Mysql 基础语句(一)
SQL 概述
结构化查询语言(Structured Query Language)简称SQL,是一种特殊目的的编程语言,是一种数据库查询和程序设计语言,用于存取数据以及查询、更新和管理关系数据库系统;同时也是数据库脚本的扩展名。
从上可以看出我们数据库相关的工作职位大概两种:DBA 和 DBD:
- DBA 是数据库管理人员 datebase administrator
- DBD 是数据库开发人员 database developer
SQL 是1986 年10月由美国国家标准局(ANSI)通过的数据库语言美国标准,接着,国际标准化组织(ISO)颁发了SQL正式国际标准。1989年4月,ISO提出了具有完整性特征的SQL89标准,1992年11月又公布了SQL92标准,在此标准中,把数据分成三个级别:基本集、标准集和完全集。
至于什么是基本集、标准集我们不用管,看看就行,牵扯到数据库原理额数学算法里面了。
SQL语句结构
结构化 查询语言 包含6个部分:
一:数据查询语言 (DQL:Data Query Language):
其语句,也称为“数据检索语句”,用以从表中获得数据,确定数据怎么样在应用程序给出保留字SELECT 是 DQL(也是所有SQL)用的最多的动词,其他DQL常用的保留字有 WHERE,ORDER BY ,GROUP BY 和 HAVING。这些DQL保留字与其他类型的SQL语句一起使用。
二:数据操作语言(DML:Data Manipulation Language):
其语句包括动词INSERT,UPDATE和DELETE。它们分别用于添加,修改和删除表中的行。也称为动作查询语言。
三:事务处理语言(TPL):跟shell有点类似 由多条sql语句组成的整体
它的语句能够确保DML语句影响的表的所有行及时得以更新,TPL语句包括BEGIN TRANSACTION,COMMT和ROLLBACK。
四:数据控制语言(DCL):
它的语句通过GRANT或REVOKE获得许可,确定单个用户和用户组对数据库对象的访问,某些RDBMS可用GRANT或REVOKE控制对单个列的访问。
五:数据定义语言(DDL):
其数据包括动词CREATE 和 DROP。在数据库中创建新表或删除表(CREAT TABLE 或DROP TABLE);为表加入索引等,DDL包括许多与数据库目录中获得数据相关的保留字。它也是动作查询的一部分。
六:指针控制语言(CCL):
它的语句,像DECLARE CURSOR,FETCH INTO 和 UPDATE WHERE CURRENT 用于对一个或多个表单独行的操作。
Mysql 语句
关于数据库的操作
- 查看数据库
mysql> show databases;
+--------------------+
| Database |
+--------------------+
| information_schema |
| mysql |
| performance_schema |
| sys |
+--------------------+
4 rows in set (0.00 sec)
注:
- information_schema 这数据量保存了 Mysql 服务器所有数据库的信息。如数据库名,数据库表,表栏的数据类型不访问权限等。
- performance_schema 这是 Mysql 5.5 新增的一个性能优化的引擎:命名 PERFORMANCE_SCHEMA 。主要用于收集数据库服务器性能参数,Mysql 用户是不能创建存储引擎为 PERFORMANCE_SCHEMA 的表。
- Mysql 库是系统库,里面保存有帐户信息,权限信息等。
- Mysql 5.7增加了 sys 系统数据库,通过这个库可以快速的了解系统的元数据信息,元数据是关于数据信息的数据,如数据名和表名,列的数据类型,或访问权限等。
mysql> show databases \G # 以行的方式显示
*************************** 1. row ***************************
Database: information_schema
*************************** 2. row ***************************
Database: mysql
*************************** 3. row ***************************
Database: performance_schema
*************************** 4. row ***************************
Database: sys
4 rows in set (0.00 sec)
[root@python ~]# mysql -e 'show databases' -uroot -p1
mysql: [Warning] Using a password on the command line interface can be insecure.
+--------------------+
| Database |
+--------------------+
| information_schema |
| mysql |
| performance_schema |
| sys |
+--------------------+
- mysql -e 后面我们接SQL语句,直接终端运行,后面写sql相关shell可以用到。
[root@python ~]# mysqlshow -uroot -p1
mysqlshow: [Warning] Using a password on the command line interface can be insecure.
+--------------------+
| Databases |
+--------------------+
| information_schema |
| mysql |
| performance_schema |
| sys |
+--------------------+
选择要操作的数据库:
使用 USE 语句将会选择一个数据成为当前数据库,后面的操作默认都在被选择的数据库中操作。
mysql> use mysql;
Reading table information for completion of table and column names
You can turn off this feature to get a quicker startup with -ADatabase changed
查看自己所处的位置及默认所在的位置:
mysql> select database();
+------------+
| database() |
+------------+
| mysql |
+------------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
默认:
mysql> select database();
+------------+
| database() |
+------------+
| NULL |
+------------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
- NuLL 意味着没有选择数据库
NULL 在数据中表示,不知道的数据,主要有 3 种意思:
- 知道数据存在,但不知道具体值
- 不知道数据是否存在
- 数据不存在
在命令行选择默认的数据库
mysql -uroot -p1 mysql
mysql> select now(),user(),database();
+---------------------+----------------+------------+
| now() | user() | database() |
+---------------------+----------------+------------+
| 2019-05-28 10:08:51 | root@localhost | mysql |
+---------------------+----------------+------------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
删除数据库
mysql> drop database `HA-test`;
删除时候没有任何提示,要慎重操作
方法2:直接到数据库存放目录移出就行
cd /usr/local/mysql/data/
mv HA@002dtest /tmp
mysql> show databases;
使用 IFEXISTS 子句以避免删除不存在的数据库时出现的 Mysql 错误信息。
mysql> drop database if exists `HA-test`;
IF EXISTS:如果存在
同理:我们创建数据库时也可以使用
mysql> create database if not exists HA;
关于表的操作
创建表:
语法:create table 表名 (字段名 类型,字段名 类型,字段名,类型);
mysql> create table student(id int(20),name char(40),age int);
查看表相关信息:
查看表:
要进入到数据库再查看
mysql> use mysql;
Database changed
mysql> show tables;
+--------------+
| Tables_in_HA |
+--------------+
| student |
查看表的结构:
Describe
mysql> desc student;
+-------+----------+------+-----+---------+-------+
| Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra |
+-------+----------+------+-----+---------+-------+
| id | int(20) | YES | | NULL | |
| name | char(40) | YES | | NULL | |
| age | int(11) | YES | | NULL | |
+-------+----------+------+-----+---------+-------+
3 rows in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> explain mysql.user;
mysql> show columns from mysql.user;
mysql> show fields from mysql.user;
mysql> show columns from mysql.user like '%user';
会一种就行
查看创建表执行了哪些命令:
mysql> show create table student \G
*************************** 1. row ***************************
Table: student
Create Table: CREATE TABLE `student` (
`id` int(20) DEFAULT NULL,
`name` char(40) DEFAULT NULL,
`age` int(11) DEFAULT NULL
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8
可以指定表的默认存储引擎和字符集:
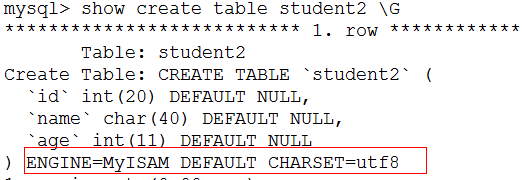
mysql> create table student2(id int(20),name char(40),age int)ENGINE=MyISAM DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
- 这两个是默认存储引擎和默认字符集
删除表:
mysql> drop table student2;
禁止预读表信息:
没有禁止前的提示
mysql> use performance_schema;
Reading table information for completion of table and column names
You can turn off this feature to get a quicker startup with -A
登录的时候加上-A参数
mysql -uroot –p123456 -A
修改表名称alter:
语法:alter table 表名 rename 新表名;
mysql> alter table student rename students; #studen表名修改为students
修改表中的字段类型:
语法:alter table 表名 modify 要修改的字段名 要修改的类型;
mysql> desc students;
+-------+----------+------+-----+---------+-------+
| Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra |
+-------+----------+------+-----+---------+-------+
| id | int(20) | YES | | NULL | |
| name | char(40) | YES | | NULL | |
| age | int(11) | YES | | NULL | |
+-------+----------+------+-----+---------+-------+
mysql> alter table students modify id int(10);
修改表中的字段类型和字段名称:
语法:alter table 表名 change 原字段名 新字段名 新字段类型;
查了一下官方文档,发现mysql还真的不支持同时修改多个字段
MODIFY [COLUMN] col_name column_definition
[FIRST | AFTER col_name]
mysql> desc students;
+-------+----------+------+-----+---------+-------+
| Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra |
+-------+----------+------+-----+---------+-------+
| id | int(10) | YES | | NULL | |
| name | char(40) | YES | | NULL | |
| age | int(11) | YES | | NULL | |
+-------+----------+------+-----+---------+-------+
mysql> alter table students change name stname char(20);
注:CHANGE 和 MODIFY的区别:
- CHANGE 对列进行重命名和更改的类型,需给定旧的列名称和新的列名称,当前的类型。
- MODIFY 可以改变列的类型,此时不需要重命名(不需给定新的列名称)
在表中添加字段:
语法:alter table 表名 add 字段名 字段类型;
mysql> alter table students add sex enum('M','W');
指定位置添加字段:
在第一列添加一个字段:
mysql> alter table students add uid int(10) first;
在age后面添加一个address字段:
mysql> alter table students add address char(40) after age;
删除表中字段:
语法:alter table 表名 drop 字段名 ;
mysql> alter table students drop address;
关于记录的操作:
插入字段<记录>insert:
语法:insert into 表名 values (字段值1,字段值2, 字段值3);
mysql> insert into student values(1,'zhangs',21);
插入记录时要对应相对的类型
mysql> insert into student values(2,'lis',24),(3,'wange',26);
同时插入多条,使用,分开
mysql> insert into students (id,name)values(4,'hangl');
指定字段插入
查询表中记录:
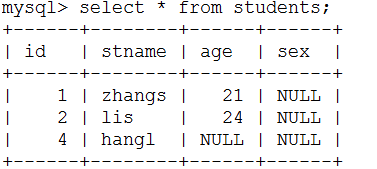
语法:select * from 表名称;
mysql> select * from student; *表示所有
当字段比较多的时候我们也可以使用\G
mysql> select * from student\G
只查询表中某个字段的内容:
mysql> select name from student;
mysql> select id,name from student;
查看别的数据库的表或者不在本数据库上进行查看:
语法:SELECT 字段 FROM 数据库名.表名;
mysql> select *from HA.student; 查看某个数据库下指定的表内容,数据库名.表名
删除记录:
删除id为3的行
mysql> delete from students where id=3;
删除age为空的行
mysql> delete from students where age is null;、
更新记录
mysql> update students set sex='M' where id=2;
mysql> update students set id=2; 所有的都变为2
update students set stname='zhangsan',age=21 where uid=1;
同时更新多个字段时候用,号隔开