史上最详 Thymeleaf 使用教程
史上最详 Thymeleaf 使用教程
-
- 前言
- 基础语法
-
- 文本标签 th:text/th:utext
- 字符串拼接
- *{...}和 ${...}表达式
- #{...}表达式
- ~{...}片段表达式
- @{...}链接网址表达式
- 条件判断 th:if/th:unless
- switch
- for循环
- th:href
- th:class
- th:attr
- th:value
- th:action
- th:id
- th:inline
- th:onclick
- th:selected
- th:src
- th:style
- th:with
- Elvis运算符
- 三元表达式
- No-Operation(_)什么都不做
- 内联
-
- 如何使用内连操作
- 禁用内联操作
- JavaScript内联
- CSS内联
- 模板布局
-
- 定义引用片段代码
- 通过id属性来声明片段
- th:insert和th:replace(和th:include)之间的区别
- 带参数的引用片段
- 删除模版片段
- 预定义的工具对象
-
- #dates
- #numbers
- #strings
- #bools
- #arrays
- #lists
- #sets
- #maps
- #aggregates
- 小结
- 代码示例
- 参考文献:
前言
操作前建议先参考我的另一篇博客:玩转 SpringBoot 2 快速整合 | Thymeleaf 篇 查看如何在SpringBoot 中使用 Thymeleaf。还有一点需要注意的是:模版页面中的 html 上需要声明 Thymeleaf 的命名空间,具体代码如下:
<html xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
接下来就可以开始 Thymeleaf 使用教程了!
全文介绍 Thymeleaf 是基于 Thymeleaf 3.0.11.RELEASE 版本进行说明的。
基础语法
文本标签 th:text/th:utext
用于文本内容的显示操作。
- th:text 进行文本替换 不会解析html
- th:utext 进行文本替换 会解析html
代码演示:
@RequestMapping("/th")
public String th(Model model){
String msg = "我是h1
";
model.addAttribute("msg",msg);
return "/course/th";
}
th:text 进行文本替换 不会解析html
<p th:text="text标签: + ${msg}">p>
结果页面:
<p>text标签:<h1>我是h1h1>p>
游览器访问的效果:
![]()
th:utext 进行文本替换 会解析html
<p th:utext="utext标签: + ${msg}">p>
游览器展示效果如下图:

使用 + 和 | | 效果是一样的,如下代码所示:
<p th:utext="utext标签: + ${msg}">p>
<p th:utext="|utext标签: ${msg}|">p>
字符串拼接
拼接字符串通过 + 或者 | 进行拼接
代码演示:
@RequestMapping("/th")
public String th(Model model){
model.addAttribute("a",1);
model.addAttribute("b",2);
return "/course/th";
}
模版页面:
<p th:text="${a}+${b}">p>
结果页面:
<p>3p>
模版页面:
<p th:text="|${a} ${b}|">p>
结果页面:
<p>1 2p>
模版页面:
<p th:text="${a} > ${b}">p>
结果是:
<p>falsep>
java代码:
@RequestMapping("/th")
public String th(Model model){
model.addAttribute("flag",true);
return "/course/th";
}
模版页面:
<p th:text="!${flag}">p>
结果页面:
<p>falsep>
*{…}和 ${…}表达式
正常情况下 *{…} 和 ${…}是一样的,但是 *{…} 一般和 th:object 进行一起使用来完成对象属性的简写。
代码演示:
@RequestMapping("/th")
public String th(Model model){
User user = new User("ljk",18);
model.addAttribute("user",user);
return "/course/th";
}
使用 ${…}操作
模版代码:
<p th:text="${user.name}">p>
<p th:text="${user.age}">p>
结果页面:
<p>ljkp><p>18p>
*使用 {…}操作
模版代码:
<p th:text="*{user.name}">p>
<p th:text="*{user.age}">p>
结果页面:
<p>ljkp><p>18p>
*使用 {…}特有操作
模版代码:
<div th:object="${user}" >
<p th:text="*{name}">p>
<p th:text="*{age}">p>
div>
结果页面:
<p>ljkp><p>18p>
#{…}表达式
用于国际化message.properties 属性读取
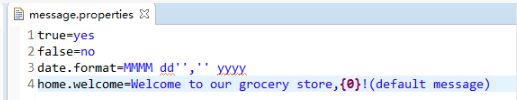
定义message.properties 配置文件
定义国际化处理转换处理类
@Configuration
public class LocaleResolverConfig {
@Bean(name="localeResolver")
public LocaleResolver localeResolverBean() {
return new SessionLocaleResolver();
}
}
定义国际化处理的controller
@Controller
public class ProductController {
@Autowired
private LocaleResolver localeResolver;
private ProductService productService = new ProductService();
@RequestMapping("/")
public String useT(Model model,HttpServletRequest request,HttpServletResponse response) {
//设置访问用户信息到session
request.getSession(true).setAttribute("user", new User("桌前", "明月", "CHINA", null));
localeResolver.setLocale(request,response,Locale.CHINA);
return "productList";
}
}
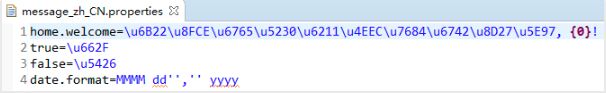
如果没有定义 message_en_US.properties 和 message_zh_CN.properties 会默认取message.properties中的信息
如果 Locale = Locale.CHINA 就取 message_zh_CN.properties
如果 Locale = Locale.US 就取 message_en_US.properties。
模版代码:
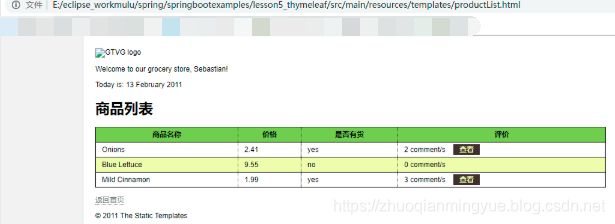
<p th:utext="#{home.welcome(${session.user.name})}">Welcome to our grocery store, Sebastian!p>
~{…}片段表达式
这个一般和模版布局的语法一起使用,具体使用方式请看下面模版布局的教程。
@{…}链接网址表达式
一般和 th:href、th:src进行结合使用,用于显示Web 应用中的URL链接。通过@{…}表达式Thymeleaf 可以帮助我们拼接上web应用访问的全路径,同时我们可以通过()进行参数的拼接
代码演示:
模版代码:
<img th:src="@{/images/gtvglogo.png}" />
结果页面:
<img src="/sbe/images/gtvglogo.png">
模版代码:
<a th:href="@{/product/comments(prodId=${prod.id})}" >查看a>
结果页面:
<a href="/sbe/product/comments?prodId=2">查看a>
模版代码:
<a th:href="@{/product/comments(prodId=${prod.id},prodId2=${prod.id})}" >查看a>
结果页面:
<a href="/sbe/product/comments?prodId=2&prodId2=2">查看a>
条件判断 th:if/th:unless
th:if 当条件为true则显示。
th:unless 当条件为false 则显示。
代码演示:
java代码:
@RequestMapping("/thif")
public String thif(Model model){
model.addAttribute("flag",true);
return "/course/thif";
}
模版页面:
<p th:if="${flag}">if判断p>
结果页面:
<p>if判断p>
模版页面:
<p th:unless="!${flag}">unless 判断p>
结果页面:
<p>unless 判断p>
switch
th:switch 我们可以通过switch来完成类似的条件表达式的操作。
代码演示:
java代码:
@RequestMapping("/thswitch")
public String thswitch(Model model){
User user = new User("ljk",23);
model.addAttribute("user",user);
return "/course/thswitch";
}
模版页面:
<div th:switch="${user.name}">
<p th:case="'ljk'">User is ljkp>
<p th:case="ljk1">User is ljk1p>
div>
结果页面:
<div><p> User is ljkp>div>
for循环
th:each 遍历集合
代码演示:
java代码:
@RequestMapping("/theach")
public String theach(Model model){
List<User> userList = new ArrayList<User>();
User user1 = new User("ljk",18);
User user2 = new User("ljk2",19);
User user3 = new User("ljk3",20);
User user4 = new User("lj4",21);
userList.add(user1);
userList.add(user2);
userList.add(user3);
userList.add(user4);
model.addAttribute("userList",userList);
List<String> strList = new ArrayList<String>();
strList.add("ljk");
strList.add("ljk2");
strList.add("ljk3");
strList.add("lj4");
model.addAttribute("strList",strList);
return "/course/theach";
}
模版页面:
<table>
<thead>
<tr>
<th>用户名称th>
<th>用户年龄th>
tr>
thead>
<tbody>
<tr th:each="user : ${userList}" th:class="${userStat.odd}? 'odd'">
<td th:text="${user.name}">Onionstd>
<td th:text="${user.age}">2.41td>
tr>
tbody>
table>
----------------------------------------------------------------------
<table>
<thead>
<tr>
<th>用户名称th>
tr>
thead>
<tbody>
<tr th:each="str : ${strList}" th:class="${strStat.odd}? 'odd'">
<td th:text="${str}">Onionstd>
tr>
tbody>
table>
我们可以通过便利的变量名+Stat 来获取索引 是否是第一个或最后一个等。
便利的变量名+Stat称作状态变量,其属性有:
- index:当前迭代对象的迭代索引,从0开始,这是索引属性;
- count:当前迭代对象的迭代索引,从1开始,这个是统计属性;
- size:迭代变量元素的总量,这是被迭代对象的大小属性;
- current:当前迭代变量;
- even/odd:布尔值,当前循环是否是偶数/奇数(从0开始计算);
- first:布尔值,当前循环是否是第一个;
- last:布尔值,当前循环是否是最后一个
for循环介绍内容参考了 CSDN博主liubin5620 Thymeleaf模板引擎常用属性之 th:each迭代循环:https://blog.csdn.net/liubin5620/article/details/80470619
th:href
用于声明在a 标签上的href属性的链接 该语法会和@{…} 表达式一起使用。
代码演示:
java代码:
@RequestMapping("/thhref")
public String thhref(Model model){
return "/course/thhref";
}
模版代码:
<a href="../home.html" th:href="@{/}">返回首页a>
结果页面:
<a href="/sbe/">返回首页a>
th:class
用于声明在标签上class 属性信息。
代码演示:
java代码:
@RequestMapping("/thclass")
public String thclass(Model model){
return "/course/thclass";
}
模版页面:
<p th:class=" 'even'? 'even' : 'odd'" th:text=" 'even'? 'even' : 'odd'">p>
结果页面:
<p class="even">evenp>
th:attr
用于声明html中或自定义属性信息。
代码演示:
java代码:
@RequestMapping("/thattr")
public String thattr(Model model){
return "/course/thattr";
}
模版页面:
<img th:attr="src=@{/images/gtvglogo.png}" />
结果页面:
<img src="/sbe/images/gtvglogo.png">
th:value
用于声明html中value属性信息。
代码演示:
java代码:
@RequestMapping("/thvalue")
public String thvalue(Model model){
model.addAttribute("name", "ljk");
return "/course/thvalue";
}
模版页面:
<input type="text" th:value="${name}" />
结果页面:
<input type="text" value="ljk">
th:action
用于声明html from标签中action属性信息。
代码演示:
java代码:
@RequestMapping("/thaction")
public String thaction(Model model){
return "/course/thaction";
}
模版页面:
<form action="subscribe.html" th:action="@{/subscribe}">
<input type="text" name="name" value="abc"/>
form>
结果页面:
<form action="/sbe/subscribe">
<input type="text" name="name" value="abc">
form>
th:id
用于声明htm id属性信息。
代码演示:
java代码:
@RequestMapping("/thid")
public String thid(Model model){
model.addAttribute("id", 123);
return "/course/thid";
}
模版页面:
<p th:id="${id}">p>
结果页面:
<p id="123">p>
th:inline
JavaScript内联 操作使用的语法,具体请参考下面内联操作相关介绍
th:onclick
用于声明htm 中的onclick事件。
代码演示:
java代码:
@RequestMapping("/thonclick")
public String honclick(Model model){
return "/course/thonclick";
}
模版页面:
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Insert title heretitle>
<script type="text/javascript">
function showUserInfo(){
alert("i am zhuoqianmingyue!")
}
script>
head>
<body>
<p th:onclick="'showUserInfo()'">点我p>
body>
html>
结果页面:
<p onclick="showUserInfo()">点我p>
th:selected
用于声明htm 中的selected属性信息。
代码演示:
java代码:
@RequestMapping("/thselected")
public String thselected(Model model){
model.addAttribute("sex", 1);
return "/course/thselected";
}
模版页面:
<select>
<option name="sex">option>
<option th:selected="1 == ${sex}">男option>
<option th:selected="0 == ${sex}">女option>
select>
结果页面:
<select>
<option name="sex">option>
<option selected="selected">男option>
<option>女option>
select>
th:src
用于声明htm 中的img中src属性信息。
代码演示:
java代码:
@RequestMapping("/thsrc")
public String thsrc(Model model){
return "/course/thsrc";
}
模版页面:
<img title="GTVG logo" th:src="@{/images/gtvglogo.png}" />
结果页面:
<img title="GTVG logo" src="/sbe/images/gtvglogo.png">
th:style
用于声明htm中的标签 css的样式信息。
代码演示:
java代码:
RequestMapping("/thstyle")
public String thstyle(Model model){
model.addAttribute("isShow", true);
return "/course/thstyle";
}
模版页面:
<p th:style="'display:' + @{
(${
isShow} ? 'none' : 'block')} + ''">p>
结果页面:
<p style="display:none">p>
th:with
用于thymeleaf 模版页面中局部变量定义的使用。
代码演示:
java代码:
@RequestMapping("/thwith")
public String thwith(Model model){
model.addAttribute("today", new Date());
return "/course/thwith";
}
模版页面:
<p th:with="df='dd/MMM/yyyy HH:mm'">
Today is: <span th:text="${#dates.format(today,df)}">13 February 2011span>
p>
结果页面:
<span>02/六月/2019 06:52span>
java代码:
@RequestMapping("/thwith")
public String thwith(Model model){
List<User> users = new ArrayList<User>();
users.add(new User("ljk",18));
users.add(new User("ljk2",18));
model.addAttribute("users",users);
return "/course/thwith";
}
模版页面:
<div th:with="firstEle=${users[0]}">
<p>
第一个用户的名称是: <span th:text="${firstEle.name}">span>.
p>
div>
结果页面:
<div>
<p>
第一个用户的名称是: <span>ljkspan>.
p>
div>
还有一种用法是在模版布局中带参数的引用片段中使用方式如下:
<div th:replace="::frag" th:with="onevar=${value1},twovar=${value2}">
具体演示请参考模版布局中的介绍。
Elvis运算符
Elvis运算可以理解成简单的判断是否为null的三元运算的简写,如果值为nullzhe显示默认值,如果不为null 则显示原有的值。
代码演示:
java代码:
@RequestMapping("/elvis")
public String elvis(Model model){
model.addAttribute("age", null);
return "/course/elvis";
}
模版页面:
<p>Age: <span th:text="${age}?: '年龄为nll'">span>p>
结果页面:
<p>Age: <span>年龄为nllspan>p>
java代码:
@RequestMapping("/elvis")
public String elvis(Model model){
model.addAttribute("age2", 18);
return "/course/elvis";
}
模版页面:
<p>Age2: <span th:text="${age2}?: '年龄为nll'">span>p>
结果页面:
<p>Age2: <span>18span>p>
三元表达式
我们可以在thymeleaf 的语法中使用三元表达式 具体使用方法是在th:x 中通过 表达式?1选项:2选项。
代码演示:
java代码:
@RequestMapping("/threeElementOperation")
public String threeElementOperation(Model model){
return "/course/threeElementOperation";
}
模版页面:
<p th:class=" 'even'? 'even' : 'odd'" th:text=" 'even'? 'even' : 'odd'">p>
结果页面:
<p class="even">evenp>
java代码:
@RequestMapping("/threeElementOperation")
public String threeElementOperation(Model model){
model.addAttribute("name", "ljk");
return "/course/threeElementOperation";
}
模版页面:
<p th:value="${name eq 'ljk' ? '帅哥':'丑男'}" th:text="${name eq 'ljk' ? '帅哥':'丑男'}">p>
结果页面:
<p value="帅哥">帅哥p>
条件表达式操作字符:
gt:great than(大于)
ge:great equal(大于等于)
eq:equal(等于)
lt:less than(小于)
le:less equal(小于等于)
ne:not equal(不等于)
No-Operation(_)什么都不做
Elvis运算符 的一种特殊简写操作,当显示的值为null 是就什么都不做。
代码演示:
java代码:
@RequestMapping("/noOperation")
public String noOperation(Model model){
model.addAttribute("name", null);
return "/course/noOperation";
}
模版页面:
<span th:text="${name} ?: _">no user authenticatedspan>
结果页面:
<span>no user authenticatedspan>
标准方言中存在以下固定值布尔属性:
| th:async | th:autofocus | th:autoplay |
|---|---|---|
| th:checked | th:controls | th:declare |
| th:default | th:defer | th:disabled |
| th:formnovalidate | th:hidden | th:ismap |
| th:loop | th:multiple | th:novalidate |
| th:nowrap | th:open | th:pubdate |
| th:readonly | th:required | th:reversed |
| th:scoped | th:seamless | th:selected |
针对特定的HTML5属性:
| th:abbr | th:accept | th:accept-charset |
|---|---|---|
| th:accesskey | th:action | th:align |
| th:alt | th:archive | th:audio |
| th:autocomplete | th:axis | th:background |
| th:bgcolor | th:border | th:cellpadding |
| th:cellspacing | th:challenge | th:charset |
| th:cite | th:class | th:classid |
| th:codebase | th:codetype | th:cols |
| th:colspan | th:compact | th:content |
| th:contenteditable | th:contextmenu | th:data |
| th:datetime | th:dir | th:draggable |
| th:dropzone | th:enctype | th:for |
| th:form | th:formaction | th:formenctype |
| th:formmethod | th:formtarget | th:fragment |
| th:frame | th:frameborder | th:headers |
| th:height | th:high | th:href |
| th:hreflang | th:hspace | th:http-equiv |
| th:icon | th:id | th:inline |
| th:keytype | th:kind | th:label |
| th:lang | th:list | th:longdesc |
| th:low | th:manifest | th:marginheight |
| th:marginwidth | th:max | th:maxlength |
| th:media | th:method | th:min |
| th:name | th:onabort | th:onafterprint |
| th:onbeforeprint | th:onbeforeunload | th:onblur |
| th:oncanplay | th:oncanplaythrough | th:onchange |
| th:onclick | th:oncontextmenu | th:ondblclick |
| th:ondrag | th:ondragend | th:ondragenter |
| th:ondragleave | th:ondragover | th:ondragstart |
| th:ondrop | th:ondurationchange | th:onemptied |
| th:onended | th:onerror | th:onfocus |
| th:onformchange | th:onforminput | th:onhashchange |
| th:oninput | th:oninvalid | th:onkeydown |
| th:onkeypress | th:onkeyup | th:onload |
| th:onloadeddata | th:onloadedmetadata | th:onloadstart |
| th:onmessage | th:onmousedown | th:onmousemove |
| th:onmouseout | th:onmouseover | th:onmouseup |
| th:onmousewheel | th:onoffline | th:ononline |
| th:onpause | th:onplay | th:onplaying |
| th:onpopstate | th:onprogress | th:onratechange |
| th:onreadystatechange | th:onredo | th:onreset |
| th:onresize | th:onscroll | th:onseeked |
| th:onseeking | th:onselect | th:onshow |
| th:onstalled | th:onstorage | th:onsubmit |
| th:onsuspend | th:ontimeupdate | th:onundo |
| th:onunload | th:onvolumechange | th:onwaiting |
| th:optimum | th:pattern | th:placeholder |
| th:poster | th:preload | th:radiogroup |
| th:rel | th:rev | th:rows |
| th:rowspan | th:rules | th:sandbox |
| th:scheme | th:scope | th:scrolling |
| th:size | th:sizes | th:span |
| th:spellcheck | th:src | th:srclang |
| th:standby | th:start | th:step |
| th:style | th:summary | th:tabindex |
| th:target | th:title | th:type |
| th:usemap | th:value | th:valuetype |
| th:vspace | th:width | th:wrap |
| th:xmlbase | th:xmllang | th:xmlspace |
内联
如何使用内连操作
我们可以通过 在父标签声明 th:inline=“text” 来开启内联操作。当然如果想整个页面使用可以直接声明在body上即可。具体使用方式如下面代码所示。
模版页面:
<div th:inline="text">
<p>Hello, [[${
user.name}]]!</p>
</div>
结果内容如下:
<div>
<p>Hello,zhuoqianmingyue!p>
div>
这样的操作和使用th:text是等同的。
<div>
<p th:text="Hello,+${user.name}">p>
div>
[[…]]对应于th:text,[(…)]对应于th:utext
禁用内联操作
这我们可以通过在父标签或者本标签上声明th:inline="none"来禁用内联的操作,如下面代码所示:
模版页面:
<p th:inline="none">A double array looks like this: [[1, 2, 3], [4, 5]]!p>
结果页面:
<p>A double array looks like this: [[1, 2, 3], [4, 5]]!p>
JavaScript内联
如果我们想在JavaScript 中使用内联操作,需要在 script 标签上声明 th:inline=“javascript” 然后我们就可以 script 标签中使用内联操作了。具体使用方式如下面代码所示:
模版页面:
<script th:inline="javascript">
var username = [[${
user.name}]];
script>
结果页面:
<script th:inline="javascript">
var username = "zhuoqianmingyue";
script>
CSS内联
我们可以通过在 style 标签上声明 th:inline=“css” 来开启在css中使用内联的操作,具体操作方式如下:
<style th:inline="css">
...
style>
例如,假设我们将两个变量设置为两个不同的String值:
classname = ‘main elems’
align = ‘center’
我们可以像以下一样使用它们:
<style th:inline="css">
.[[${
classname}]] {
text-align: [[${
align}]];
}
style>
结果页面:
<style th:inline="css">
.main\ elems {
text-align: center;
}
style>
模板布局
定义引用片段代码
SpringBoot2.0 使用模版模版布局需要先引入 thymeleaf的 thymeleaf-layout-dialect依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>nz.net.ultraq.thymeleafgroupId>
<artifactId>thymeleaf-layout-dialectartifactId>
dependency>
定义footer.html页面 该页面就是我们的引用片段代码
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Titletitle>
head>
<body>
<div th:fragment="copy">
© 2011 The Good Thymes Virtual Grocery
div>
body>
html>
我们可以通过 th:fragment 来定义引用片段,然后可以在其他页面进行引用。
定义引用页面 index.html
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Titletitle>
head>
<body>
<div th:insert="~{footer :: copy}">div>
body>
html>
通过 th:insert 和 ~{…}片段引用表达式 进行引入footer.html中定义的片段
定义访问index页面的 controller
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/layout")
public class LayOutController {
@RequestMapping("/index")
public String index(){
return "/layout/index";
}
}
进行测试
http://localhost:8090/sbe/layout/index
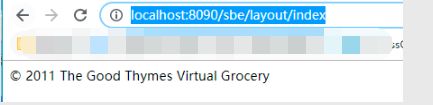
结果页面:
<div>
<div>
© 2011 The Good Thymes Virtual Grocery
div>
div>
如下面的代码2种方式的写法是一致的。如果你觉得~{footer :: copy}写法比较麻烦可以采用简写的方式footer :: copy。
<div th:insert="footer :: copy">div>
<div th:insert="~{footer :: copy}">div>
通过id属性来声明片段
我们可以通过 th:fragment 来定义引用片段,但是我们也可以通过在引用片段代码上声明id属性的方式进行片段的引用,具体操作方式如下:
定义引用片段代码模版页面 footer.html
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Titletitle>
head>
<body>
<div id="copy-section" >
© 2011 The Good Thymes Virtual Grocery
div>
body>
html>
引用引用片段的模版页面:index.html
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Titletitle>
head>
<body>
<div th:insert="~{footer :: #copy-section}">div>
body>
html>
结果页面:
<div>
<div id="copy-section">
© 2011 The Good Thymes Virtual Grocery
div>
div>
footer :: #copy-section和~{footer :: #copy-section} 结果是一致的。
th:insert和th:replace(和th:include)之间的区别
- th:insert 是最简单的:他会将使用th:insert的标签 和引用片段的内容都显示出来
- th:replace 插入引用片段的标签和内容
- th:include类似于th:insert,只插入此片段的内容。
th:insert
java代码:
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/layout")
public class LayoutController {
@RequestMapping("/index2")
public String index2(Model model) {
return "/layout/index2";
}
}
声明引用片段模版页面:footer2.html
<html xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Insert title heretitle>
head>
<body>
<footer th:fragment="copy">
© 2011 The Good Thymes Virtual Grocery
footer>
body>
html>
引用片段模版页面:index2.html
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Insert title heretitle>
head>
<body>
<div th:insert="footer2 :: copy">div>
<div th:replace="footer2 :: copy">div>
<div th:include="footer2:: copy">div>
body>
html>
th:insert 结果:
<div>
<footer>
© 2011 The Good Thymes Virtual Grocery
footer>
div>
th:replace结果:
<footer>
© 2011 The Good Thymes Virtual Grocery
footer>
th:include结果:
<div>
© 2011 The Good Thymes Virtual Grocery
div>
带参数的引用片段
定义引用片段代码模版页面 footer.html
<html xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Insert title heretitle>
head>
<body>
<div th:fragment="frag (onevar,twovar)">
<p th:text="${onevar} + ' - ' + ${twovar}">...p>
div>
body>
html>
引用引用片段的模版页面:index.html
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Insert title heretitle>
head>
<body>
<div th:insert="footer :: frag('a','b')">div>
body>
html>
结果页面:
<div>
<div>
<p>a - bp>
div>
div>
th:insert=“footer ::frag (onevar=‘a’,twovar=‘b’)” 和th:insert=“footer :: frag(‘a’,‘b’)效果是相等的。还有另一种写法就是使用th:with
th:insert=”::frag" th:with=“onevar=‘a’,twovar=‘b’”
删除模版片段
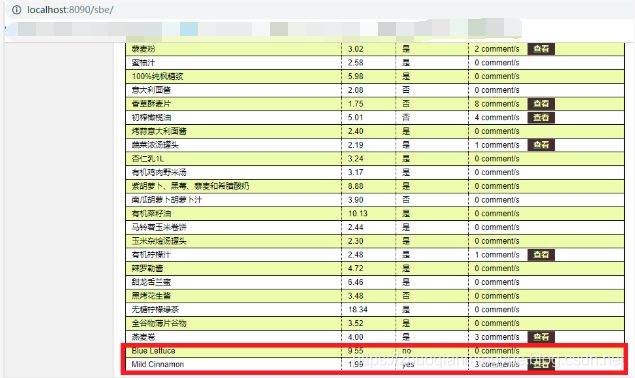
我们为了方便通过直接查看下面的页面 productList.html (主要是为了作为原型页面进行查看)我们需要添加一些模拟数据。
<table>
<tr>
<th>NAMEth>
<th>PRICEth>
<th>IN STOCKth>
<th>COMMENTSth>
tr>
<tr th:each="prod : ${prods}" th:class="${prodStat.odd}? 'odd'">
<td th:text="${prod.name}">Onionstd>
<td th:text="${prod.price}">2.41td>
<td th:text="${prod.inStock}? #{true} : #{false}">yestd>
<td>
<span th:text="${#lists.size(prod.comments)}">2span> comment/s
<a href="comments.html"
th:href="@{/product/comments(prodId=${prod.id})}"
th:unless="${#lists.isEmpty(prod.comments)}">viewa>
td>
tr>
<tr class="odd">
<td>Blue Lettucetd>
<td>9.55td>
<td>notd>
<td>
<span>0span> comment/s
td>
tr>
<tr>
<td>Mild Cinnamontd>
<td>1.99td>
<td>yestd>
<td>
<span>3span> comment/s
<a href="comments.html">viewa>
td>
tr>
table>
在上面的代码中模拟数据的代码,但是我们通过正常的controller访问该页面的时候会显示出下面的模拟数据。
<tr class="odd">
<td>Blue Lettucetd>
<td>9.55td>
<td>notd>
<td>
<span>0span> comment/s
td>
tr>
<tr>
<td>Mild Cinnamontd>
<td>1.99td>
<td>yestd>
<td>
<span>3span> comment/s
<a href="comments.html">viewa>
td>
tr>
thymeleaf 为我们提供了 th:remove 帮助我们解决这个问题:
<tr class="odd" th:remove="all">
<td>Blue Lettucetd>
<td>9.55td>
<td>notd>
<td>
<span>0span> comment/s
td>
tr>
<tr th:remove="all">
<td>Mild Cinnamontd>
<td>1.99td>
<td>yestd>
<td>
<span>3span> comment/s
<a href="comments.html">viewa>
td>
tr>
我们在模拟数据上声明th:remove=“all” 后在此通过url访问 没有了我们之前的模拟数据
all属性中的这个值是什么意思?th:remove可以根据其价值以五种不同的方式表现:
- all:删除包含标记及其所有子标记。
- body:不要删除包含标记,但删除其所有子标记。
- tag:删除包含标记,但不删除其子项。
- all-but-first:删除除第一个之外的所有包含标记的子项。
- none: 没做什么。此值对于动态评估很有用。
当我们知道没有属性的含义后我们可以通过在 声明一次即可,无需在通过定义多个 th:remove=“all”
预定义的工具对象
#dates
处理日期数据 生成,转换,获取日期的具体天数 年数。
代码演示:
java代码:
@RequestMapping("/dates")
public String dates(Model model) throws ParseException{
Date date = new Date();
model.addAttribute("date",date);
String dateStr = "2018-05-30";
SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd");
Date date2 = sdf.parse(dateStr);
Date[] datesArray = new Date[2];
datesArray[0] = date;
datesArray[1] = date2;
model.addAttribute("datesArray",datesArray);
List<Date> datesList = new ArrayList<Date>();
datesList.add(date);
datesList.add(date2);
model.addAttribute("datesList",datesList);
return "/course/dates";
}
format操作
java代码:
Date date = new Date();
模版页面:
<span th:text="${#dates.format(date)}">4564546span>
结果页面:
<span>2019年5月30日 上午10时03分24秒 span>
java代码:
Date date = new Date();
模版页面:
<span th:text="${#dates.format(date, 'dd/MMM/yyyy HH:mm')}">4564546span>
结果页面:
<span>30/五月/2019 10:03 span>
java代码:
Date[] datesArray = new Date[2];
datesArray[0] = date;
datesArray[1] = date2;
模版页面:
<p th:text="${#dates.format(datesArray, 'yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm')}">p>
结果页面:
<p>2019-05-30 10:03p>
不知为何这里只是取出了一个日期数据
java代码:
List<Date> datesList = new ArrayList<Date>();
datesList.add(date);
datesList.add(date2);
model.addAttribute("datesList",datesList);
模版页面:
<p th:text="${#dates.listFormat(datesList, 'dd/MMM/yyyy HH:mm')}">p>
结果页面:
<p>[30/五月/2019 10:03, 30/五月/2018 00:00]p>
获取日期属性操作
java代码:
Date date = new Date();
模版页面:
<p th:text="${#dates.day(date)} ">p>
结果页面:
<p>30p>
java代码:
Date date = new Date();
模版页面:
<p th:text="${#dates.month(date)}">p>
结果页面:
<p>5p>
java代码:
Date date = new Date();
模版页面:
<p th:text="${#dates.monthName(date)}">p>
结果页面:
<p>五月p>
java代码:
Date date = new Date();
模版页面:
<p th:text="${#dates.monthNameShort(date)} ">p>
结果页面:
<p>五月p>
java代码:
Date date = new Date();
模版页面:
<p th:text="${#dates.year(date)}">p>
结果页面:
<p>2019p>
java代码:
Date date = new Date();
模版页面:
<p th:text="${#dates.dayOfWeek(date)}">p>
结果页面:
<p>5p>
java代码:
Date date = new Date();
模版页面:
<p th:text="${#dates.dayOfWeekName(date)}">p>
结果页面:
<p>星期四p>
java代码:
Date date = new Date();
模版页面:
<p th:text="${#dates.dayOfWeekNameShort(date)}">p>
结果页面:
<p>星期四p>
java代码:
Date date = new Date();
模版页面:
<p th:text="${#dates.hour(date)}">p>
结果页面:
<p>10p>
java代码:
Date date = new Date();
模版页面:
<p th:text="${#dates.minute(date)}">p>
结果页面:
<p>10p>
java代码:
Date date = new Date();
模版页面:
<p th:text="${#dates.second(date)}">p>
结果页面:
<p>45p>
java代码:
Date date = new Date();
模版页面:
<p th:text="${#dates.millisecond(date)} ">p>
结果页面:
<p>853p>
生成日期操作
模版页面:
<p th:text="${#dates.createNow()}">p>
结果页面:
<p>Thu May 30 10:15:55 CST 2019p>
模版页面:
<p th:text="${#dates.format(#dates.createNow())}">p>
结果页面:
<p>2019年5月30日 上午10时15分55秒p>
模版页面:
<p th:text="${#dates.create('2019','05','30')}">p>
结果页面:
<p>Thu May 30 00:00:00 CST 2019p>
模版页面:
<p th:text="${#dates.create('2019','05','31','10','18')}">p>
结果页面:
<p>Fri May 31 10:18:00 CST 2019p>
模版页面:
<p th:text="${#dates.create('2019','05','30','10','18','34')}">p>
结果页面:
<p>Thu May 30 10:18:34 CST 2019p>
模版页面:
<p th:text="${#dates.createToday()}">p>
结果页面:
<p>Thu May 30 00:00:00 CST 2019p>
#numbers
处理数字数据的转换。包括:
- 对不够位数的数字进行补0(formatInteger )
- 设置千位分隔符(formatInteger)
- 精确小数点(formatDecimal )
- 设置百分号(formatPercent )
- 生成数组(sequence )
代码演示:
@RequestMapping("/numbers")
public String numbers(Model model) throws ParseException{
return "/course/numbers";
}
数字进行补0操作
模板代码:
<p th:text="${#numbers.formatInteger('123',4)}">p>
结果页面:
<p>0123p>
模板代码:
<p th:text="${#numbers.formatInteger('123',3)}">p>
结果页面:
<p>123p>
模板代码:
<p th:text="${#numbers.formatInteger('123',2)}">p>
结果页面:
<p>123p>
Java代码
@RequestMapping("/numbers")
public String numbers(Model model) throws ParseException{
List<Integer> numList = new ArrayList<Integer>();
numList.add(1);
numList.add(12);
numList.add(13);
model.addAttribute("numList",numList);
return "/course/numbers";
}
模板代码:
<p th:text="${#numbers.listFormatInteger(numList,3)}">p>
结果页面:
<p>[001, 012, 013]p>
千位分隔符操作
模板代码:
<p th:text="${#numbers.formatInteger('1000',2,'POINT')}">p>
结果页面:
<p>1.000p>
模板代码:
<p th:text="${#numbers.formatInteger('1000',6,'POINT')}">p>
结果页面:
<p>001.000p>
模板代码:
<p th:text="${#numbers.formatInteger('1000',7,'POINT')}">p>
结果页面:
<p>0.001.000p>
模板代码:
<p th:text="${#numbers.formatInteger('1000',2,'COMMA')}">p>
结果页面:
<p>1,000p>
模板代码:
<p th:text="${#numbers.formatInteger('1000',2,'WHITESPACE')}">p>
结果页面:
<p>1 000p>
模板代码:
<p th:text="${#numbers.formatInteger('1000',2,'NONE')}">p>
结果页面:
<p>1000p>
模板代码:
<p th:text="${#numbers.formatInteger('1000',2,'DEFAULT')}">p>
结果页面:
<p>1,000p>
精确小数点操作
模板代码:
<p th:text="${#numbers.formatDecimal('10.123',3,2)}">p>
结果页面:
<p>010.12p>
模板代码:
<p th:text="${#numbers.formatDecimal('1000.123',5,'POINT',2,'COMMA')}">p>
结果页面:
<p>01.000,12p>
钱显示符号操作
模板代码:
<p th:text="${#numbers.formatCurrency('1000')}">p>
结果页面:
<p>¥1,000.00p>
百分比操作
模板代码:
<p th:text="${#numbers.formatPercent('0.2',2, 4)}">p>
结果页面:
<p>20.0000%p>
模板代码:
<p th:text="${#numbers.formatPercent('0.2',3, 2)}">p>
结果页面:
<p>020.00%p>
生成数组操作
模板代码:
<div th:each="num : ${#numbers.sequence(0,4)}" >
<p th:text="${num}">p>
div>
结果页面:
<div><p>0p>div>
<div><p>1p>div>
<div><p>2p>div>
<div><p>3p>div>
<div><p>4p>div>
模板代码:
<div th:each="num : ${#numbers.sequence(0,4,1)}" >
<p th:text="${num}">p>
div>
结果页面:
<div><p>0p>div>
<div><p>1p>div>
<div><p>2p>div>
<div><p>3p>div>
<div><p>4p>div>
模板代码:
<div th:each="num : ${#numbers.sequence(0,10,2)}" >
<p th:text="${num}">p>
div>
结果页面:
<div><p>0p>div>
<div><p>2p>div>
<div><p>4p>div>
#strings
处理String的相关操作,包括:
- 字符串转换(toString)
- 检查字符串是否为空(isEmpty)
- 字符串是为空替换操作(defaultString)
- 检查字符串中是否包含某个字符串(contains containsIgnoreCase)
- 检查字符串是以片段开头还是结尾(startsWith endsWith)
- 截取(substring substringAfter)
- 替换(replace)
- 追加(prepend append)
- 变更大小写(toUpperCase toLowerCase)
- 拆分和组合字符串(arrayJoin arraySplit)
- 去空格(trim)
- 缩写文本(abbreviate)
- 字符串连接(concat)
代码演示:
java 代码
@RequestMapping("/strings")
public String strings(Model model){
Object object = "123";
model.addAttribute("object",object);
List<Integer> numList = new ArrayList<Integer>();
numList.add(1);
numList.add(12);
numList.add(13);
model.addAttribute("numList",numList);
}
Java代码
Object object = "123";
模板代码:
<p th:text="${object}">p>
结果页面:
<p>123p>
toString操作
Java代码
Object object = "123";
模板代码:
<p th:text="${#strings.toString(object)}">p>
结果页面:
<p>123p>
Java代码
List<Integer> numList = new ArrayList<Integer>();
numList.add(1);
numList.add(12);
numList.add(13);
模板代码:
<p th:text="${#strings.toString(numList)}">p>
结果页面:
<p>[1, 12, 13]p>
isEmpty操作
Java代码
String name = null;
模板代码:
<p th:text="${#strings.isEmpty(name)}">p>
结果页面:
<p>truep>
Java代码
List<String> nameList = new ArrayList<String>();
nameList.add("1");
nameList.add(null);
模板代码:
<p th:text="${#strings.listIsEmpty(nameList)}">p>
结果页面:
<p>[false, true]p>
Java代码
Set<String> nameSet = new HashSet<String>();
nameSet.add(null);
nameSet.add("1");
模板代码:
<p th:text="${#strings.setIsEmpty(nameSet)}">p>
结果页面:
<p>[true, false]p>
defaultString操作
Java代码
String name = null;
模板代码:
<p th:text="${#strings.defaultString(text,'该值为null')}">p>
结果页面:
<p>该值为nullp>
Java代码
List<String> nameList = new ArrayList<String>();
nameList.add("1");
nameList.add(null);
模板代码:
<p th:text="${#strings.listDefaultString(textList,'该值为null')}">p>
结果页面:
<p>[abc, 该值为null]p>
contains操作
模板代码:
<p th:text="${#strings.contains('abcez','ez')}">p>
结果页面:
<p>truep>
模板代码:
<p th:text="${#strings.containsIgnoreCase('abcEZ','ez')}">p>
结果页面:
<p>truep>
startsWith endsWith 操作
模板代码:
<p th:text="${#strings.startsWith('Donabcez','Don')}">p>
结果页面:
<p>truep>
模板代码:
<p th:text="${#strings.endsWith('Donabcezn','n')}">p>
结果页面:
<p>truep>
indexOf操作
模板代码:
<p th:text="${#strings.indexOf('abcefg','e')}">p>
结果页面:
<p>3p>
substring操作
模板代码:
<p th:text="${#strings.substring('abcefg',3,5)}">p>
结果页面:
<p>efp>
replace操作
模板代码:
<p th:text="${#strings.replace('lasabce','las','ler')}">p>
结果页面:
<p>lerabcep>
prepend操作
模板代码:
<p th:text="${#strings.prepend('abc','012')}">p>
结果页面:
<p>012abcp>
append操作
模板代码:
<p th:text="${#strings.append('abc','456')}">p>
结果页面:
<p>abc456p>
toUpperCase操作
模板代码:
<p th:text="${#strings.toUpperCase('abc')}">p>
结果页面:
<p>ABCp>
toLowerCase操作
模板代码:
<p th:text="${#strings.toLowerCase('ABC')}">p>
结果页面:
<p>abcp>
length操作
模板代码:
<p th:text="${#strings.length('abc')}">p>
结果页面:
<p>3p>
trim操作
模板代码:
<p th:text="${#strings.trim(' abc ')}">p>
结果页面:
<p>abcp>
abbreviate操作
模板代码:
<p th:text="${#strings.abbreviate('12345678910',10)}">p>
结果页面:
<p>1234567...p>
#objects
处理Object对象的操作 包含obj不为空返回改值如果为空返回默认值(nullSafe)
java代码
@RequestMapping("/objects")
public String objects(Model model){
Object obj = null;
model.addAttribute("obj",obj);
}
模板代码:
<p th:text="${#objects.nullSafe(obj,'该对象为null')}">p>
结果页面:
<p>该对象为nullp>
#bools
判断对象是否为ture或者是否为false的操作。
- 数字 1 为 ture , 0 为 false;
- “on” 为 true, “off” 为false;
- “true” 为true, "false"为 false;
isTrue操作
模板代码:
<p th:text="${#bools.isTrue(true)} ">p>
结果页面:
<p>truep>
模板代码:
<p th:text="${#bools.isTrue(false)} ">p>
结果页面:
<p>falsep>
模板代码:
<p th:text="${#bools.isTrue('on')} ">p>
结果页面:
<p>truep>
模板代码:
<p th:text="${#bools.isTrue('off')} ">p>
结果页面:
<p>falsep>
模板代码:
<p th:text="${#bools.isTrue('true')} ">p>
结果页面:
<p>truep>
模板代码:
<p th:text="${#bools.isTrue('false')} ">p>
结果页面:
<p>falsep>
模板代码:
<p th:text="${#bools.isTrue(1)} ">p>
结果页面:
<p>truep>
模板代码:
<p th:text="${#bools.isTrue(0)} ">p>
结果页面:
<p>falsep>
#arrays
处理数组的相关操作的内置对象,包含:
- 转换数组 toStringArray toIntegerArray,
- 获取数组的长度(length ),
- 判断数组是否为空(isEmpty )
- 是否包含某个元素(contains)
- 是否包含一批元素(containsAll)
其中 toStringArray 等操作接受的是Object对象,containsAll 接受一批元素支持数组和集合的参数。
toStringArray操作
java代码
@RequestMapping("/arrays")
public String arrays(Model model){
List<String> object = new ArrayList<String>();
object.add("1");
object.add("2");
model.addAttribute("object",object);
}
模板代码:
<p th:text="${#arrays.toStringArray(object)} ">p>
结果页面:
<p>[Ljava.lang.String;@3cca655dp>
length操作
java代码
Integer[] array = {
1,2,3};
模板代码:
<p th:text="${#arrays.length(array)} ">p>
结果页面:
<p>3p>
isEmpty操作
java代码
Integer[] array = {
1,2,3};
模板代码:
<p th:text="${#arrays.isEmpty(array)} ">p>
结果页面:
<p>falsep>
contains操作
java代码
Integer[] array = {
1,2,3};
模板代码:
<p th:text="${#arrays.contains(array,1)} ">p>
结果页面:
<p>truep>
containsAll操作
java代码
Integer[] array = {
1,2,3};
Integer[] array2 = {
1,3};
模板代码:
<p th:text="${#arrays.containsAll(array,array2)} ">p>
结果页面:
<p>truep>
#lists
处理 list 相关操作的内置对象,包括:
- 计算长度(size)
- 检查list是否为空(isEmpty)
- 检查元素是否包含在list中(contains,containsAll)
- 对给定list的副本排序(sort)
java代码
@RequestMapping("/lists")
public String lists(Model model){
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<Integer>();
list.add(1);
list.add(3);
list.add(2);
model.addAttribute("list",list);
}
模板代码:
<p th:text="${#lists.size(list)} ">p>
结果页面:
<p>3p>
java代码:
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<Integer>();
list.add(1);
list.add(3);
list.add(2);
模板代码:
<p th:text="${#lists.isEmpty(list)} ">p>
结果页面:
<p>falsep>
java代码:
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<Integer>();
list.add(1);
list.add(3);
list.add(2);
模板代码:
<p th:text="${#lists.contains(list, 1)}">p>
结果页面:
<p>truep>
java代码:
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<Integer>();
list.add(1);
list.add(3);
list.add(2);
List<Integer> list2 = new ArrayList<Integer>();
list2.add(1);
list2.add(2);
模板代码:
<p th:text="${#lists.containsAll(list,list2)}">p>
结果页面:
<p>truep>
java代码:
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<Integer>();
list.add(1);
list.add(3);
list.add(2);
模板代码:
<p th:text="${#lists.sort(list)}">p>
结果页面:
<p>[1, 2, 3]p>
#sets
处理 set 相关操作的内置对象,包括:
- 转换为Set(toSet)
- 计算长度(size)
- 检查set是否为空(isEmpty)
- 检查元素是否包含在set中 (contains,containsAll)
size操作
java代码
@RequestMapping("/sets")
public String sets(Model model){
Set<Integer> set = new HashSet<Integer>();
set.add(1);
set.add(2);
set.add(3);
set.add(4);
model.addAttribute("set",set);
}
模板代码:
<p th:text="${#sets.size(set)} ">p>
结果页面:
<p>3p>
isEmpty 操作
java代码:
Set<Integer> set = new HashSet<Integer>();
set.add(1);
set.add(2);
set.add(3);
set.add(4);
模板代码:
<p th:text="${#sets.isEmpty(set)} ">p>
结果页面:
<p>falsep>
contains操作
java代码:
Set<Integer> set = new HashSet<Integer>();
set.add(1);
set.add(2);
set.add(3);
set.add(4);
模板代码:
<p th:text="${#sets.contains(set, 1)}">p>
结果页面:
<p>truep>
containsAll操作
java代码
Set<Integer> set = new HashSet<Integer>();
set.add(1);
set.add(2);
set.add(3);
set.add(4);
Integer[] elements = {
1,2};
model.addAttribute("elements",elements);
模板代码:
<p th:text="${#sets.containsAll(set, elements)}">p>
结果页面:
<p>truep>
sort操作
java代码:
Set<Integer> set = new HashSet<Integer>();
set.add(1);
set.add(2);
set.add(3);
set.add(4);
模板代码:
<p th:text="${#lists.sort(list)}">p>
结果页面:
<p>[1, 2, 3]p>
#maps
处理 map相关操作的内置对象,包括:
- 计算长度(size)
- 检查map是否为空(isEmpty)
- 检查映射中是否包含键或值(containsKey,containsAllKeys,containsValue)
java代码:
@RequestMapping("/maps")
public String maps(Model model){
Map<String,Integer> map = new HashMap<String,Integer>();
map.put("1",1);
map.put("2",2);
map.put("3",3);
model.addAttribute("map",map);
}
模板代码:
<p th:text="${#maps.size(map)} ">p>
结果页面:
<p>3p>
java代码:
Map<String,Integer> map = new HashMap<String,Integer>();
map.put("1",1);
map.put("2",2);
map.put("3",3);
模板代码:
<p th:text="${#maps.isEmpty(map)} ">p>
结果页面:
<p>falsep>
java代码:
Map<String,Integer> map = new HashMap<String,Integer>();
map.put("1",1);
map.put("2",2);
map.put("3",3);
模板代码:
<p th:text="${#maps.containsKey(map, '1')}">p>
结果页面:
<p>truep>
java代码:
Map<String,Integer> map = new HashMap<String,Integer>();
map.put("1",1);
map.put("2",2);
map.put("3",3);
String[] keys = {
"1","2"};
model.addAttribute("keys",keys);
模板代码:
<p th:text="${#maps.containsAllKeys(map, keys)}">p>
结果页面:
<p>truep>
java代码:
Map<String,Integer> map = new HashMap<String,Integer>();
map.put("1",1);
map.put("2",2);
map.put("3",3);
模板代码:
<p th:text="${#maps.containsValue(map, 2)}">p>
结果页面:
<p>truep>
java代码:
Map<String,Integer> map = new HashMap<String,Integer>();
map.put("1",1);
map.put("2",2);
map.put("3",3);
Integer[] values = {
1,2};
model.addAttribute("values",values);
模板代码:
<p th:text="${#maps.containsAllValues(map, values)}">p>
结果页面:
<p>truep>
#aggregates
用户处理集合或者数组的一些统计操作,包括:
- 求和(sum)
- 求平均值(avg)
- 处理包装类型或基本类型的数组或集合
求和操作
java代码:
@RequestMapping("/aggregates")
public String aggregates(Model model){
Integer[] array = {
1,2,3,4};
model.addAttribute("array",array);
return "/course/aggregates";
}
模板代码:
<p th:text="${#aggregates.sum(array)} ">p>
结果页面:
<p>10p>
java代码:
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<Integer>();
list.add(1);
list.add(2);
list.add(3);
list.add(4);
模板代码:
<p th:text="${#aggregates.sum(list)} ">p>
结果页面:
<p>10p>
求平均值操作
java代码:
Integer[] array = {
1,2,3,4};
模板代码:
<p th:text="${#aggregates.avg(array)} ">p>
结果页面:
<p>2.5p>
java代码:
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<Integer>();
list.add(1);
list.add(2);
list.add(3);
list.add(4);
模板代码:
<p th:text="${#aggregates.avg(list)} ">p>
结果页面:
<p>2.5p>
小结
本文主要介绍 Thymeleaf 的基础用法、内联、模板布局、预定义的工具对象。整体来看Thymeleaf 使用语法还是很强大的,但是我这里不会强烈安利你使用 Thymeleaf,正如 Thymeleaf 官方所说:“无论如何,比较技术的最好方法是自己使用它们,并感觉哪个最适合你!” 你同样可以选择使用 Velocity 或 FreeMarker。
代码示例
具体代码示例请查看我的GitHub 仓库 springbootexamples 中的 spring-boot-2.x-thymeleaf 下的 course 包下查看。
GitHub:https://github.com/zhuoqianmingyue/springbootexamples
参考文献:
https://www.thymeleaf.org/doc/tutorials/3.0/usingthymeleaf.html
https://blog.csdn.net/liubin5620/article/details/80470619