spring源码解析之SpringIOC源码解析(上)
SpringIOC源码解析(上)
一、什么是SpringIOC
spring ioc指的是控制反转,IOC容器负责实例化、定位、配置应用程序中的对象及建立这些对象间的依赖。交由Spring容器统一进行管理,从而实现松耦合。
二、SpringIOC源码解析
在开始之前我们先通过一个简单的示意图来了解一下大概的一个流程
从示意图可以看出,当web容器启动的时候,spring的全局bean的管理器会去xml配置文件中扫描的包下面获取到所有的类,并根据你使用的注解,进行对应的封装,封装到全局的bean容器中进行管理,一旦容器初始化完毕,beanID以及bean实例化的类对象信息就全部存在了,现在我们需要在某个service里面调用另一个bean的某个方法的时候,我们只需要依赖注入进来另一个bean的Id即可,调用的时候,spring会去初始化完成的bean容器中获取即可,如果存在就把依赖的bean的类的实例化对象返回给你,你就可以调用依赖的bean的相关方法或属性等;
本文会分析Spring的IOC模块的整体流程,分析过程需要使用一个简单的demo工程来启动Spring,需要的童鞋可自行下载
https://github.com/cjinjun/spring-framework-demo
工程示例代码
写一个简单的接口和接口实现类
public interface IOCService {
String helloIoc();
}
public class IOCServiceImpl implements IOCService {
@Override
public String helloIoc() {
return "Hello,IOC";
}
}
新建一个application-ioc.xml
启动spring
public class IOCDemo {
public static void main (String args[]){
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("classpath:application-ioc.xml");
IOCService iocService=context.getBean(IOCService.class);
System.out.println(iocService.helloIoc());
}
}
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext
在看具体源码之前先看一下这兄弟的类图
最下边ClassPathXmlApplicationContext就是咱们今天要撸的、分析的主角。
看一下这个类的源码
里边的方法基本上都是重载方法,整体来看源码也比较简单只有setConfigLocations和refresh两个方法没有看到具体的实现。但是如果你因为这个而小瞧了Spring那可就大错特错了,setConfigLocations只是一个开胃小菜,refresh才是核心重点。
setConfigLocations方法的主要工作有两个:创建环境对象ConfigurableEnvironment和处理ClassPathXmlApplicationContext传入的字符串中的占位符
这里的getEnironment就涉及到创建环境变量的操作。
这个接口ConfigurableEnvironment比较重要的就是两部分内容了,一个是设置Spring的环境就是我们经常用的spring.profile配置。另外就是系统资源Property。
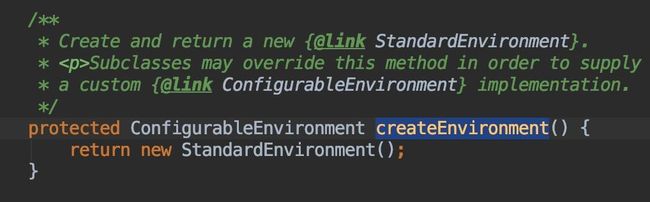
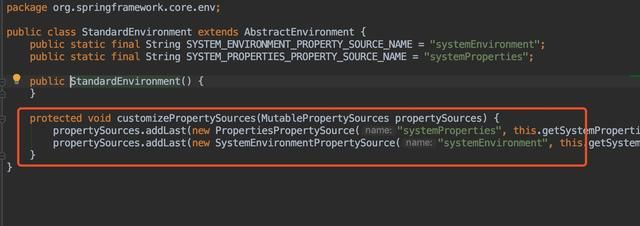
接着看`createEnvironment()`方法,发现它返回了一个`StandardEnvironment`类,而这个类中的`customizePropertySources`方法就会往资源列表中添加Java进程中的变量和系统的环境变量
处理占位符
再次回到 `resolvePath`方法后跟进通过上方获取的`ConfigurableEnvironment`接口的`resolveRequiredPlaceholders`方法,终点就是下方的这个方法。这个方法主要就是处理所有使用${}方式的占位符
开胃小菜已经说完了,现在才是本文重中之重refresh
refresh
方法内容比较多,以下将用较长的篇幅来解析说明这个方法,童鞋们可以提前做好心里准备。
先看一下refresh方法里边内容
public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) {
// Prepare this context for refreshing.
prepareRefresh();
// Tell the subclass to refresh the internal bean factory.
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory();
// Prepare the bean factory for use in this context.
prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory);
try {
// Allows post-processing of the bean factory in context subclasses.
postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);
// Invoke factory processors registered as beans in the context.
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// Register bean processors that intercept bean creation.
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// Initialize message source for this context.
initMessageSource();
// Initialize event multicaster for this context.
initApplicationEventMulticaster();
// Initialize other special beans in specific context subclasses.
onRefresh();
// Check for listener beans and register them.
registerListeners();
// Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons.
finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory);
// Last step: publish corresponding event.
finishRefresh();
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
logger.warn("Exception encountered during context initialization - " +
"cancelling refresh attempt: " + ex);
}
// Destroy already created singletons to avoid dangling resources.
destroyBeans();
// Reset 'active' flag.
cancelRefresh(ex);
// Propagate exception to caller.
throw ex;
}
finally {
// Reset common introspection caches in Spring's core, since we
// might not ever need metadata for singleton beans anymore...
resetCommonCaches();
}
}
}
看着东西是不是比较多,容易懵?不要慌,咱们一步一步分析。与它死磕到底,不研究明白不罢休。
- 第一行 synchronized 这个关键字作用我就不多说了把,如果想深入了解可以自行百度,在这里为了避免`refresh()` 还没结束,再次发起启动或者销毁容器引起的冲突
- `prepareRefresh()` 从字面意思来看说 “预准备refresh" 主要做一些准备工作,记录容器的启动时间、标记“已启动”状态、检查环境变量等
- `obtainFreshBeanFactory()` 乍一看这个方法也没几行代码,但是这个方法在执行refreshBeanFactory时候创建一个默认的BeanFactory:DefaultListableBeanFactory,并加载BeanDefinition。
- prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory),为beanFactory设置一些属性如ClassLoader,BeanExpressionResolver,PropertyEditorRegistrar,BeanPostProcessor等
- postProcessBeanFactory()这个比较简单,是Spring的一个扩展点,如果有Bean实现了BeanFactoryPostProcessor接口,那么在容器初始化以后,Spring 会负责调用里面的 postProcessBeanFactory 方法
- invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory),为beanFactory注册BeanFactoryPostProcessor
- registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory),注册当Bean创建时候的BeanPostProcessor
- initMessageSource()初始化上下文的消息源:DelegatingMessageSource
- initApplicationEventMulticaster()初始化了一个事件传播器:SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster
- `onRefresh()` 又是一个扩展点,子类可以在这里来做一些想做的事情
- registerListeners()获取ApplicationListener,并在事件传播器中注册他们
- finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory),获取LoadTimeWeaverAware并初始化他们,初始化单例并且非懒加载的Bean
- finishRefresh()完成refresh Context操作,初始化LifecycleProcessor并start,发布ContextRefreshedEvent事件
- resetCommonCaches()主要是清理缓存
一个ClassPathXmlApplicationContext的初始化过程基本如上,详细的BeanDefinition加载过程,获取Bean操作期待下篇。