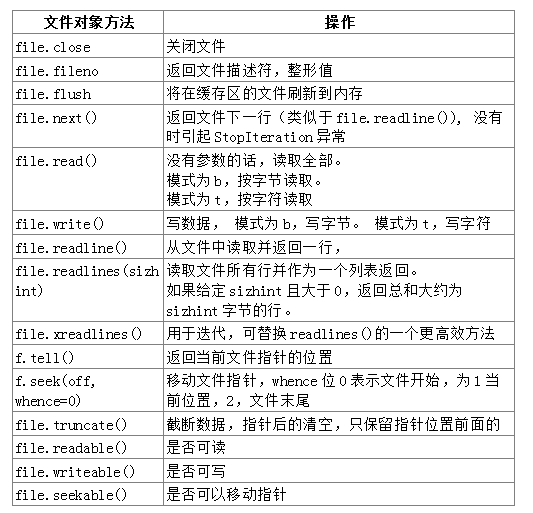
1 文件与IO
1.1读写文本数据
读写各种不同的文本数据,如ASCII,UTF-8,UTF-9编码等。
使用带有rt模式的open()函数读取文本文件。
例如: with open('db', 'rt') as f: data = f.read() print(data) with open('db', 'rt') as f: for line in f: print(line.strip('\n'))
使用带有wt的open()函数写入一个文本文件,如果之前文件内容存在则清除并覆盖掉。
例如: with open('db', 'wt') as f: f.write('python|python235')
如果是已存在文件中添加内容,使用at的open()函数。
操作文件时指定默认编码
with open('somefile.txt', 'rt', encoding='latin-1') as f: ...
注意:
当使用with语句时,不需要手动关闭文件,当with控制块结束时,文件会自动关闭。不用with时,需要手动关闭。
1.2文件不存在时写入
在一个文件中写入数据,如果文件不存在写入,而不是直接覆盖原文件内容。
例如: with open('db', 'xt') as f: f.write('hello') db文件存在抛出FileExistsError异常 Traceback (most recent call last): File "C:/Users/hexm/Desktop/python/s13/day3/file01.py", line 9, inwith open('db', 'xt') as f: FileExistsError: [Errno 17] File exists: 'db' 替代方案: import os if not os.path.exists('db'): with open('db', 'wt') as f: f.write('hello\n') else: print('File already exists')
1.3读写二进制文件
例如: f = open('db', 'rb') res = f.read() print(res, type(res)) #b'ssssssssss'text = res.decode('utf-8') print(text) f = open('db', 'ab') text = 'hello,世界' f.write(bytes(text, encoding='utf-8')) f.write(text.encode('utf-8')) f = open('db', 'ab') f.write(b'Hello world.')
1.4 打印输出到文本文件
打印输出至文件中,将print()函数输出重定向到一个文件中。
例如: with open('db', 'wt') as f: print('python1|python279', file=f)
1.5 使用其他分隔符或行终止符打印
可以在print()函数中使用sep和end关键字。
例如: print('xiaoming', 2, 3, 5) print('xiaoming', 2, 3, 5, sep=',', end='!!!\n') for x in range(10): print(x, end=' ') #0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
使用str.join()也可以做到,不过str.join()仅使用于字符串。
例如: print(','.join(str(x)for x in name)) #xiaoming,2,3,5 print(*name, sep = ',') #xiaoming,2,3,5
1.6 format格式化输出
#format格式化输出 s1 = 'I am {0}, age {1}'.format('hexm', 18) print(s1) #I am hexm, age 18 s2 = 'I am {0}, age {1}'.format(*['hexm', 18]) print(s2) #I am hexm, age 18 s3 = 'I am {name}, age {age}'.format(name='hexm', age=18) print(s3) #I am hexm, age 18 s4 = 'I am {name}, age {age}'.format(**{ 'name': 'hexm', 'age': 18}) print(s4) #I am hexm, age 18
监控文件尾部,并打印
#!/usr/bin/env python # coding=utf-8 import time def follow(thefile): thefile.seek(0,2) while True: line = thefile.readline() if not line: time.sleep(0.1) continue yield line if __name__ == '__main__': logfile = open('/tmp/access.log', 'r') loglines = follow(logfile) for line in loglines: print(line.strip())
监控文件尾部,并打印,退出后从退出位置监控
#!/usr/bin/env python # coding=utf-8 import time import os def follow(seek_bytes, file): seek_bytes = int(seek_bytes) file.seek(seek_bytes) # 跳到位置信息 while True: line = file.readline() if not line: time.sleep(0.1) continue else: # 保存位置信息 with open('/tmp/linenumber.log', 'w+') as f: f.write(str(file.tell())) yield line if __name__ == '__main__': logfile = open('/tmp/access.log', 'r') # 如果位置文件存在,打开并读取 if os.path.exists('/tmp/seek_bytes.log'): with open('/tmp/seek_bytes.log', 'r') as f: seek_bytes = f.readline().strip() # 位置设置为0 else: seek_bytes = '0' # 将位置信息和文件对象传给follow函数 loglines = follow(seek_bytes, logfile) for line in loglines: print(line.strip())