LLVM PASS 分析【1】:Rotate Loops
1. Introduction
1.1 循环相关概念
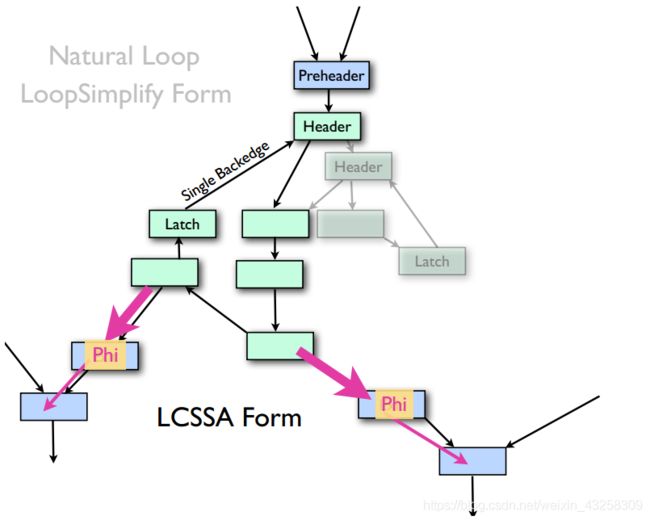
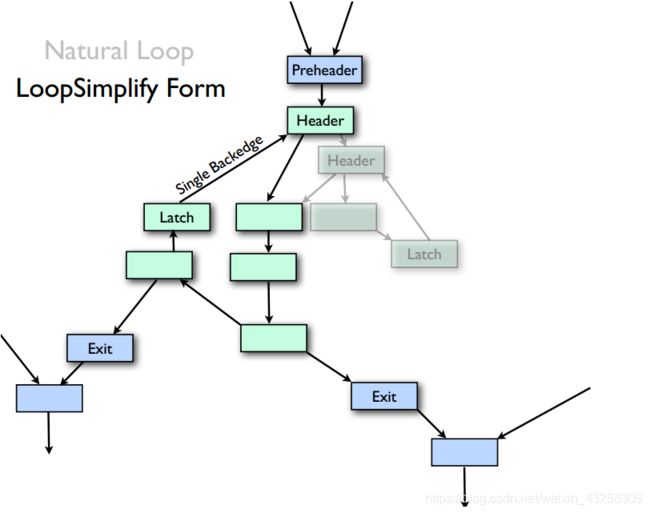
通常情况下,一个Natural Loop(自然循环),有一个Entry Block(Header)和几个指向Header的回边的基本快(Latch),常常几个Latch共享一个Header. 实际上这种Loop结构是不方便后续的处理,常常需要简化成只有一个Latch的结构,在loop exit 之前增加加入一个PHI节点,这个loop形式又叫做Loop-closed SSA form,简称(LCSSA).

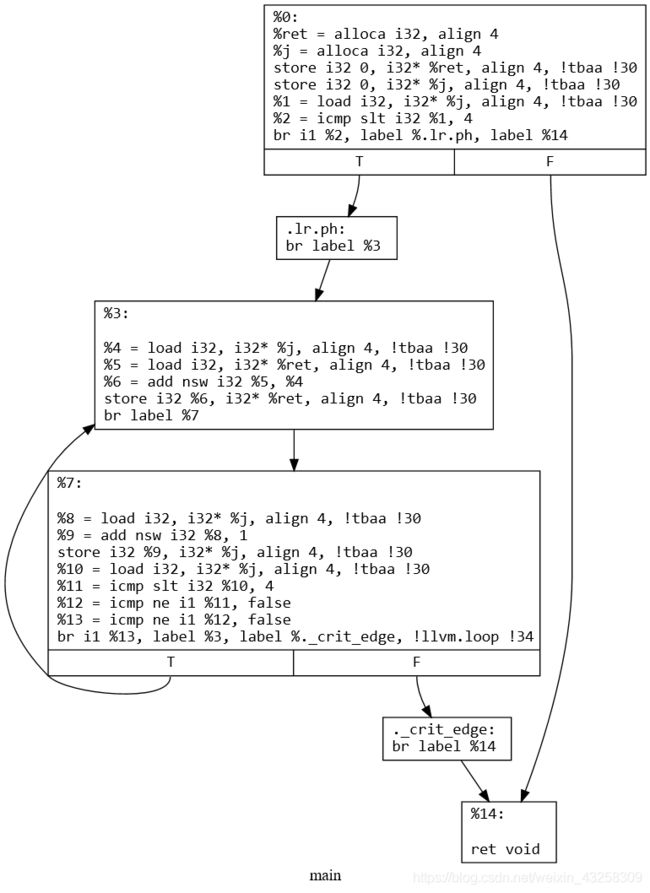
1.2 Loop Rotate 可视化
源代码
void main() {
int ret = 0;
for( int j = 0; j < 4; j++ ) {
ret += j;
}
}
for只是一个语法糖,实际是下面的执行顺序
void main() {
int ret = 0; | 基本块 0 PreHeader
int j = 0; | 基本块 0 PreHeader
while(j < 4){
| 基本块 1 Header
ret += j; | 基本块 2
j++; | 基本块 3 Latch
}
return ; | 基本块 4 Exit
}
转换前CFG

Loop Rotate 将执行顺序改编为 if-do-while结构,从CFG图里面可以看出,直觉上可以看出,Rotate以后的,通过插入前后两个基本块,使得循环主体变得相对独立,也就是Loop-closed。
void main() {
int ret = 0; | 基本块 0
int j = 0; | 基本块 0
if(j<4) | 基本块 0
{
do{
ret += j; | 基本块 1 Header
j++; | 基本块 1 Header
}while(j<4); | 基本块 2 Latch
}
return 0; | 基本块 3 Exit
}
2. 源码分析
Rotate Loops相关文件有:
llvm-9.0.0.src\lib\Transforms\Scalar\LoopRotation.cpp
llvm-9.0.0.src\include\llvm\Transforms\Scalar\LoopRotation.h
llvm-9.0.0.src\lib\Transforms\Utils\LoopRotationUtils.cpp
llvm-9.0.0.src\include\llvm\Transforms\Utils\LoopRotationUtils.h
LoopRotation.cpp 是Pass相关代码,
LoopRotationUtils.cpp 是真正Loops Rotate 动作的代码。
2.1 Pass 相关代码
初始化:
char LoopRotateLegacyPass::ID = 0;
INITIALIZE_PASS_BEGIN(LoopRotateLegacyPass, "loop-rotate", "Rotate Loops",false, false)
INITIALIZE_PASS_DEPENDENCY(AssumptionCacheTracker)
INITIALIZE_PASS_DEPENDENCY(LoopPass)
INITIALIZE_PASS_DEPENDENCY(TargetTransformInfoWrapperPass)
INITIALIZE_PASS_DEPENDENCY(MemorySSAWrapperPass)
INITIALIZE_PASS_END(LoopRotateLegacyPass, "loop-rotate", "Rotate Loops", false,false)
Pass *llvm::createLoopRotatePass(int MaxHeaderSize) {
return new LoopRotateLegacyPass(MaxHeaderSize);
}
从初始化相关代码可以看出,LoopRotateLegacyPass依赖于AssumptionCacheTracker,LoopPass,TargetTransformInfoWrapperPass,MemorySSAWrapperPass这几个Pass的分析结果。
LoopRotateLegacyPass:
class LoopRotateLegacyPass : public LoopPass {
unsigned MaxHeaderSize;
public:
static char ID; // Pass ID, replacement for typeid
LoopRotateLegacyPass(int SpecifiedMaxHeaderSize = -1) : LoopPass(ID) {
initializeLoopRotateLegacyPassPass(*PassRegistry::getPassRegistry());
if (SpecifiedMaxHeaderSize == -1)
MaxHeaderSize = DefaultRotationThreshold;
else
MaxHeaderSize = unsigned(SpecifiedMaxHeaderSize);
}
// LCSSA form makes instruction renaming easier.
void getAnalysisUsage(AnalysisUsage &AU) const override {
AU.addRequired<AssumptionCacheTracker>();
AU.addRequired<TargetTransformInfoWrapperPass>();
if (EnableMSSALoopDependency) {
AU.addRequired<MemorySSAWrapperPass>();
AU.addPreserved<MemorySSAWrapperPass>();
}
getLoopAnalysisUsage(AU);
}
- LoopRotateLegacyPass 是一个Loop Pass.
- 分析强制依赖于AssumptionCacheTracker,TargetTransformInfoWrapperPass。
- 根据EnableMSSALoopDependency开关,决定需不需要MemorySSAWrapperPass。
- MaxHeaderSize: 代表
runOnLoop:
bool runOnLoop(Loop *L, LPPassManager &LPM) override {
if (skipLoop(L))
return false;
Function &F = *L->getHeader()->getParent();
auto *LI = &getAnalysis<LoopInfoWrapperPass>().getLoopInfo();
const auto *TTI = &getAnalysis<TargetTransformInfoWrapperPass>().getTTI(F);
auto *AC = &getAnalysis<AssumptionCacheTracker>().getAssumptionCache(F);
auto *DTWP = getAnalysisIfAvailable<DominatorTreeWrapperPass>();
auto *DT = DTWP ? &DTWP->getDomTree() : nullptr;
auto *SEWP = getAnalysisIfAvailable<ScalarEvolutionWrapperPass>();
auto *SE = SEWP ? &SEWP->getSE() : nullptr;
const SimplifyQuery SQ = getBestSimplifyQuery(*this, F);
Optional<MemorySSAUpdater> MSSAU;
if (EnableMSSALoopDependency) {
MemorySSA *MSSA = &getAnalysis<MemorySSAWrapperPass>().getMSSA();
MSSAU = MemorySSAUpdater(MSSA);
}
return LoopRotation(L, LI, TTI, AC, DT, SE,
MSSAU.hasValue() ? MSSAU.getPointer() : nullptr, SQ,
false, MaxHeaderSize, false);
}
};
- runOnLoop(),主要获取LoopRotation需要的相关依赖信息,包括LoopInfo,TargetTransformInfo,AssumptionCacheTracker,DominatorTree,ScalarEvolution,MemorySSA(可选)并调用LoopRotation(LoopRotationUtils.cpp)构造函数。
2.2 Loops Rotate 动作相关代码
LoopRotation 类:
class LoopRotate {
const unsigned MaxHeaderSize;
LoopInfo *LI;
const TargetTransformInfo *TTI;
AssumptionCache *AC;
DominatorTree *DT;
ScalarEvolution *SE;
MemorySSAUpdater *MSSAU;
const SimplifyQuery &SQ;
bool RotationOnly;
bool IsUtilMode;
public:
LoopRotate(unsigned MaxHeaderSize, LoopInfo *LI,
const TargetTransformInfo *TTI, AssumptionCache *AC,
DominatorTree *DT, ScalarEvolution *SE, MemorySSAUpdater *MSSAU,
const SimplifyQuery &SQ, bool RotationOnly, bool IsUtilMode)
: MaxHeaderSize(MaxHeaderSize), LI(LI), TTI(TTI), AC(AC), DT(DT), SE(SE),
MSSAU(MSSAU), SQ(SQ), RotationOnly(RotationOnly),
IsUtilMode(IsUtilMode) {
}
bool processLoop(Loop *L);
private:
bool rotateLoop(Loop *L, bool SimplifiedLatch);
bool simplifyLoopLatch(Loop *L);
};
从类的public接口来看,processLoop应该真正的处理循环,决定整个rotate动作处理流程,Private的接口,应该是这个流程的分解。
processLoop:
bool LoopRotate::processLoop(Loop *L) {
// Save the loop metadata.
MDNode *LoopMD = L->getLoopID();
bool SimplifiedLatch = false;
// Simplify the loop latch before attempting to rotate the header
// upward. Rotation may not be needed if the loop tail can be folded into the
// loop exit.
if (!RotationOnly)
SimplifiedLatch = simplifyLoopLatch(L);
bool MadeChange = rotateLoop(L, SimplifiedLatch);
assert((!MadeChange || L->isLoopExiting(L->getLoopLatch())) &&
"Loop latch should be exiting after loop-rotate.");
// Restore the loop metadata.
// NB! We presume LoopRotation DOESN'T ADD its own metadata.
if ((MadeChange || SimplifiedLatch) && LoopMD)
L->setLoopID(LoopMD);
return MadeChange || SimplifiedLatch;
}
processLoop 先简化simplifyLoopLatch,最后真正的rotateLoop,将信息保存,还回值表示是否rotateLoop成功。
simplifyLoopLatch:
bool LoopRotate::simplifyLoopLatch(Loop *L) {
BasicBlock *Latch = L->getLoopLatch();
if (!Latch || Latch->hasAddressTaken())
return false;
BranchInst *Jmp = dyn_cast<BranchInst>(Latch->getTerminator());
if (!Jmp || !Jmp->isUnconditional())
return false;
BasicBlock *LastExit = Latch->getSinglePredecessor();
if (!LastExit || !L->isLoopExiting(LastExit))
return false;
BranchInst *BI = dyn_cast<BranchInst>(LastExit->getTerminator());
if (!BI)
return false;
if (!shouldSpeculateInstrs(Latch->begin(), Jmp->getIterator(), L))
return false;
LLVM_DEBUG(dbgs() << "Folding loop latch " << Latch->getName() << " into "
<< LastExit->getName() << "\n");
// Hoist the instructions from Latch into LastExit.
Instruction *FirstLatchInst = &*(Latch->begin());
LastExit->getInstList().splice(BI->getIterator(), Latch->getInstList(),
Latch->begin(), Jmp->getIterator());
// Update MemorySSA
if (MSSAU)
MSSAU->moveAllAfterMergeBlocks(Latch, LastExit, FirstLatchInst);
unsigned FallThruPath = BI->getSuccessor(0) == Latch ? 0 : 1;
BasicBlock *Header = Jmp->getSuccessor(0);
assert(Header == L->getHeader() && "expected a backward branch");
// Remove Latch from the CFG so that LastExit becomes the new Latch.
BI->setSuccessor(FallThruPath, Header);
Latch->replaceSuccessorsPhiUsesWith(LastExit);
Jmp->eraseFromParent();
// Nuke the Latch block.
assert(Latch->empty() && "unable to evacuate Latch");
LI->removeBlock(Latch);
if (DT)
DT->eraseNode(Latch);
Latch->eraseFromParent();
if (MSSAU && VerifyMemorySSA)
MSSAU->getMemorySSA()->verifyMemorySSA();
return true;
}
rotateLoop:
/// Rotate loop LP. Return true if the loop is rotated.
///
/// \param SimplifiedLatch is true if the latch was just folded into the final
/// loop exit. In this case we may want to rotate even though the new latch is
/// now an exiting branch. This rotation would have happened had the latch not
/// been simplified. However, if SimplifiedLatch is false, then we avoid
/// rotating loops in which the latch exits to avoid excessive or endless
/// rotation. LoopRotate should be repeatable and converge to a canonical
/// form. This property is satisfied because simplifying the loop latch can only
/// happen once across multiple invocations of the LoopRotate pass.
bool LoopRotate::rotateLoop(Loop *L, bool SimplifiedLatch) {
// If the loop has only one block then there is not much to rotate.
if (L->getBlocks().size() == 1)
return false;
BasicBlock *OrigHeader = L->getHeader();
BasicBlock *OrigLatch = L->getLoopLatch();
BranchInst *BI = dyn_cast<BranchInst>(OrigHeader->getTerminator());
if (!BI || BI->isUnconditional())
return false;
// If the loop header is not one of the loop exiting blocks then
// either this loop is already rotated or it is not
// suitable for loop rotation transformations.
if (!L->isLoopExiting(OrigHeader))
return false;
// If the loop latch already contains a branch that leaves the loop then the
// loop is already rotated.
if (!OrigLatch)
return false;
// Rotate if either the loop latch does *not* exit the loop, or if the loop
// latch was just simplified. Or if we think it will be profitable.
if (L->isLoopExiting(OrigLatch) && !SimplifiedLatch && IsUtilMode == false &&
!shouldRotateLoopExitingLatch(L))
return false;
// Check size of original header and reject loop if it is very big or we can't
// duplicate blocks inside it.
{
SmallPtrSet<const Value *, 32> EphValues;
CodeMetrics::collectEphemeralValues(L, AC, EphValues);
CodeMetrics Metrics;
Metrics.analyzeBasicBlock(OrigHeader, *TTI, EphValues);
if (Metrics.notDuplicatable) {
LLVM_DEBUG(
dbgs() << "LoopRotation: NOT rotating - contains non-duplicatable"
<< " instructions: ";
L->dump());
return false;
}
if (Metrics.convergent) {
LLVM_DEBUG(dbgs() << "LoopRotation: NOT rotating - contains convergent "
"instructions: ";
L->dump());
return false;
}
if (Metrics.NumInsts > MaxHeaderSize)
return false;
}
// Now, this loop is suitable for rotation.
BasicBlock *OrigPreheader = L->getLoopPreheader();
// If the loop could not be converted to canonical form, it must have an
// indirectbr in it, just give up.
if (!OrigPreheader || !L->hasDedicatedExits())
return false;
// Anything ScalarEvolution may know about this loop or the PHI nodes
// in its header will soon be invalidated. We should also invalidate
// all outer loops because insertion and deletion of blocks that happens
// during the rotation may violate invariants related to backedge taken
// infos in them.
if (SE)
SE->forgetTopmostLoop(L);
LLVM_DEBUG(dbgs() << "LoopRotation: rotating "; L->dump());
if (MSSAU && VerifyMemorySSA)
MSSAU->getMemorySSA()->verifyMemorySSA();
// Find new Loop header. NewHeader is a Header's one and only successor
// that is inside loop. Header's other successor is outside the
// loop. Otherwise loop is not suitable for rotation.
BasicBlock *Exit = BI->getSuccessor(0);
BasicBlock *NewHeader = BI->getSuccessor(1);
if (L->contains(Exit))
std::swap(Exit, NewHeader);
assert(NewHeader && "Unable to determine new loop header");
assert(L->contains(NewHeader) && !L->contains(Exit) &&
"Unable to determine loop header and exit blocks");
// This code assumes that the new header has exactly one predecessor.
// Remove any single-entry PHI nodes in it.
assert(NewHeader->getSinglePredecessor() &&
"New header doesn't have one pred!");
FoldSingleEntryPHINodes(NewHeader);
// Begin by walking OrigHeader and populating ValueMap with an entry for
// each Instruction.
BasicBlock::iterator I = OrigHeader->begin(), E = OrigHeader->end();
ValueToValueMapTy ValueMap, ValueMapMSSA;
// For PHI nodes, the value available in OldPreHeader is just the
// incoming value from OldPreHeader.
for (; PHINode *PN = dyn_cast<PHINode>(I); ++I)
ValueMap[PN] = PN->getIncomingValueForBlock(OrigPreheader);
// For the rest of the instructions, either hoist to the OrigPreheader if
// possible or create a clone in the OldPreHeader if not.
Instruction *LoopEntryBranch = OrigPreheader->getTerminator();
// Record all debug intrinsics preceding LoopEntryBranch to avoid duplication.
using DbgIntrinsicHash =
std::pair<std::pair<Value *, DILocalVariable *>, DIExpression *>;
auto makeHash = [](DbgVariableIntrinsic *D) -> DbgIntrinsicHash {
return {
{
D->getVariableLocation(), D->getVariable()}, D->getExpression()};
};
SmallDenseSet<DbgIntrinsicHash, 8> DbgIntrinsics;
for (auto I = std::next(OrigPreheader->rbegin()), E = OrigPreheader->rend();
I != E; ++I) {
if (auto *DII = dyn_cast<DbgVariableIntrinsic>(&*I))
DbgIntrinsics.insert(makeHash(DII));
else
break;
}
while (I != E) {
Instruction *Inst = &*I++;
// If the instruction's operands are invariant and it doesn't read or write
// memory, then it is safe to hoist. Doing this doesn't change the order of
// execution in the preheader, but does prevent the instruction from
// executing in each iteration of the loop. This means it is safe to hoist
// something that might trap, but isn't safe to hoist something that reads
// memory (without proving that the loop doesn't write).
if (L->hasLoopInvariantOperands(Inst) && !Inst->mayReadFromMemory() &&
!Inst->mayWriteToMemory() && !Inst->isTerminator() &&
!isa<DbgInfoIntrinsic>(Inst) && !isa<AllocaInst>(Inst)) {
Inst->moveBefore(LoopEntryBranch);
continue;
}
// Otherwise, create a duplicate of the instruction.
Instruction *C = Inst->clone();
// Eagerly remap the operands of the instruction.
RemapInstruction(C, ValueMap,
RF_NoModuleLevelChanges | RF_IgnoreMissingLocals);
// Avoid inserting the same intrinsic twice.
if (auto *DII = dyn_cast<DbgVariableIntrinsic>(C))
if (DbgIntrinsics.count(makeHash(DII))) {
C->deleteValue();
continue;
}
// With the operands remapped, see if the instruction constant folds or is
// otherwise simplifyable. This commonly occurs because the entry from PHI
// nodes allows icmps and other instructions to fold.
Value *V = SimplifyInstruction(C, SQ);
if (V && LI->replacementPreservesLCSSAForm(C, V)) {
// If so, then delete the temporary instruction and stick the folded value
// in the map.
ValueMap[Inst] = V;
if (!C->mayHaveSideEffects()) {
C->deleteValue();
C = nullptr;
}
} else {
ValueMap[Inst] = C;
}
if (C) {
// Otherwise, stick the new instruction into the new block!
C->setName(Inst->getName());
C->insertBefore(LoopEntryBranch);
if (auto *II = dyn_cast<IntrinsicInst>(C))
if (II->getIntrinsicID() == Intrinsic::assume)
AC->registerAssumption(II);
// MemorySSA cares whether the cloned instruction was inserted or not, and
// not whether it can be remapped to a simplified value.
ValueMapMSSA[Inst] = C;
}
}
// Along with all the other instructions, we just cloned OrigHeader's
// terminator into OrigPreHeader. Fix up the PHI nodes in each of OrigHeader's
// successors by duplicating their incoming values for OrigHeader.
for (BasicBlock *SuccBB : successors(OrigHeader))
for (BasicBlock::iterator BI = SuccBB->begin();
PHINode *PN = dyn_cast<PHINode>(BI); ++BI)
PN->addIncoming(PN->getIncomingValueForBlock(OrigHeader), OrigPreheader);
// Now that OrigPreHeader has a clone of OrigHeader's terminator, remove
// OrigPreHeader's old terminator (the original branch into the loop), and
// remove the corresponding incoming values from the PHI nodes in OrigHeader.
LoopEntryBranch->eraseFromParent();
// Update MemorySSA before the rewrite call below changes the 1:1
// instruction:cloned_instruction_or_value mapping.
if (MSSAU) {
ValueMapMSSA[OrigHeader] = OrigPreheader;
MSSAU->updateForClonedBlockIntoPred(OrigHeader, OrigPreheader,
ValueMapMSSA);
}
SmallVector<PHINode*, 2> InsertedPHIs;
// If there were any uses of instructions in the duplicated block outside the
// loop, update them, inserting PHI nodes as required
RewriteUsesOfClonedInstructions(OrigHeader, OrigPreheader, ValueMap,
&InsertedPHIs);
// Attach dbg.value intrinsics to the new phis if that phi uses a value that
// previously had debug metadata attached. This keeps the debug info
// up-to-date in the loop body.
if (!InsertedPHIs.empty())
insertDebugValuesForPHIs(OrigHeader, InsertedPHIs);
// NewHeader is now the header of the loop.
L->moveToHeader(NewHeader);
assert(L->getHeader() == NewHeader && "Latch block is our new header");
// Inform DT about changes to the CFG.
if (DT) {
// The OrigPreheader branches to the NewHeader and Exit now. Then, inform
// the DT about the removed edge to the OrigHeader (that got removed).
SmallVector<DominatorTree::UpdateType, 3> Updates;
Updates.push_back({
DominatorTree::Insert, OrigPreheader, Exit});
Updates.push_back({
DominatorTree::Insert, OrigPreheader, NewHeader});
Updates.push_back({
DominatorTree::Delete, OrigPreheader, OrigHeader});
DT->applyUpdates(Updates);
if (MSSAU) {
MSSAU->applyUpdates(Updates, *DT);
if (VerifyMemorySSA)
MSSAU->getMemorySSA()->verifyMemorySSA();
}
}
// At this point, we've finished our major CFG changes. As part of cloning
// the loop into the preheader we've simplified instructions and the
// duplicated conditional branch may now be branching on a constant. If it is
// branching on a constant and if that constant means that we enter the loop,
// then we fold away the cond branch to an uncond branch. This simplifies the
// loop in cases important for nested loops, and it also means we don't have
// to split as many edges.
BranchInst *PHBI = cast<BranchInst>(OrigPreheader->getTerminator());
assert(PHBI->isConditional() && "Should be clone of BI condbr!");
if (!isa<ConstantInt>(PHBI->getCondition()) ||
PHBI->getSuccessor(cast<ConstantInt>(PHBI->getCondition())->isZero()) !=
NewHeader) {
// The conditional branch can't be folded, handle the general case.
// Split edges as necessary to preserve LoopSimplify form.
// Right now OrigPreHeader has two successors, NewHeader and ExitBlock, and
// thus is not a preheader anymore.
// Split the edge to form a real preheader.
BasicBlock *NewPH = SplitCriticalEdge(
OrigPreheader, NewHeader,
CriticalEdgeSplittingOptions(DT, LI, MSSAU).setPreserveLCSSA());
NewPH->setName(NewHeader->getName() + ".lr.ph");
// Preserve canonical loop form, which means that 'Exit' should have only
// one predecessor. Note that Exit could be an exit block for multiple
// nested loops, causing both of the edges to now be critical and need to
// be split.
SmallVector<BasicBlock *, 4> ExitPreds(pred_begin(Exit), pred_end(Exit));
bool SplitLatchEdge = false;
for (BasicBlock *ExitPred : ExitPreds) {
// We only need to split loop exit edges.
Loop *PredLoop = LI->getLoopFor(ExitPred);
if (!PredLoop || PredLoop->contains(Exit) ||
ExitPred->getTerminator()->isIndirectTerminator())
continue;
SplitLatchEdge |= L->getLoopLatch() == ExitPred;
BasicBlock *ExitSplit = SplitCriticalEdge(
ExitPred, Exit,
CriticalEdgeSplittingOptions(DT, LI, MSSAU).setPreserveLCSSA());
ExitSplit->moveBefore(Exit);
}
assert(SplitLatchEdge &&
"Despite splitting all preds, failed to split latch exit?");
} else {
// We can fold the conditional branch in the preheader, this makes things
// simpler. The first step is to remove the extra edge to the Exit block.
Exit->removePredecessor(OrigPreheader, true /*preserve LCSSA*/);
BranchInst *NewBI = BranchInst::Create(NewHeader, PHBI);
NewBI->setDebugLoc(PHBI->getDebugLoc());
PHBI->eraseFromParent();
// With our CFG finalized, update DomTree if it is available.
if (DT) DT->deleteEdge(OrigPreheader, Exit);
// Update MSSA too, if available.
if (MSSAU)
MSSAU->removeEdge(OrigPreheader, Exit);
}
assert(L->getLoopPreheader() && "Invalid loop preheader after loop rotation");
assert(L->getLoopLatch() && "Invalid loop latch after loop rotation");
if (MSSAU && VerifyMemorySSA)
MSSAU->getMemorySSA()->verifyMemorySSA();
// Now that the CFG and DomTree are in a consistent state again, try to merge
// the OrigHeader block into OrigLatch. This will succeed if they are
// connected by an unconditional branch. This is just a cleanup so the
// emitted code isn't too gross in this common case.
DomTreeUpdater DTU(DT, DomTreeUpdater::UpdateStrategy::Eager);
MergeBlockIntoPredecessor(OrigHeader, &DTU, LI, MSSAU);
if (MSSAU && VerifyMemorySSA)
MSSAU->getMemorySSA()->verifyMemorySSA();
LLVM_DEBUG(dbgs() << "LoopRotation: into "; L->dump());
++NumRotated; // NumRotated这个是STATICS宏表达的次数,用于统计信息
return true;
3. 参考资料
[1] llvm-9.0.0源码
[2] https://www.llvm.org/devmtg/2009-10/ScalarEvolutionAndLoopOptimization.pdf
[3] https://reviews.llvm.org/D22630