源码解析:Oops ! JDK源码---集合类(二)之LinkedList源码
本文基于jdk1.8
本文首发于本人博客:https://totalo.top
编程小白,正在学习,各位大佬指正呀,点点广告呀,谢谢!
I’m studying, I’d like to point out the deficiencies, and please help me with the ad. Thank you.
0x00 概述
linkedList是链表实现的集合,元素有序可以重复。
0x01 类图
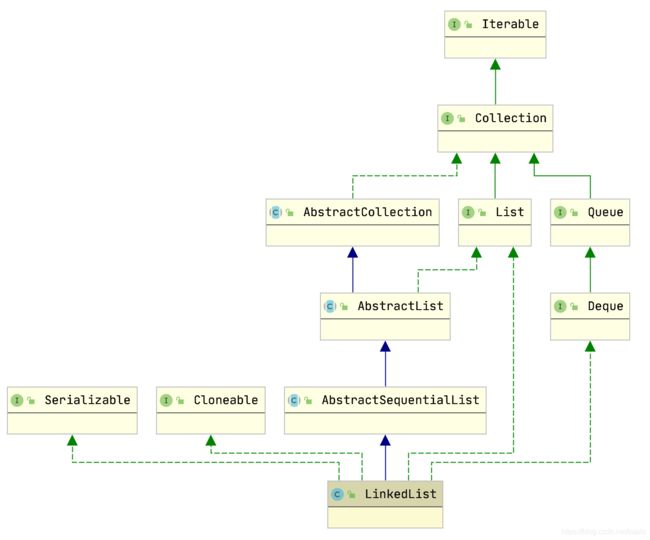
由类图可知:
1、与arraylist相同的三个接口
java.util.List 接口
java.io.Serializable 接口
java.lang.Cloneable 接口
2、少于arraylist的接口
java.util.RandomAccess 接口
LinkedList 不同于 ArrayList ,使用链表实现,不支持随机访问
3、多于arraylist的接口
java.util.Deque 接口,
表示支持双端队列的功能,LinkedList 支持快速的在头尾添加元素和读取元素。
继承 java.util.AbstractSequentialList 抽象类。如下:
public abstract class AbstractSequentialList,由此可知,AbstractSequentialList是AbstractList的子类,可以实现只能连续访问的数据存储的连续操作。查看类中的方法主要是如#get(int index)、#add(int index, E element)等方法。
0x02 详细解析
主要属性
// transient关键字防止变量被持久化
// 链表元素(节点)的个数
transient int size = 0;
/**
* Pointer to first node.
* Invariant: (first == null && last == null) ||
* (first.prev == null && first.item != null)
*/
// 内部类 也是不可持久化
// 指向第一节点的指针
transient Node<E> first;
/**
* Pointer to last node.
* Invariant: (first == null && last == null) ||
* (last.next == null && last.item != null)
*/
// 指向最后一个节点的指针
transient Node<E> last;
主要方法
1、构造方法
/**
* Constructs an empty list.
*/
// 空构造
public LinkedList() {
}
/**
* Constructs a list containing the elements of the specified
* collection, in the order they are returned by the collection's
* iterator.
*
* @param c the collection whose elements are to be placed into this list
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified collection is null
*/
// 集合构造
public LinkedList(Collection<? extends E> c) {
this();
// 添加进入链表
addAll(c);
}
2、添加元素
尾插法:
/**
* Appends the specified element to the end of this list.
*
* This method is equivalent to {@link #addLast}.
*
* @param e element to be appended to this list
* @return {@code true} (as specified by {@link Collection#add})
*/
public boolean add(E e) {
// 尾插入链表中
linkLast(e);
return true;
}
/**
* Links e as last element.
*/
void linkLast(E e) {
// 记录插入的last节点
final Node<E> l = last;
// 创建新节点,前一个节点为l, 节点元素为e,新节点的后续节点为null
final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(l, e, null);
// last指向新节点
last = newNode;
// 判断last节点是否为null,为null则说明first节点也为空,则将first也指向新节点
if (l == null)
first = newNode;
// 不为空,则将last节点的next指向新节点
else
l.next = newNode;
// 增加链表大小
size++;
// 增加修改次数
modCount++;
}
添加到指定位置:
/**
* Inserts the specified element at the specified position in this list.
* Shifts the element currently at that position (if any) and any
* subsequent elements to the right (adds one to their indices).
*
* @param index index at which the specified element is to be inserted
* @param element element to be inserted
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc}
*/
public void add(int index, E element) {
// 检查下标是否在范围之内
checkPositionIndex(index);
// 若正好等于链表的大小,直接添加至尾部
if (index == size)
linkLast(element);
else
// 添加到第index元素之前
linkBefore(element, node(index));
}
........
/**
* Inserts element e before non-null Node succ.
* 在某个元素之前插入
*/
void linkBefore(E e, Node<E> succ) {
// assert succ != null;
// 获取当前元素的前一个元素
final Node<E> pred = succ.prev;
// 创建新节点
final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(pred, e, succ);
// 将下游节点关联上上一个
succ.prev = newNode;
// 若上一个为空,则链表为空,将首节点置为该新节点
if (pred == null)
first = newNode;
else
// 否则将新节点放入前一个节点与后一个之间。
pred.next = newNode;
// 修改链表大小,修改次数加1
size++;
modCount++;
}
........
/**
* Returns the (non-null) Node at the specified element index.
* 获取指定下表的节点
*/
Node<E> node(int index) {
// assert isElementIndex(index);
// 若指定位置小于原链的一半,则从前往后找。否则从后往前
if (index < (size >> 1)) {
Node<E> x = first;
for (int i = 0; i < index; i++)
x = x.next;
return x;
} else {
Node<E> x = last;
for (int i = size - 1; i > index; i--)
x = x.prev;
return x;
}
}
3、获取元素
获取指定位置的元素:
// LinkedList
/**
* Returns the element at the specified position in this list.
*
* @param index index of the element to return
* @return the element at the specified position in this list
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc}
*/
public E get(int index) {
// 检查下标
checkElementIndex(index);
// 借助node(int index) 实现节点的查找
return node(index).item;
}
基于Deque接口实现的方法:
// LinkedList实现了Deque接口,所以实现了peekFirst和peekLast
/**
* Retrieves, but does not remove, the first element of this list,
* or returns {@code null} if this list is empty.
*
* @return the first element of this list, or {@code null}
* if this list is empty
* @since 1.6
* 获取头部元素
*/
public E peekFirst() {
final Node<E> f = first;
return (f == null) ? null : f.item;
}
/**
* Retrieves, but does not remove, the last element of this list,
* or returns {@code null} if this list is empty.
*
* @return the last element of this list, or {@code null}
* if this list is empty
* @since 1.6
* 获取尾部元素
*/
public E peekLast() {
final Node<E> l = last;
return (l == null) ? null : l.item;
}
基于Queue接口实现的方法:
// Queue operations.
/**
* Retrieves, but does not remove, the head (first element) of this list.
*
* @return the head of this list, or {@code null} if this list is empty
* @since 1.5
* 返回首部元素
*/
public E peek() {
final Node<E> f = first;
return (f == null) ? null : f.item;
}
/**
* Retrieves, but does not remove, the head (first element) of this list.
*
* @return the head of this list
* @throws NoSuchElementException if this list is empty
* @since 1.5
* 获取头部元素
*/
public E element() {
return getFirst();
}
/**
* Returns the first element in this list.
*
* @return the first element in this list
* @throws NoSuchElementException if this list is empty
*/
public E getFirst() {
final Node<E> f = first;
if (f == null)
// 当元素为空,抛出NoSuchElementException异常
throw new NoSuchElementException();
return f.item;
}
4、设置元素
设置指定位置的元素
/**
* Replaces the element at the specified position in this list with the
* specified element.
*
* @param index index of the element to replace
* @param element element to be stored at the specified position
* @return the element previously at the specified position
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc}
*/
public E set(int index, E element) {
// 检查下标
checkElementIndex(index);
// 获取原来index元素上的元素
Node<E> x = node(index);
E oldVal = x.item;
// 修改对应的index节点的值
x.item = element;
// 返回old value
return oldVal;
}
5、转化数组
Object数组:
/**
* Returns an array containing all of the elements in this list
* in proper sequence (from first to last element).
*
* The returned array will be "safe" in that no references to it are
* maintained by this list. (In other words, this method must allocate
* a new array). The caller is thus free to modify the returned array.
*
*
This method acts as bridge between array-based and collection-based
* APIs.
*
* @return an array containing all of the elements in this list
* in proper sequence
*/
public Object[] toArray() {
// 创建Object数组
Object[] result = new Object[size];
int i = 0;
// 遍历所有节点,挨个元素添加到数组中
for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; x = x.next)
result[i++] = x.item;
return result;
}
泛型数组:
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public <T> T[] toArray(T[] a) {
// 若传入的数组小于size大小,则直接复制一个新的数组返回
if (a.length < size)
a = (T[])java.lang.reflect.Array.newInstance(
a.getClass().getComponentType(), size);
int i = 0;
// 顺序遍历链表,复制进a
Object[] result = a;
for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; x = x.next)
result[i++] = x.item;
// 传入的数组长度大于size,将size处置为null
if (a.length > size)
a[size] = null;
return a;
}
6、序列化与反序列化
序列化:
private void writeObject(java.io.ObjectOutputStream s)
throws java.io.IOException {
// 写入非transient属性以及非静态属性
s.defaultWriteObject();
// 写入链表的大小
s.writeInt(size);
// 顺序遍历并序列化每个元素
for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; x = x.next)
s.writeObject(x.item);
}
反序列化:
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
private void readObject(java.io.ObjectInputStream s)
throws java.io.IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
// 读取非transient属性以及非静态属性
s.defaultReadObject();
// 读取size
int size = s.readInt();
// 顺序遍历逐个反序列化添加到链表尾部
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
linkLast((E)s.readObject());
}