Spring核心之事务管理
文章目录
- 1、事务定义
- 2、@Transactional
-
-
- 2.1、@Transactional属性
- 2.2、propagation
-
-
- 2.2.1、事务传播行为
- 2.2.2、Propagation.REQUIRE
- 2.2.3、Propagation.REQUIRE_NEW
-
- 2.3、isolation
-
-
- 2.3.1、事务隔离级别问题的提出
- 2.3.2、事务隔离级别问题的解决
-
- 2.4、timeout
- 2.5、readOnly
- 2.6、rollbackFor
- 2.7、noRollbackFor
-
1、事务定义
事务是数据库操作的基本单位,简单的理解事务就是一组操作(可以是一条SQL语句,多条SQL语句或整个程序)中要么都成功,其中一个操作失败则全部失败。Spring作为Java技术栈的最强框架,除了IOC和AOP之外,事务也是其核心功能之一,本文将使用Spring集成的jdbc来演示Spring对事务的操作。先来了解事务具有的四个属性(ACID):
- 原子性:一个事务是一个不可分割的工作单位,事务中包括的操作要么都做,要么都不做。
- 一致性:事务必须是使数据库从一个一致性状态变到另一个一致性状态,即操作前后的总的量不变,一致性与原子性是密切相关的。
- 隔离性:一个事务的执行不能被其他事务干扰,即一个事务内部的操作及使用的数据对并发的其他事务是隔离的,并发执行的各个事务之间不能互相干扰。
- 持久性:指一个事务一旦提交,它对数据库中数据的改变就应该是永久性的,接下来的其他操作或故障不应该对其有任何影响。
2、@Transactional
2.1、@Transactional属性
| 属性 | 类型 | 作用 |
|---|---|---|
| value | String | 对指定的事务限定符值,可被用于确定目标的事务管理器 |
| propagation | enum:Propagatio | 事务传播的行为 |
| isolation | enum:Isolation | 事务隔离的级别 |
| timeout | int | 标识事务的超时时间,事务须在此时间内提交,不提交则进行回滚 |
| readOnly | boolean | 设置是否只读操作,默认未false可进行增删查改操作 |
| rollbackFor | Class[] | 设置出现异常进行回滚的对象数组 |
| noRollbackFor | Class[] | 设置出现异常不进行回滚的对象数 |
2.2、propagation
2.2.1、事务传播行为
propagation即事务的传播行为,指的是一个事务方法调用另一个或另外几个事务方法这些事务方法是如何进行的,既然为传播则必须存在两个或以上的事务才会发生的行为。spring定义了以下七种事务行为,本文详解REQUIRE和REQUIRE_NEW。
| 传播属性 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| REQUIRED | 默认值,如果当前方法有事务在运行则使用当前事务,反之开启新的事务 |
| REQUIRES_NEW | 当前方法开启新的事务,如果有事务存在则挂起 |
| SUPPORTS | 如果当前方法有事务在运行则使用当前事务,反之以无事务方式运行 |
| NOT_SUPPORTED | 以无事务的方法运行,如果存在事务则挂起 |
| MANDATORY | 当前方法必须存在正在运行的事务,反之则抛出异常 |
| NEVER | 当前方法不应该存在运行的事务,反之存在事务则报错 |
| NESTED | 如果当前方法存在事务则在嵌套事务内执行,反之开启一个新的事务 |
2.2.2、Propagation.REQUIRE
package com.config;
import com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.EnableAspectJAutoProxy;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate;
import org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.EnableTransactionManagement;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
/**
* @author lin
* @version V1.0
*/
@Configuration //声明为配置类
@ComponentScan(basePackages = "com") //开启组件扫描
@EnableTransactionManagement //开启事务支持
@EnableAspectJAutoProxy //开启AOP支持
public class SpringConfig {
/**
* 创建数据库连接池
*/
@Bean
public DruidDataSource getDataSource() {
DruidDataSource dataSource = new DruidDataSource();
dataSource.setUsername("root");
dataSource.setPassword("root");
dataSource.setUrl("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/nba");
dataSource.setDriverClassName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
return dataSource;
}
/**
* 创建jdbcTemplate
*/
@Bean
public JdbcTemplate getJdbcTemplate(DataSource dataSource) {
JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate = new JdbcTemplate();
jdbcTemplate.setDataSource(dataSource);
return jdbcTemplate;
}
/**
* 创建事务管理器
*/
@Bean
public DataSourceTransactionManager getDataSourceTransactionManager(DataSource dataSource) {
DataSourceTransactionManager transactionManager = new DataSourceTransactionManager();
transactionManager.setDataSource(dataSource);
return transactionManager;
}
}
- model
package com.model;
import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;
import lombok.Data;
import lombok.NoArgsConstructor;
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
public class Student {
private String name;
private int age;
private String gender;
}
- dao
package com.dao.impl;
import com.dao.AddDao;
import com.model.Student;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Propagation;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional;
@Repository
public class AddDaoImpl implements AddDao {
@Autowired
private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
public void addStudent(Student student) {
String sql = "insert into student(name,age,gender) values (?,?,?)";
Object[] args = {
student.getName(), student.getAge(), student.getGender()};
jdbcTemplate.update(sql, args);
}
@Transactional(propagation = Propagation.REQUIRED)
public void addRequired(Student student) {
addStudent(student);
}
@Transactional(propagation = Propagation.REQUIRED)
public void addRequiredException(Student student) {
addStudent(student);
throw new RuntimeException(this.getClass() + "抛出异常!");
}
@Transactional(propagation = Propagation.REQUIRES_NEW)
public void addRequiredNew(Student student) {
addStudent(student);
}
@Transactional(propagation = Propagation.REQUIRES_NEW)
public void addRequiredNewException(Student student) {
addStudent(student);
throw new RuntimeException(this.getClass() + "抛出异常!");
}
}
package com.dao.impl;
import com.dao.DelDao;
import com.model.Student;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Propagation;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional;
@Repository
public class DelDaoImpl implements DelDao {
@Autowired
private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
public void delStudent(String name) {
String sql = "delete from student where name = ?";
jdbcTemplate.update(sql, name);
}
@Transactional(propagation = Propagation.REQUIRED)
public void delRequired(String name) {
delStudent(name);
}
@Transactional(propagation = Propagation.REQUIRED)
public void delRequiredException(String name) {
delStudent(name);
throw new RuntimeException(this.getClass() + "抛出异常!");
}
@Transactional(propagation = Propagation.REQUIRES_NEW)
public void delRequiredNew(String name) {
delStudent(name);
}
@Transactional(propagation = Propagation.REQUIRES_NEW)
public void delRequiredNewException(String name) {
delStudent(name);
throw new RuntimeException(this.getClass() + "抛出异常!");
}
}
- service
package com.service;
import com.dao.AddDao;
import com.dao.DelDao;
import com.model.Student;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
@Service(value = "service")
public class StudentService {
@Autowired
private AddDao addDao;
@Autowired
private DelDao delDao;
public void studentOpt() {
//测试代码...
}
}
- 测试
import com.config.SpringConfig;
import com.service.StudentService;
import org.junit.Before;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
public class TestAccount {
private StudentService service;
@Before
public void loadService() {
ApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(SpringConfig.class);
service = context.getBean("service", StudentService.class);
}
@Test
public void test() {
service.studentOpt();
}
}
1)场景一:service的studentOpt()方法不开启事务,内层方法开启事务模拟抛出异常
public void studentOpt() {
addDao.addRequired(new Student("Irving", 18, "男"));
//抛出异常
delDao.delRequiredException("Jordan");
}

查看数据看到数据库插入Irving这条记录,但没有删除Jordan这条记录,因为外层方法studentOpt没有开启事务,所以addRequired和delRequiredException分别开启了事务且在各自的事务中独立运行,delRequiredException方法发生异常进行回滚并不影响到addRequired方法。同样地若外层方法studentOpt不开启事务模拟抛出异常,并不影响到addRequired和delRequiredException方法。
2)场景二:service的studentOpt()方法开启事务,内层方法开启事务模拟抛出异常
@Transactional(propagation = Propagation.REQUIRED)
public void studentOpt() {
addDao.addRequired(new Student("Kevin ", 18, "男"));
//抛出异常
delDao.delRequiredException("Jordan");
}
程序同样是报错了但查看数据库记录数未改变,因外层方法studentOpt开启事务且传播级别为REQUIRED,因此addRequired和delRequiredException也和studentOpt方法内的事务为同一事务,内层方法delRequiredException抛出异常不管外层方法是否捕获都导致事务进行回滚,因此所有方法都需要回滚。同样地若外层方法studentOpt方法开启事务模拟抛出异常,所有方法都进行回滚。
3)总结
⭐⭐当外层方法开启事务并定义传播级别为Propagation.REQUIRED,所有内层方法使用Propagation.REQUIRE修饰的事务和外层方法均属于同一个事务,只要一个方法抛出异常回滚则同一事务的所有方法都进行回滚。若外层方法不开启事务则内层事务是相互独立的互不干扰的。

2.2.3、Propagation.REQUIRE_NEW
1)场景一:service的studentOpt()方法不开启事务,内层方法开启事务模拟抛出异常
public void studentOpt() {
delDao.delRequiredNew("Jordan");
//addRequiredNewException模拟抛出异常
addDao.addRequiredNewException(new Student("Kevin", 18, "男"));
}

结果和上面场景一一致的,在外层方法不开启事务的情况下内层方法的事务相互独立,只回滚当前抛出错误的事务方法不影响到其它事务。同样地不开启事务的外层方法抛出异常也不影响到内层方法的事务。
2)场景二:service的studentOpt()方法开启事务(REQUIRES_NEW),内层方法开启事务模拟抛出异常
@Transactional(propagation = Propagation.REQUIRES_NEW)
public void studentOpt() {
delDao.delRequiredNew("Kobe");
//addRequiredNewException模拟抛出异常
addDao.addRequiredException(new Student("Kevin", 18, "男"));
}

从数据库记录可以看到delRequiredNew删除"Kobe"记录成功而addRequiredException方法回滚添加"Irving"记录失败,因此外层方法即使开启了事务且感知到异常也无法进行所有操作的回滚。原因是Propagation.REQUIRES_NEW会开启新的事务则导致外层方法和两个内层方法均不为同一个事务,因此这个方法的外层事务和两个内层事务都是相互独立互不干扰的。同样地若外层方法发生错误,只会回滚外层方法的事务并不影响到内层方法的事务。
3)场景三:service的studentOpt()方法开启事务(REQUIRED),外层方法开启事务模拟抛出异常,可指定何种内层事务方法不用回滚
@Transactional(propagation = Propagation.REQUIRED)
public void studentOpt() {
addDao.addRequiredNew(new Student("Kevin", 18, "男"));
delDao.delRequired("Irving");
throw new RuntimeException(this.getClass() + "抛出异常!");
}

外层方法studentOpt事务定义为REQUIRED和内层方法delRequired一致因此使用的是同一个事务,而另一个内层事务addRequiredNew使用REQUIRES_NEW修饰因此会新建一个事务和外层事务相互独立,因此addRequiredNew方法并不会回滚。
⭐⭐注意:把delDao.delRequired(“Irving”);和addDao.addRequiredNew(new Student(“Kevin”, 18, “男”));这两句语句调换一下位置运行可查看到死锁现象,原因是外层方法和delRequired方法为同一个事务,当先执行delRequired方法删除Irving这条记录由于外层方法未执行完毕而事务未提交,因此当前事务还会持有student表导致addRequiredNew方法无法操作表,直到事务等待超时出错!
4)场景四:service的studentOpt()方法开启事务(REQUIRED),内层方法开启事务模拟抛出异常,且外层方法捕获异常使程序正常运行
@Transactional(propagation = Propagation.REQUIRED)
public void studentOpt() {
try {
addDao.addRequiredNewException(new Student("Jordan", 18, "男"));
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println(e.toString() + "---程序继续继续!");
}
delDao.delRequired("Irving");
}
程序中捕获了addRequiredNewException抛出的异常,使程序继续向下执行因此delRequired执行成功删除了Jordan这条记录,而addRequiredNewException发生错误进行回滚导致添加失败。
4)总结
⭐⭐当外层方法开启事务并定义传播级别为REQUIRES_NEW,与内层方法的其它事务相互独立互不干扰。当外层方法开启事务并使用REQUIRED修饰则与内层方法使用REQUIRED修饰的事务为同一事务,常用于控制事务操作是否需要回滚,且需注意多事务操作同一张表的情况下避免出现死锁,如下流程图为外层方法事务为REQUIRED内层方法事务为REQUIRES_NEW。

2.3、isolation
2.3.1、事务隔离级别问题的提出
在数据库操作中,为了有效保证并发读取数据的正确性,提出了事务隔离级别。下面的为读取数据时候可能出现的几种情况:
- 脏读:一个事务读取到另外一个事务未提交的数据操作结果,若加入未提交的事务发生异常进行回滚那么将发生很严重的后果
- 不可重复读:一个事务重复读取到另一个事务的数据,得到不同的结果,如读取到另一个事务未提交前的数据和提交后的数据其结果是不一致的
- 幻读:一个事务读取到了当前的数据与上一次的数据不一致,有可能是此过程中有数据的插入或删除导致的
2.3.2、事务隔离级别问题的解决
| 脏读 | 不可重复读 | 幻读 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| READ_UNCOMMITTED(读未提交) | √ | √ | √ |
| READ_COMMITTED(读已提交) | × | √ | √ |
| REPEATABLE_READ(可重复读) | × | × | √ |
| SERIALIZABLE(串行化) | × | × | × |
为了解决上述问题,在标准SQL规范中定义了上面四个隔离级别,不同的隔离级别对事务的处理如上描述。在Spring的隔离级别中还多了一个DEFAULT级别即默认的级别,该级别默认使用底层数据存储的默认隔离级别,也就是与数据库隔离级别一致。另外四个级别与JDBC的隔离级别相对应。如使用可重复读级别使用注解表示:@Transactional( isolation = Isolation.REPEATABLE_READ)。
2.4、timeout
int timeout() default TransactionDefinition.TIMEOUT_DEFAULT;
事务的超时时间即事务要在指定时间内提交,如果不提交则进行回滚。值为int类型单位为秒,若不指定默认为TransactionDefinition.TIMEOUT_DEFAULT=-1。
2.5、readOnly
boolean readOnly() default false;
设置当前事务是否为只读,默认为false可进行增删查改。可设置为true只允许读操作,若当前事务进行增删该将抛出异常,如下定义当前事务为只读事务,因此进行删除操作将抛出异常。
@Transactional(propagation = Propagation.REQUIRED, readOnly = true)
public void studentOpt() {
delDao.delRequired("Jordan");
}
2.6、rollbackFor

关于rollbackFor属性的使用重点看上面圈起来两句源码注释
- 第一个圈指明rollbackFor接收的参数类型为零个或多个异常类的数组
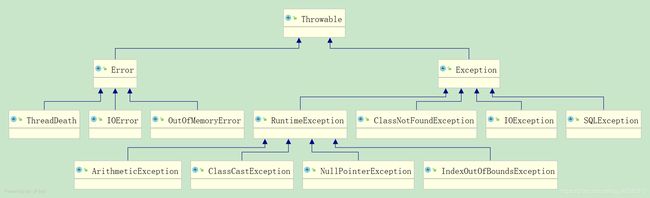
- 第二个圈说明了默认情况下会进行回滚的异常类参考DefaultTransactionAttribute下的rollbackOn()方法,可以看到该方法定义运行时异常(RuntimeException)为业务异常因此发生此类型异常会进行回滚,此外也会回滚Error,从异常的继承体系中看到编译时异常如IOException,SQLException等异常是不作回滚的
@Override
public boolean rollbackOn(Throwable ex) {
return (ex instanceof RuntimeException || ex instanceof Error);
}
- 验证:通过模拟抛出检查时异常IOException查看结果看到Kevin这条记录是插入数据库的,因此抛出错误并不会进行回滚,如需回滚IOException异常需显式指定回滚的异常类:@Transactional(propagation = Propagation.REQUIRED, rollbackFor = {java.io.IOException.class})
@Transactional(propagation = Propagation.REQUIRED)
public void studentOpt() throws IOException {
addDao.addRequired(new Student("Kevin", 18, "男"));
throw new IOException(this.getClass() + "抛出异常!");
}
2.7、noRollbackFor
String[] rollbackForClassName() default {
};
和rollbackFor使用一致,指定那些异常类不进行回滚,可自行验证。