PAT甲级1065 A+B and C (64bit) (20分) string大数加法 、大数比较的其他办法、long double 和double 的详解有效位数 ****
1065 A+B and C (64bit) (20分)
Given three integers A, B and C in [−263,263], you are supposed to tell whether A+B>C.
Input Specification:
The first line of the input gives the positive number of test cases, T (≤10). Then T test cases follow, each consists of a single line containing three integers A, B and C, separated by single spaces.
Output Specification:
For each test case, output in one line Case #X: true if A+B>C, or Case #X: false otherwise, where X is the case number (starting from 1).
Sample Input:
3
1 2 3
2 3 4
9223372036854775807 -9223372036854775808 0
Sample Output:
Case #1: false
Case #2: true
Case #3: false
强烈推荐参看这个老哥的博客https://blog.csdn.net/chch1996/article/details/100162168?utm_source=app
给出了很好的方法和解释,尤其第三个string 大数比较,天秀,我就没想到变变符号换算成加法实现,不用考虑正数 负数相加那么麻烦了
pat的数据集很好过,测试数据和测试点都没有牛客的多,建议去牛客测试一下,PAT过了并不代表程序真的没问题
目录
-
- 自己使用string实现大数加法
- 一个老哥的博客,大力推荐
-
- 方法一
- 方法2
- 方法3
自己使用string实现大数加法
我自己使用string实现大数比较,思路如下:
因为a b 两个数字都是可正可负的,所以考虑情况很多,但是一步一步来,就并没有那么难了。
首先考虑a,b两个可正可负数字的大数比较,先实现一个比较简单的正的大数比较函数
//a b均为正数 比较大小 a大于b 返回1
bool absCmp(string a,string b)
{
if(a.size()>b.size())
return 1;
else if(a.size()b;
}
然后实现可比较正负大数的函数
// a b 正负数均可判断
bool cmp(string a,string b)
{
if(a[0]=='-'&&b[0]!='-')
return 0;
else if(a[0]!='-'&&b[0]=='-')
return 1;
else if (a[0]=='-'&&b[0]=='-')
{
if(absCmp(b.substr(1),a.substr(1))==1)
return 1;
else return 0;
}
else
return absCmp(a,b);
}
这样比较部分完结了,考虑实现大数加法,因为大数可正可负,所以我们先实现两个正的大数的加法
//a b 均为正数 不区分大小
string add(string a,string b)
{
为了方便阅读,这里就说几个主要注意的点
1: 需要一个进位变量sign 参与加法运算,当8 +9时候进位变量为1 数字为是7
2: 考虑a或者b没有遍历完的情况
3:考虑a b同时遍历完了,sign还有进位1的情况
}
有大数可正可负,正负大数相加其实就是两个正的大数相减,所以先实现一个大的正数减去一个小的正数
// a b均为正数,且a大于于等于b
string AsubB(string a,string b)
{
为了方便阅读 仅仅书写需要考虑的点
1:需要结尾变量sign参与运算
2:因为a 比b大,所以需要检测a是否遍历完毕了
3: 需要考虑输出时候高位为0 的情况
}
然后实现两个正的大数相减,不论谁大谁小
//a b,均为正数,a-b 不论谁大
string sub(string a,string b)
{
if(cmp(a,b))
{
return AsubB(a,b);
}
else
{
//b-a 再加个负号
return "-"+AsubB(b,a);
}
}
这样我们所有需要的运算就考虑全了,直接一个函数分配情况就好了
string calculate(string a,string b)
{
if(a[0]=='-'&&b[0]=='-')
{
a=a.substr(1);
b=b.substr(1);
//相加,然后加负号
return "-"+add(a,b);
}
else if(a[0]=='-'&&b[0]!='-')
{
return sub(b,a.substr(1));
}
else if(a[0]!='-'&&b[0]=='-')
{
//a-b
return sub(a,b.substr(1));
}
else
{
//a+b
return add(a,b);
}
}
整体代码如下
#include
#include
using namespace std;
#include
//a b均为正数 比较大小 a大于b 返回1
bool absCmp(string a,string b)
{
if(a.size()>b.size())
return 1;
else if(a.size()b;
}
// a b 正负数均可判断
bool cmp(string a,string b)
{
if(a[0]=='-'&&b[0]!='-')
return 0;
else if(a[0]!='-'&&b[0]=='-')
return 1;
else if (a[0]=='-'&&b[0]=='-')
{
if(absCmp(b.substr(1),a.substr(1))==1)
return 1;
else return 0;
}
else
return absCmp(a,b);
}
// a b均为正数,且a大于于等于b
string AsubB(string a,string b)
{
vector vec;
auto ait=a.crbegin(),bit=b.crbegin();
int sign=0;
while(!(ait==a.crend()||bit==b.crend()))
{
if(*ait+sign>=*bit)
{
vec.push_back(*ait+sign-*bit);
sign=0;
}
else
{
vec.push_back(*ait+sign+10-*bit);
sign=-1;
}
ait++;
bit++;
}
//因为是a大于等于b,所以只需要判断a是否读取完毕
while(ait!=a.crend())
{
if(sign==-1)
{
vec.push_back(*ait-'0'+sign);
sign=-1;
}
else
vec.push_back(*ait-'0');
ait++;
}
string out="";
int pos=-1;
for(int i=vec.size()-1; i>=0; i--)
{
int get=vec[i];
if(vec[i]!=0)
{
pos=i;
break;
}
}
if(pos==-1)
return "0";
else
{
for(int i=pos; i>=0; i--)
{
out=out+to_string(vec[i]);
}
}
return out;
}
//a b,均为正数,a-b 不论谁大
string sub(string a,string b)
{
if(cmp(a,b))
{
return AsubB(a,b);
}
else
{
//b-a 再加个负号
return "-"+AsubB(b,a);
}
}
//a b 均为正数 不区分大小
string add(string a,string b)
{
vector vec;
auto ait=a.crbegin(),bit=b.crbegin();
int sign=0;
while(!(ait==a.crend()||bit==b.crend()))
{
if(*ait-'0'+sign+*bit-'0'>=10)
{
vec.push_back(*ait-'0'+sign+*bit-'0'-10);
sign=1;
}
else
{
vec.push_back(*ait-'0'+sign+*bit-'0');
sign=0;
}
ait++;
bit++;
}
//因为是a大于等于b,所以只需要判断a是否读取完毕
while(ait!=a.crend())
{
if(sign==1)
{
vec.push_back(*ait-'0'+sign);
sign=0;
}
else
vec.push_back(*ait-'0');
ait++;
}
while(bit!=b.crend())
{
if(sign==1)
{
vec.push_back(*bit-'0'+sign);
sign=0;
}
else
vec.push_back(*bit-'0');
bit++;
}
string out;
if(sign==1)
out="1";
else
out="";
int pos=-1;
for(int i=vec.size()-1; i>=0; i--)
{
int get=vec[i];
if(vec[i]!=0)
{
pos=i;
break;
}
}
if(pos==-1)
return "0";
else
{
for(int i=pos; i>=0; i--)
{
out=out+to_string(vec[i]);
}
}
return out;
}
string calculate(string a,string b)
{
if(a[0]=='-'&&b[0]=='-')
{
a=a.substr(1);
b=b.substr(1);
//相加,然后加负号
return "-"+add(a,b);
}
else if(a[0]=='-'&&b[0]!='-')
{
return sub(b,a.substr(1));
}
else if(a[0]!='-'&&b[0]=='-')
{
//a-b
return sub(a,b.substr(1));
}
else
{
//a+b
return add(a,b);
}
}
int main()
{
int N;
cin>>N;
string sn[N][3];
for(int i=0; i>sn[i][0]>>sn[i][1]>>sn[i][2];
}
for(int i=0; i 一个老哥的博客,大力推荐
方法一
这一需要注意,PAT应该是写错,右侧应该是开区间的,闭区间的PAT也没有考察a+b>=2^63
c>=2^63 的这种情况,这样 longlong 的sum和c 都应该是溢出为负数
Solution1: long long int 取值为[-263,263),左右区间刚好能表示出来a b c三个数字,剩下就是考虑a+b的益处问题,如果用long long int 存储 A B C,需要考虑 A + B的溢出。具体而言,如果① A > 0, B > 0,A+B <= 0,说明正溢出,则必定有 A + B > C; ② 如果 A < 0 , B < 0, A + B >= 0,说明负溢出,则必定有 A + B < C; ③ 非这两种情形,则没有发生溢出,正常比较 A+B 和 C 的大小即可。
还要注意的是,不能直接判断 A + B 的溢出,而要也用long long 型变量存储 A+B的结果,才能判断溢出情况,否则测试点1和2过不了。
#include
using namespace std ;
int main()
{
int T ;
cin >> T ;
for( int i = 1; i <= T; ++i )
{
printf("Case #%d: ", i);
long long a, b, c, sum;
cin >> a >> b >> c;
sum = a + b;
if(a > 0 && b > 0 && sum <= 0)//a +b 两个相加正益处了,肯定比c大了
printf("true\n");
else if(a < 0 && b < 0 && sum >= 0) a +b 两个相加负益处了,肯定比c小了
printf("false\n");
else sum > c? printf("true\n"):printf("false\n");
}
return 0 ;
}
方法2
2^63 = 9,223,372,036,854,775,808 使用浮点数表示的话需要能够表示19位有效数字
关于浮点数的有效位数分析见这个微博:https://blog.csdn.net/VonSdite/article/details/76575247
无论是float还是double,在内存中的存储主要分成三部分,分别是:
(1)符号位(Sign): 0代表正数,1代表负数
(2)指数位(Exponent): 用于存储科学计数法中的指数部分,并且采用移位存储方式
(3)尾数位(Mantissa): 用于存储尾数部分
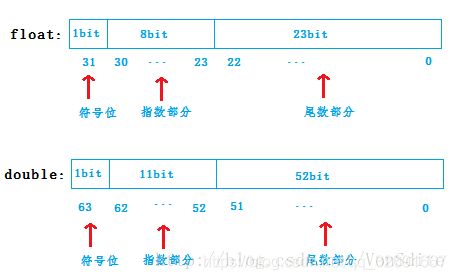
float 是 32位, 其中有23位用于存放尾数, 带有一个固定隐含位… 所以float的有24个二进制有效位位数.
- 2^24共有8个十进制位. 所以有些编译器 float的有效数字位是 8位 , 有些有效数字位是 7位.(注意不是小数的位数, 是有效数字位)
double也一样,是64位, 其中有52位用于存放尾数, 一个固定隐含位. 共有 53个二进制有效位位数.
- 2^53次方有15个十进制位, 所以有些编译器double的有效数字位是15位, 有些是16位
结论:
- 有些编译器 float的有效数字位是 8位 , 有些有效数字位是 7位
- 有些编译器double的有效数字位是 15位, 有些是 16位
- 注意printf("%f", x); // 默认输出6位小数(不要和有效数字混淆)
- 区别最大值和有效位数
- 32位下,long double 的有效位数是18 到19位
因为 2^63> 10^18, 2^64 > 10^19,用 double 存储的精度不够,但是long double 是够的,直接用 long double 类型进行判断。注意,如果用scanf的话,long double的输入格式是 “%Lf”。也可以直接用 cin>>a>>b>>c输入。
#include
using namespace std ;
int main()
{
int T ;
cin >> T ;
for( int i = 1; i <= T; ++i )
{
printf("Case #%d: ", i);
long double a, b, c;
scanf("%Lf%Lf%Lf", &a, &b, &c);
(a + b > c)?printf("true\n"):printf("false\n");
}
return 0 ;
}
方法3
Solution3: 手动实现大数加法,注意这里还有负数,因此需要结合 A B C的符号情况,共有8种情形,将 A + B > C这个不等式转换为正数相加的等价形式再判断,例如 当 A >= 0 , B < 0,C >=0时,转换的等价形式就是 A > C + (-B),其余同理。
大数加法的代码如下:代码中,每个数的符号单独以bool量sign表示,所有数字存储在 vector中,sign = true,表示非负,sign = false, 表示为负; 0 的存储方式是 空的vector,这是考虑到在比较大小时应当是长度越长的正数越大。
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
void add(vector a, vector b, vector &ret) // a > 0, b > 0
{
ret.clear();
reverse(a.begin(), a.end());
reverse(b.begin(), b.end());
int size = max(a.size(),b.size());
while(a.size() < size) a.push_back(0);
while(b.size() < size) b.push_back(0);
int carry = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < size; ++i)
{
int sum = a[i] + b[i] + carry;
if(sum < 10)
{
ret.push_back(sum);
carry = 0;
}
else
{
ret.push_back(sum - 10);
carry = 1;
}
}
if(carry) ret.push_back(carry);
if(ret.size() > 0) while(ret[ret.size() - 1] == 0) ret.pop_back();
reverse(ret.begin(), ret.end());
}
bool cmp(vector &a, vector &b) // true: a > b; false : a <= b
{
if(a.size() > b.size()) return true;
else if(a.size() < b.size()) return false;
else
{
for (int i = 0; i < a.size(); ++i)
{
if(a[i] > b[i]) return true;
else if(a[i] < b[i]) return false;
}
return false;
}
}
void convert(string s, vector &v, bool &sign)
{
int index = 0;
if(s[0] == '-')
{
sign = false;
index++;
}
while(index < s.size() && s[index] == '0') index++;
if(index < s.size())
{
for (int i = index; i < s.size(); ++i)
{
v.push_back(s[i] - '0');
}
}
else sign = true;
}
int main()
{
int T;
cin >> T;
for (int i = 1; i <= T; ++i)
{
printf("Case #%d: ", i);
string sa, sb, sc;
cin >> sa >> sb >> sc;
vector a, b, c, ret, zero;
bool signA = true, signB = true, signC = true; // sign == true :>=0; sign == false: < 0;
convert(sa, a, signA);
convert(sb, b, signB);
convert(sc, c, signC);
if(signA && signB && signC)
{
add(a, b, ret);
cmp(ret, c) ? printf("true\n"): printf("false\n");
}
else if(signA && signB && !signC) printf("true\n");
else if(signA && !signB && signC)
{
add(b, c, ret);
cmp(a, ret) ? printf("true\n"): printf("false\n");
}
else if(signA && !signB && !signC)
{
add(a, c, ret);
cmp(ret, b) ? printf("true\n"): printf("false\n");
}
else if(!signA && signB && signC)
{
add(a,c,ret);
cmp(b, ret) ? printf("true\n"): printf("false\n");
}
else if(!signA && signB && !signC)
{
add(b,c,ret);
cmp(ret, a) ? printf("true\n"): printf("false\n");
}
else if(!signA && !signB && signC) printf("false\n");
else if(!signA && !signB && !signC)
{
add(a, b, ret);
cmp(c, ret) ? printf("true\n"): printf("false\n");
}
}
return 0;
}