binlog的寻找过程可能的场景如下:
- instance第一次启动
- 发生数据库主备切换
- canal server HA情况下的切换
所以这个过程是能够保证binlog不丢失的关键点。
本文从源码的角度来分析下启动过程中的binlog寻找过程。
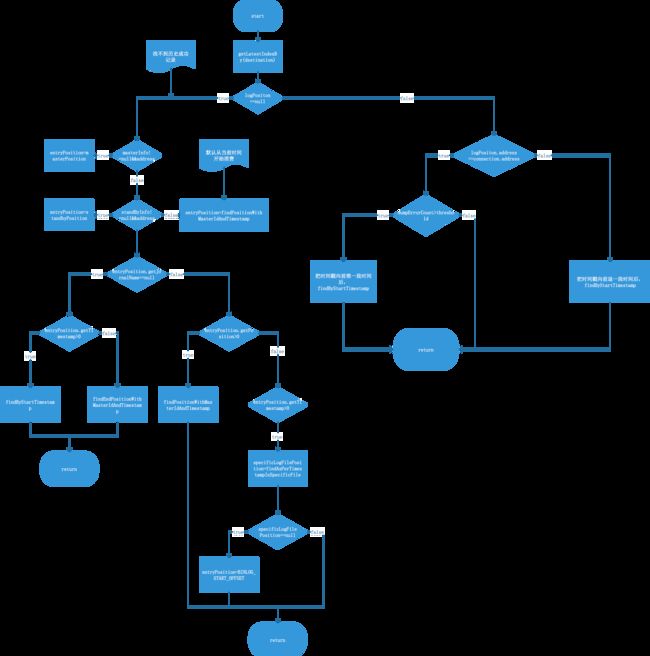
一、流程图
二、源码分析
入口在AbstractEventParser的start()方法中,这个start方法其实是instance的整个启动过程。具体启动过程中都做了哪些事情,请见另一篇文章的分析。这块不再赘述。我们主要看的地方是
// 4. 获取最后的位置信息
EntryPosition position = findStartPosition(erosaConnection);这一行就是获取binlog的解析位置,也是本文着重要分析的地方。因为我们目前所配置的都是MysqlEventParser,所以我们分析的也是这个类中的相关代码。
protected EntryPosition findStartPosition(ErosaConnection connection) throws IOException {
if (isGTIDMode()) {
// GTID模式下,CanalLogPositionManager里取最后的gtid,没有则取instanc配置中的
LogPosition logPosition = getLogPositionManager().getLatestIndexBy(destination);
if (logPosition != null) {
return logPosition.getPostion();
}
if (StringUtils.isNotEmpty(masterPosition.getGtid())) {
return masterPosition;
}
}
EntryPosition startPosition = findStartPositionInternal(connection);
if (needTransactionPosition.get()) {
logger.warn("prepare to find last position : {}", startPosition.toString());
Long preTransactionStartPosition = findTransactionBeginPosition(connection, startPosition);
if (!preTransactionStartPosition.equals(startPosition.getPosition())) {
logger.warn("find new start Transaction Position , old : {} , new : {}",
startPosition.getPosition(),
preTransactionStartPosition);
startPosition.setPosition(preTransactionStartPosition);
}
needTransactionPosition.compareAndSet(true, false);
}
return startPosition;
}2.1 GTID模式
我们目前的数据库架构一般都是M-S,所以binlog的位点很可能不一致,这就需要开启数据库GTID模式(通过在instance.properties中配置canal.instance.gtidon=true即可开启),这是一个全局的事务ID,能够防止主从位点不一致的情况下,找不到位点的问题。目前这块是从CanalLogPositionManager中取最后的GTID。default-instance.xml中,使用的CanalLogPositionManager是FailbackLogPositionManager,一个两级的位点管理器,XML配置如下:
一级是放到本地缓存中,第二级直接打了个info日志,有点弱,其实考虑的情况是性能,另一个考虑可能是因为DB的主从切换,并不会导致instance挂掉,内存中还是存储了之前DB的一些解析位点信息。其实都没有放到zk中,不利于做HA,所以这块目前还不是很完善,真正要使用GTID的话,需要对CanalLogPositionManager进行修改。目前已经提供了其他的一些实现,包括定时刷新到zk中等等。
如果CanalLogPositionManager中没有存储的话,也可以在instance.properties里面指定位点和GTID信息,也能从binlog中获取。
2.2 非GTID模式
如果canal没有开启GTID模式,那么我们就需要走一个binlog的寻找过程。
EntryPosition startPosition = findStartPositionInternal(connection);这个方法是个冗长的方法,里面的判断逻辑就是上面的流程图,我们来梳理一下。
首先还是从CanalLogPositionManager中获取,也就是基本上从内存中获取LogPosition。
LogPosition logPosition = logPositionManager.getLatestIndexBy(destination);2.2.1 内存中不存在LogPosition
2.2.1.1
首先判断配置文件中的主库信息是否与当前的数据库连接connection的地址一致,如果一致,如果一致,那么直接取properties文件中的master的位点信息。
2.2.1.2
如果主库不一致,那么判断从库standby的connection地址,如果是从库,那么直接取从库的位点信息。
我们可以在xml配置中看到properties的一些信息。
2.2.1.3
如果内存中没有,配置文件中也没有,那么系统默认从当前时间开始消费。
entryPosition = findEndPositionWithMasterIdAndTimestamp(mysqlConnection); // 默认从当前最后一个位置进行消费
protected EntryPosition findEndPositionWithMasterIdAndTimestamp(MysqlConnection connection) {
MysqlConnection mysqlConnection = (MysqlConnection) connection;
final EntryPosition endPosition = findEndPosition(mysqlConnection);//获取当前最新的位点信息
if (tableMetaTSDB != null) {
long startTimestamp = System.currentTimeMillis();
return findAsPerTimestampInSpecificLogFile(mysqlConnection,
startTimestamp,
endPosition,
endPosition.getJournalName(),
true);
} else {
return endPosition;
}
}这里的findEndPosition()方法,其实就是执行了一个Mysql命令:
show master status返回的内容中,包含binlog文件信息和位点position,甚至包括GTID信息。
找到了最新的binlog位点信息后,根据当前时间戳和binlog的时间戳等信息,去服务器上面寻找binlog。其实逻辑基本上都在findAsPerTimestampInSpecificLogFile()中,这个方法是根据时间戳去寻找,离时间戳最近(小于时间戳)的一个事务起始位置。由于这块的代码比较长,所以我们只做分析,不做代码粘贴,具体的代码在MysqlEventParser这个类中。整个寻找的过程如下:
先看一下这个seek的过程,见代码注释:
/**
* 加速主备切换时的查找速度,做一些特殊优化,比如只解析事务头或者尾
*/
public void seek(String binlogfilename, Long binlogPosition, SinkFunction func) throws IOException {
updateSettings();//在mysql中执行一些dump之前的命令
sendBinlogDump(binlogfilename, binlogPosition);//指定位点和binlog文件,发送dump命令,COM_BINLOG_DUMP
DirectLogFetcher fetcher = new DirectLogFetcher(connector.getReceiveBufferSize());
fetcher.start(connector.getChannel());//开始获取
LogDecoder decoder = new LogDecoder();
decoder.handle(LogEvent.ROTATE_EVENT);
decoder.handle(LogEvent.FORMAT_DESCRIPTION_EVENT);
decoder.handle(LogEvent.QUERY_EVENT);
decoder.handle(LogEvent.XID_EVENT);
LogContext context = new LogContext();
while (fetcher.fetch()) {//遍历获取
LogEvent event = null;
event = decoder.decode(fetcher, context);//解析为event
if (event == null) {
throw new CanalParseException("parse failed");
}
if (!func.sink(event)) {//调用SinkFunction.sink()过滤
break;
}
}
}下面我们看下数据过滤这块:
- 起始位置为4,也就是跳过一个魔法值,具体可以看binlog的结构说明
- 之后就是一个过滤的过程
- 首先把事件event解析一个entry,这个entry使用的是消息模型EntryProtocol.proto
- 首先判断当前事件是否为事务开始或者结束的位置,如果是,判断事件的时间,如果在我们需要的时间之后,直接过滤这条entry
- 如果当前entry的binlog文件名和最新的binlog文件名相同,并且最新的位点小于entry的位点,那么直接过滤
- 如果当前entry的类型表示的是事务开始或者事务结束,那么直接取当前entry的位点信息,利用当前entry构建位点信息,也就是找到了我们需要的事务起点。
2.2.1.4
如果binlog文件名为空,首先判断时间戳是否存在,如果存在,那么直接按照时间戳去取,否则默认从当前最后一个位置进行消费。
// 如果没有指定binlogName,尝试按照timestamp进行查找
if (entryPosition.getTimestamp() != null && entryPosition.getTimestamp() > 0L) {
logger.warn("prepare to find start position {}:{}:{}",
new Object[] { "", "", entryPosition.getTimestamp() });
return findByStartTimeStamp(mysqlConnection, entryPosition.getTimestamp());
} else {
logger.warn("prepare to find start position just show master status");
return findEndPositionWithMasterIdAndTimestamp(mysqlConnection); // 默认从当前最后一个位置进行消费
}这块我们看下findByStartTimestamp()这个方法,也就是只根据时间来查找binlog。这块的逻辑是这样的:
- 首先获取最新和最老的binlog文件
- 从最新的binlog中,根据时间去找,调用的方法也是findAsPerTimestampInSpecificLogFile()
- 如果已经从最新的到最老的binlog文件中找遍了,没找到,说明根本没有对应时间的binlog
- 否则不断的遍历binlog文件,因为binlog文件名的后缀都是连续的,所以可以很快的寻找
2.2.1.5
binlog文件名不为空,首先判断是否有位点信息,如果有的话,直接根据当前内存中存储的位点和文件信息去Mysql获取。
否则,根据当前内存中管理的时间戳去获取,根据时间戳和binlog文件名去获取位点。当然,如果时间戳也不存在,直接从binlog文件名的文件开头去获取binlog。
2.2.2 内存中存在历史成功记录
2.2.2.1 内存中的位点信息对应的数据库ip和当前连接的ip一致
如果dump错误的次数超过了一定的阈值,默认是2次,也就是连续几次定位失败,有几种情况:
- binlog位点被删除
- vip模式的mysql,发生了主备切换
这种需要进行一次判断,判断内容:
boolean case2 = (standbyInfo == null || standbyInfo.getAddress() == null)
&& logPosition.getPostion().getServerId() != null
&& !logPosition.getPostion().getServerId().equals(findServerId(mysqlConnection));判断几个,第一个配置文件中的standby为空,第二个内存中的logPosition存在数据库ip,第三个内存中的logPosition的数据库ip和当前数据库连接connection的数据库ip不一致。
满足这三个条件,说明发生了vip的主备切换,此时需要把logPosition中的时间戳向前推一个回退时间,默认60s,然后根据新的时间戳去找binlog文件和位点信息。
if (case2) {
long timestamp = logPosition.getPostion().getTimestamp();
long newStartTimestamp = timestamp - fallbackIntervalInSeconds * 1000;
logger.warn("prepare to find start position by last position {}:{}:{}", new Object[] { "", "",
logPosition.getPostion().getTimestamp() });
EntryPosition findPosition = findByStartTimeStamp(mysqlConnection, newStartTimestamp);
// 重新置为一下
dumpErrorCount = 0;
return findPosition;
}2.2.2.2 不一致的情况
说明发生了主从切换,这种情况下,直接把logPosition中的时间回退60s,然后根据回退后的时间去binlog中寻找,然后返回。