set容器及multiset容器
导航
1.set容器及multiset容器基础知识
2.set交换与大小
3.set容器插入与删除
4.set容器查找与统计
5.set与multiset容器的区别
6.pair对组的创建方式
7.set容器排序(改变排序规则)
———————————————————————————————————
1.set容器及multiset容器基础知识
set与multiset都是关联式容器,所有被插入时都会自动排序
set与multiset容器区别:
1.set不能再容器中有重复的数
2.multiset允许容器中有重复的元素
构造函数:
set< T > st
set(const set& st)
赋值:
operator= //赋值
set例子:
#include 运行结果:

———————————————————————————————————
2.set交换与大小
size() //容量
empty(); //若是容器空为1,不空为0
swap() //交换容器
———————————————————————————————————
3.set容器插入与删除
insert() //插入
clear() //清除
erase(pos) //清除pos迭代器所指元素,返回下一个元素
erase(beg,end) //迭代器指向的区间
erase(elem) //删除容器中为elem的元素
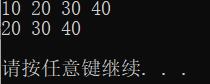
例子:
#include 运行结果:
———————————————————————————————————
4.set容器查找与统计
find(key) //找到返回对应元素的迭代器,没有找到返回.end()
cout(key) //set容器中没有重复的数,所以返回0或1
例子:
#include 运行程序:

———————————————————————————————————
5.set与multiset容器的区别
set插入数据时会返回插入的结果,结果表示插入是否成功
multiset不会检测数据,因此可以插入重复的数据
检验:
#include 运行结果:

———————————————————————————————————
6.pair对组的创建方式
说明:成对成线的数据,利用对组可以返回两个数据
两种创建方式:
pair< type,type>p(value,value)
pair< type,typoe> p = make_pair(value,value)
例子:
#include 运行结果:

———————————————————————————————————
7.set容器排序(改变排序规则)
set容器默认插入时从小到大排序,如何改变排序规则?
利用仿函数,可以改变排序规则,必须在插入数之前确定排序方式
例子:
#include 若插入自定义数据,如何指定排序规则
例子:
#include 
