Nginx之常用配置案例
Nginx之常用配置案例
文章目录
- Nginx之常用配置案例
-
- 1. Nginx 虚拟主机配置
-
- 1.1 基于不同域名和不同端口的虚拟主机
- 1.2 基于不同IP和不同端口的虚拟主机
- 1.3 基于通配符的虚拟主机
- 1.4 基于正则表达式的虚拟主机
- 2. Nginx 访问控制
- 3. Nginx 基于用户认证
- 4. Nginx 下载站点
- 5. Nginx 状态监控
- 6. Nginx 重写规则
- 7. Nginx if判断
- 8. Nginx 防盗链
- 9. Nginx 代理服务及缓存
-
- 9.1 Nginx代理简述
- 9.2 Nginx反向代理模块详解
- 2.1 反向代理常用指令
- 9.3 Nginx正向代理配置
- 9.4 Nginx反向代理配置
- 9.5 Nginx反向代理缓存配置
- 10. Nginx 静态资源压缩
-
- 10.1 静态资源类型
- 10.2 静态资源压缩场景
- 10.3 配置案例
-
- 10.3.1 全局压缩案例
- 10.3.2 图片压缩案例
- 10.3.3 文件压缩案例
- 11. Nginx 静态资源浏览器缓存
- 12. Nginx 七层负载均衡
1. Nginx 虚拟主机配置
在web服务器里,虚拟主机是一个独立的网站,这个站点对应独立的域名/IP/PORT,具有独立的处理配置及资源目录,可以独立的向外提供web服务,供用户访问。
1.1 基于不同域名和不同端口的虚拟主机
## 配置域名解析,创建站点目录和文件
[root@lbserver ~]# echo '10.241.96.103 web01.chan.com web01' >> /etc/hosts
[root@lbserver ~]# echo '10.241.96.103 web02.chan.com web02' >> /etc/hosts
[root@lbserver ~]# mkdir /web/static/{web01,web02} -p
[root@lbserver ~]# echo 'web01.chan.com' > /web/static/web01/index.html
[root@lbserver ~]# echo 'web02.chan.com' > /web/static/web02/index.html
[root@lbserver nginx]# cat /etc/nginx/conf.d/{web01,web02}.conf
server {
listen 8080;
server_name web01.chan.com;
location / {
root /web/static/web01;
index index.html;
}
}
server {
listen 8081;
server_name web02.chan.com;
location / {
root /web/static/web02;
index index.html;
}
}
[root@lbserver ~]# curl http://web02.chan.com:8080/
web01.chan.com
[root@lbserver ~]# curl http://web02.chan.com:8081/
web02.chan.com
1.2 基于不同IP和不同端口的虚拟主机
## 配置虚拟主机
[root@lbserver conf.d]# cat /etc/nginx/conf.d/{web01,web02}.conf
server {
listen 10.241.96.104:8080;
server_name web01.chan.com;
location / {
root /web/static/web01;
index index.html;
}
}
server {
listen 10.241.96.105:8081;
server_name web02.chan.com;
location / {
root /web/static/web02;
index index.html;
}
}
## 访问测试
[root@lbserver ~]# curl http://10.241.96.104:8080/
web01.chan.com
[root@lbserver ~]# curl http://10.241.96.105:8081/
web02.chan.com
## 无法通过其他IP访问
[root@lbserver ~]# curl http://10.241.96.104:8081/
curl: (7) Failed connect to 10.241.96.104:8081; Connection refused
[root@lbserver ~]# curl http://10.241.96.105:8080/
curl: (7) Failed connect to 10.241.96.105:8080; Connection refused
1.3 基于通配符的虚拟主机
## 配置虚拟主机
[root@lbserver ~]# cat /etc/nginx/conf.d/web01.conf
server {
listen 8080;
server_name *.chan.com;
location / {
root /web/static/web01;
index index.html;
}
}
## 访问测试
[root@lbserver ~]# curl http://web01.chan.com:8080/
web01.chan.com
1.4 基于正则表达式的虚拟主机
## 配置虚拟主机
server {
listen 8081;
server_name ~^ .*\.chan\.com$;
location / {
root /web/static/web02;
index index.html;
}
}
## 访问测试
[root@lbserver ~]# curl http://web02.chan.com:8081/
web02.chan.com
更多的配置方法参照官方手册
2. Nginx 访问控制
配置基于IP的访问控制
## 允许10.241.96.1访问,拒绝其他所有IP访问
server {
listen 8080;
server_name *.chan.com;
location / {
root /web/static/web01;
index index.html;
allow 10.241.96.1;
deny all;
}
}
## 拒绝某个网段访问,允许其他所有;
server {
listen 8080;
server_name *.chan.com;
location / {
root /web/static/web01;
index index.html;
deny 10.241.96.0/24;
allow all;
}
}
3. Nginx 基于用户认证
nginx的用户认证依赖于httpd-tools工具
## 安装依赖工具
[root@lbserver ~]# yum install httpd-tools
## 创建用户认证配置文件
[root@lbserver ~]# htpasswd -c /etc/nginx/auth_config chan
New password:
Re-type new password:
Adding password for user chan
## 配置虚拟主机
[root@lbserver ~]# cat /etc/nginx/conf.d/web01.conf
server {
listen 8080;
server_name *.chan.com;
auth_basic "test";
auth_basic_user_file /etc/nginx/auth_config;
location / {
root /web/static/web01;
index index.html;
allow 10.241.96.1;
deny all;
}
}
4. Nginx 下载站点
Nginx默认是没有列出整个目录浏览下载的
## 虚拟主机配置如下,开启/autoindex目录的站点下载选项
[root@lbserver nginx]# cat conf.d/web01.conf
server {
listen 8080;
server_name *.chan.com;
default_type "text/html";
charset utf-8; ## 解决中文乱码
location /autoindex {
root /web/static/web01;
index index.html;
autoindex on;
autoindex_localtime on;
autoindex_exact_size off;
}
}
5. Nginx 状态监控
可以指定URI输出stub_status,它记录了nginx的客户端基本访问连接的状态信息;
## 配置stub_status
[root@lbserver ~]# cat /etc/nginx/nginx.conf
...
location /status {
stub_status on;
access_log off;
allow 127.0.0.1;
deny all;
}
...
## 测试
[root@lbserver ~]# curl http://127.0.0.1/status
Active connections: 1
server accepts handled requests
5 5 16
Reading: 0 Writing: 1 Waiting: 0
以上各字段的含义如下:
Active connections #Nginx正在处理的活动连接数为 2
accepts #Nginx启动到现在接受并处理了6个连接
handled #Nginx启动到现在成功创建了6次握手
requests #Nginx总共处理了15次请求
Reading #Nginx读取到客户端连接请求的Header信息数为 0
Writing #Nginx响应给客户端连接请求的Header信息数为 1
Waiting #Nginx已经处理完正在等候下一次请求的驻留链接数为 1,开启keep-alive的情况下,这个值等于Active - ( Reading + Writing )。
丢失请求数 = ( accepts - server ),从以上状态结果可以看出没有丢失请求。
6. Nginx 重写规则
语法: rewrite regex replacement [flag];
默认: —
位置: server, location, if
regex:正则表达式,用于匹配用户请求的URL;
replacement:重写为新的URL;
flag:标志位,包含last | break | redirect | permanet,每个标志位代表不同的含义;
-
last:重写完成后,停止对用户请求的URL进一步处理,重新为新的URL后,重新为的URL进行处理并进行匹配;相当于循环,最多循环10次,10次之后返回500错误;
-
break:重写完成后,停止对用户请求的URL进一步处理,继续执行后面的配置;
-
redirect:重写完成后,会返回给客户端一个临时重定向,由客户端对新的URL重新发起请求(302);
-
permanent:重写完成后,会返回给客户端一个永久重定向,由客户端对新的URL重新发起请求(301);
PCRE正则表达式元字符:
字符匹配:., [ ], [^]
次数匹配:*, +, ?, {m}, {m,}, {m,n}
位置锚定:^, $
或者:|
分组:(), 后向引用, $1, $2, …
1)last标志位示例:循环10次并返回500错误
## 配置rewrite
[root@lbserver html]# cat /etc/nginx/nginx.conf
...
location / {
root /web/html;
index index.html index.htm;
## 匹配/config-a/index.html后重写URL为/rewrite/index.html,并继续处理新的URL
rewrite ^/config-a/(.*\.html)$ /rewrite/$1 last;
## 匹配/rewrite/index.html后重写URL为/config-a/index.html,并继续处理新的URL
rewrite ^/rewrite/(.*\.html)$ /config-a/$1 last;
## 循环10次后返回给客户端500错误
}
...
## 访问测试
[root@lbserver ~]# curl http://10.241.96.103/config-a/index.html
500 Internal Server Error
500 Internal Server Error
nginx/1.12.2
[root@lbserver ~]# curl http://10.241.96.103/rewrite/index.html
500 Internal Server Error
500 Internal Server Error
nginx/1.12.2
## 查看日志
[root@lbserver ~]# tail -f /var/log/nginx/error.log
2018/12/29 22:59:44 [error] 1743#0: *1 rewrite or internal redirection cycle while processing "/rewrite/index.html", client: 10.241.96.103, server: localhost, request: "GET /config-a/index.html HTTP/1.1", host: "10.241.96.103"
2018/12/29 23:01:09 [error] 1743#0: *2 rewrite or internal redirection cycle while processing "/config-a/index.html", client: 10.241.96.103, server: localhost, request: "GET /rewrite/index.html HTTP/1.1", host: "10.241.96.103"
由此,我们可以看到测试结果返回了500错误,并且error.log也给出了错误日志;
在生产环境,严禁出现这种配置;
2)break标志位示例:
- 简单重写规则
[root@lbserver ~]# cat /web/html/config-a/index.html
config-a
[root@lbserver ~]# cat /web/html/rewrite/index.html
重写后的URL
## 配置rewrite规则
[root@lbserver html]# cat /etc/nginx/nginx.conf
...
location / {
root /web/html;
index index.html index.htm;
rewrite ^/config-a/(.*\.html)$ /rewrite/$1 break;
}
...
[root@lbserver ~]# curl http://10.241.96.103/config-a/index.html
重写后的URL
用户请求http://10.241.96.103/config-a/index.html后匹配到了如上rewrite规则,重写URL为http://10.241.96.103/rewrite/index.html后返回给客户端
- 多条rewrite规则,break和last配合使用;
[root@lbserver html]# cat /etc/nginx/nginx.conf
...
location / {
root /web/html;
index index.html index.htm;
rewrite ^/(config-b)/(.*\.html)$ /config-c/test/$2 break; ## 第一条
rewrite ^/config-a/(.*\.html)$ /rewrite/$1 last; ## 第二条
rewrite ^/rewrite/(.*\.html)$ /config-b/$1 last; ## 第三条
}
...
用户请求http://10.241.96.103/config-a/index.html后匹配到了如上第二条规则,重写URL为http://10.241.96.103/rewrite/index.html,last继续处理匹配到了如上第三条规则,重写URL为http://10.241.96.103/config-b/index.html,last继续处理匹配到第一条规则,重写URL为http://10.241.96.103/config-c/test/index.html,break结束并返回给客户端。
3)redirect标志位示例:302重定向
在生产环境,我们可能需要将用户访问的旧就域名,临时重定向到新的域名。
302 Found 请求的资源现在临时从不同的URI响应请求。由于这样的重定向是临时的,客户端应当继续向原有地址发送以后的请求。只有在Cache-Control或Expires中进行了指定的情况下,这个响应才是可缓存的。
## 配置如下
[root@lbserver ~]# cat /etc/nginx/conf.d/web01.conf
server {
listen 8080;
server_name *.chan.com;
default_type "text/html";
charset utf-8;
location / {
root /web/static/web01;
index index.html;
rewrite ^/(.*\.html)$ http://web02.chan.com:8081/$1 redirect;
#autoindex on;
#autoindex_localtime on;
#autoindex_exact_size off;
}
}
## 测试
[root@lbserver ~]# curl http://web01.chan.com:8080/index.html
302 Found
302 Found
nginx/1.12.2
4)parmenent标志位示例:
在生产环境,我们可能需要将用户访问的旧就域名,临时重定向到新的域名。
301 Moved Permanently 被请求的资源已永久移动到新位置,并且将来任何对此资源的引用都应该使用本响应返回的若干个URI之一。如果可能,拥有链接编辑功能的客户端应当自动把请求的地址修改为从服务器反馈回来的地址。除非额外指定,否则这个响应也是可缓存的。
注意: 301请求是可以缓存的, 即通过看status code,可以发现后面写着from cache。
[root@lbserver ~]# cat /etc/nginx/conf.d/web01.conf
server {
listen 8080;
server_name *.chan.com;
default_type "text/html";
charset utf-8;
location / {
root /web/static/web01;
index index.html;
rewrite ^/(.*\.html)$ http://web02.chan.com:8081/$1 permanent;
}
}
## 测试
[root@lbserver ~]# curl http://web01.chan.com:8080/index.html
301 Moved Permanently
301 Moved Permanently
nginx/1.12.2
redirect(302)重定向和permanent(301)重定向的区别:
302重定向只是暂时的重定向,搜索引擎会抓取新的内容而保留旧的地址,因为服务器返回302,所以,搜索搜索引擎认为新的网址是暂时的。而301重定向是永久的重定向,搜索引擎在抓取新的内容的同时也将旧的网址替换为了重定向之后的网址。
7. Nginx if判断
8. Nginx 防盗链
所谓防盗链即指当我们的网站的图片、视频等媒体文件被其他网站非法链接引用时,就需要采取判断机制对除本网站以外的其他网站采用一种防盗用措施;
- 在web01.chan.com站点配置防盗链
## 配置虚拟机主机
[root@lbserver ~]# cat /etc/nginx/conf.d/web01.conf
server {
listen 8080;
server_name *.chan.com;
default_type "text/html";
charset utf-8;
location / {
root /web/static/web01;
index index.html;
}
## 配置防盗链
location ~* \.(jpg|jpeg|png|gif|bmp)$ {
root /web/static/web01;
valid_referers none blocked web01.chan.com; ## 合法的引用者为web01.chan.com站点
if ($invalid_referer) {
rewrite ^/ http://web01.chan.com/403.html;
}
}
}
- 在web02.chan.com引用web01.chan.com的图片
[root@lbserver ~]# cat /web/static/web02/index.html
web02

- 访问测试
访问web01.chan.com站点图片可正常显示
访问web02.chan.com站点无法正常显示;
9. Nginx 代理服务及缓存
9.1 Nginx代理简述
1)什么是正向代理?
正向代理(forward proxy)通常指的是客户端和原始服务器之间的代理服务器。当客户端想要从原始服务器获取相应的资源时,客户端会想代理服务器发送请求报文并指定原始服务器,代理服务器在收到客户端请求后,代替客户端向原始服务器发送请求报文,原始服务器将响应报文返回给代理服务器,代理服务器再返回给客户端。该代理服务器即为正向代理服务器
一般正向代理的使用场景是局域网中的客户端无法上网,却希望上网,就需要通过内网中能上网的代理服务器代替其向因特网获取资源,并由其返回给客户端。
正向代理:客户端 <------> 代理服务器 <------> internet <------> 原始服务器
正向代理的代理对象是客户端
2)什么是反向代理?
反向代理(reverse proxy)通常指的是以代理服务器来接受来自internet的客户端连接请求,然后将请求转发给内网服务器处理,并将内网服务器返回的结果返回给internet上发送请求的客户端。该代理服务器即为反向代理服务器。
正向代理:客户端 <------> internet <------> 代理服务器 <------> 原始服务器
反向代理的代理对象是服务器
9.2 Nginx反向代理模块详解
Nginx的反向代理模块是ngx_http_proxy_module。在作为web反向代理服务器时,nginx负责接收客户端请求,并能够根据URI、客户端请求报文、参数或其他处理逻辑将用户的请求调度至上游服务器(upstream server)。Nginx在实现reverse proxy时,最重要的指令便是proxy_pass,它能够将location定义的URI代理至上游服务器上。如下面的示例中,location中的URI被替换至上游服务器的/newuri
location /uri {
proxy_pass http://10.241.96.104:8000/newuri;
proxy_set_header Host $host;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
}
Nginx的如上反向代理机制有两个例外:
1)第一个例外
如果location使用模式匹配定义URI,那么其URI将直接被传递至上游服务器,而不能指定转换为上游服务器上的另一个URI。如下面示例中/uri将被代理为http://10.241.96.1:8000/uri。
location ~ /uri {
proxy_pass http://10.241.96.104:8000;
proxy_set_header Host $host;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
}
2)第二个例外
如果在location中的proxy_pass之前使用了rewrite重定向,那么,nginx将使用重定向后的URI处理请求,而不再考虑上游服务器定义的URI。如下面示例中,传递给上游服务器的是/index.php?page=$1,而不是/index
location / {
rewirte /(.*)$ /index.php?page=$1 break;
proxy_pass http://10.241.96.104:8000/index;
proxy_set_header Host $host;
}
2.1 反向代理常用指令
官方文档URL:http://nginx.org/en/docs/http/ngx_http_proxy_module.html
1)常用配置指令
proxy模块的可用配置指令非常多,它们分别用于定义proxy模块工作时的诸多属性,如连接超时时长、代理时使用http协议版本等。
-
proxy_connect_timeout
nginx将一个请求发送至upstream server之前等待的最大时长;
-
proxy_cookie_domain
将upstream server通过Set-Cookie首部设定的domain属性修改为指定的值,其值可以为一个字符串、正则表达式的模式或一个引用的变量;
-
proxy_cookie_path
将upstream server通过Set-Cookie首部设定的path属性修改为指定的值,其值可以为一个字符串、正则表达式的模式或一个引用的变量;
-
proxy_hide_header
设定发送给客户端的报文中需要隐藏的首部;
-
proxy_pass
指定将请求代理至upstream server的URL路径;
-
proxy_set_header
将发送至upsream server的报文的某首部进行重写;
-
proxy_redirect
重写location并刷新从upstream server收到的报文的首部;
-
proxy_send_timeout
在连接断开之前两次发送至upstream server的写操作的最大间隔时长;
-
proxy_read_timeout
在连接断开之前两次从接收upstream server接收读操作的最大间隔时长;
如下面的示例:
proxy_redirect off;
proxy_set_header Host $host;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
client_max_body_size 10m;
client_body_buffer_size 128k;
proxy_connect_timeout 30;
proxy_send_timeout 15;
proxy_read_timeout 15;
2)常用缓存指令
nginx做为反向代理时,能够将来自upstream的响应缓存至本地,并在后续的客户端请求同样内容时直接从本地构造响应报文。
-
proxy_cache zone|off
定义一个用于缓存的共享内存区域,其可被多个地方调用;缓存将遵从upstream服务器的响应报文首部中关于缓存的设定,如 “Expires”、“Cache-Control: no-cache”、 “Cache-Control: max-age=XXX”、“private"和"no-store” 等,但nginx在缓存时不会考虑响应报文的"Vary"首部。为了确保私有信息不被缓存,所有关于用户的私有信息可以upstream上通过"no-cache" or "max-age=0"来实现,也可在nginx设定proxy_cache_key必须包含用户特有数据如$cookie_xxx的方式实现,但最后这种方式在公共缓存上使用可能会有风险。因此,在响应报文中含有以下首部或指定标志的报文将不会被缓存。
Set-Cookie
Cache-Control containing “no-cache”, “no-store”, “private”, or a “max-age” with a non-numeric or 0 value
Expires with a time in the past
X-Accel-Expires: 0 -
proxy_cache_key
$uri设定在存储及检索缓存时用于“键”的字符串,可以使用变量为其值,但使用不当时有可能会为同一个内容缓存多次;另外,将用户私有信息用于键可以避免将用户的私有信息返回给其它用户;
-
proxy_cache_lock
启用此项,可在缓存未命令中阻止多个相同的请求同时发往upstream,其生效范围为worker级别;
-
proxy_cache_lock_timeout
proxy_cache_lock功能的锁定时长;
-
proxy_cache_min_uses
某响应报文被缓存之前至少应该被请求的次数;
-
proxy_cache_path
定义一个用记保存缓存响应报文的目录,及一个保存缓存对象的键及响应元数据的共享内存区域(keys_zone=name:size),其可选参数有:
levels:每级子目录名称的长度,有效值为1或2,每级之间使用冒号分隔,最多为3级;
inactive:非活动缓存项从缓存中剔除之前的最大缓存时长;
max_size:缓存空间大小的上限,当需要缓存的对象超出此空间限定时,缓存管理器将基于LRU算法对其进行清理;
loader_files:缓存加载器(cache_loader)的每次工作过程最多为多少个文件加载元数据;
loader_sleep:缓存加载器的每次迭代工作之后的睡眠时长;
loader_threashold:缓存加载器的最大睡眠时长;
例如:
proxy_cache_path /data/nginx/cache/one levels=1 keys_zone=one:10m;
proxy_cache_path /data/nginx/cache/two levels=2:2 keys_zone=two:100m;
proxy_cache_path /data/nginx/cache/three levels=1:1:2 keys_zone=three:1000m;
-
proxy_cache_use_stale
在无法联系到upstream服务器时的哪种情形下(如error、timeout或http_500等)让nginx使用本地缓存的过期的缓存对象直接响应客户端请求;其格式为:
proxy_cache_use_stale error | timeout | invalid_header | updating | http_500 | http_502 | http_503 | http_504 | http_404 | off -
proxy_cache_valid [ code …] time
用于为不同的响应设定不同时长的有效缓存时长,例如:proxy_cache_valid 200 302 10m;
-
proxy_cache_methods [GET HEAD POST]
为哪些请求方法启用缓存功能;
-
proxy_cache_bypass string
设定在哪种情形下,nginx将不从缓存中取数据;例如:
proxy_cache_bypass $cookie_nocache $arg_nocache $arg_comment;
proxy_cache_bypass $http_pragma $http_authorization;
-
proxy_connect_timeout
定义与后端服务器建立连接的超时时长;默认为60s,不建议超出75s;
-
proxy_send_timeout
把请求发送给后端服务器的超时时长;默认为60s;
-
proxy_read_timeout
等待后端服务器发送响应报文的超时时长;
9.3 Nginx正向代理配置
server {
listen 80;
resolver 10.241.96.7 ipv6=off;
location / {
proxy_pass http://$http_host$request_uri;
proxy_set_header Host $http_host;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
}
}
//客户端使用SwitchySharp浏览器插件配置正向代理
9.4 Nginx反向代理配置
上游服务器是zabbix server:10.241.96.121,并且上游服务器是LAMP的站点架构,nginx作为代理服务器如下场景配置
示例配置一:
location / {
proxy_pass http://10.241.96.121;
proxy_set_header Host $host;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
}
访问测试
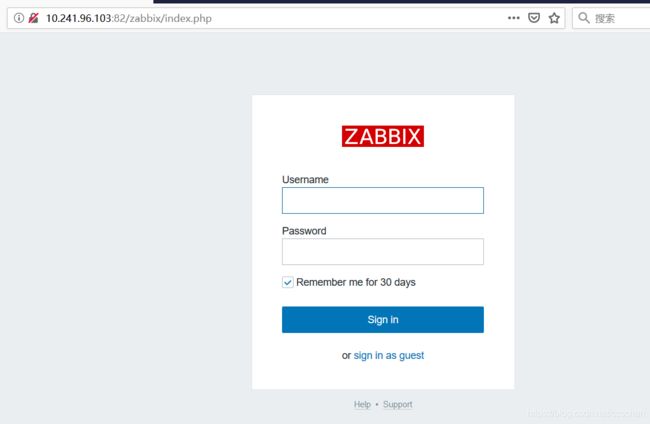
[root@lbserver ~]# curl -I http://10.241.96.103:82/zabbix/
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Server: nginx/1.12.2
Date: Wed, 02 Jan 2019 15:09:19 GMT
Content-Type: text/html; charset=UTF-8
Connection: keep-alive
X-Powered-By: PHP/5.4.16
Set-Cookie: zbx_sessionid=214c8aed8456c9514b4791e9957d13ca; httponly
Set-Cookie: PHPSESSID=4ctmt8j12978sj7cmh4v3ao110; path=/zabbix/; HttpOnly
Expires: Thu, 19 Nov 1981 08:52:00 GMT
Cache-Control: no-store, no-cache, must-revalidate, post-check=0, pre-check=0
Pragma: no-cache
X-Content-Type-Options: nosniff
X-XSS-Protection: 1; mode=block
X-Frame-Options: SAMEORIGIN
示例配置二:
location / {
root html;
index index.html index.htm;
}
location ~ /zabbix {
proxy_pass http://10.241.96.121;
proxy_set_header Host $host;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
}
访问测试
[root@lbserver ~]# curl -I http://10.241.96.103:82/zabbix/
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Server: nginx/1.12.2
Date: Wed, 02 Jan 2019 15:07:09 GMT
Content-Type: text/html; charset=UTF-8
Connection: keep-alive
X-Powered-By: PHP/5.4.16
Set-Cookie: zbx_sessionid=80f7add490643c5c6935885fc7ca6bd1; httponly
Set-Cookie: PHPSESSID=60bp2ejd7hujgd1vgvsjttc8n7; path=/zabbix/; HttpOnly
Expires: Thu, 19 Nov 1981 08:52:00 GMT
Cache-Control: no-store, no-cache, must-revalidate, post-check=0, pre-check=0
Pragma: no-cache
X-Content-Type-Options: nosniff
X-XSS-Protection: 1; mode=block
X-Frame-Options: SAMEORIGIN
示例配置三:
location / {
rewrite /(.*)$ /$1 break;
proxy_pass http://10.241.96.121/test;
proxy_set_header Host $host;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
}
访问测试:
[root@lbserver ~]# curl -I http://10.241.96.103:82/zabbix/
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Server: nginx/1.12.2
Date: Wed, 02 Jan 2019 15:05:15 GMT
Content-Type: text/html; charset=UTF-8
Connection: keep-alive
X-Powered-By: PHP/5.4.16
Set-Cookie: zbx_sessionid=016f5b6155f1d4b1deeeab732caec000; httponly
Set-Cookie: PHPSESSID=lepogt22l0b9rpgrou6r6trig3; path=/zabbix/; HttpOnly
Expires: Thu, 19 Nov 1981 08:52:00 GMT
Cache-Control: no-store, no-cache, must-revalidate, post-check=0, pre-check=0
Pragma: no-cache
X-Content-Type-Options: nosniff
X-XSS-Protection: 1; mode=block
X-Frame-Options: SAMEORIGIN
9.5 Nginx反向代理缓存配置
## 缓存配置
[root@lbserver ~]# cat /etc/nginx/nginx.conf
http {
...
proxy_cache_path /cache/mycache levels=2:2 keys_zone=mycache:32m inactive=24h max_size=1g;
...
server {
listen 82;
server_name localhost;
#charset koi8-r;
#access_log logs/host.access.log main;
location / {
proxy_pass http://10.241.96.121;
proxy_set_header Host $host;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
proxy_cache mycache;
proxy_cache_valid 200 1h;
proxy_cache_valid 301 302 10m;
proxy_cache_valid any 1m;
proxy_cache_use_stale error timeout invalid_header updating http_500 http_502 http_503 http_504;
proxy_connect_timeout 30s;
proxy_send_timeout 30s;
proxy_read_timeout 30s;
}
}
}
## 创建缓存目录,并修改属主属组为nginx
[root@lbserver nginx]# mkdir /cache/mycache -pv
mkdir: created directory ‘/cache’
mkdir: created directory ‘/cache/mycache’
[root@lbserver nginx]# chown -R nginx:nginx /cache/
访问测试之后,/cache/mycache目录已经缓存响应的缓存文件;
[root@lbserver nginx]# tree /cache/mycache/
/cache/mycache/
├── 5d
│ └── e9
│ └── e3853a16eef4c318c1884f98799fe95d
├── 60
│ └── 12
│ └── 726a69a4bd5162f9852731cf461f1260
├── 65
│ └── e0
│ └── 108e280ae84be248571aa76b26bde065
├── 6a
│ └── 0c
│ └── 11ec30c52554d28a6f8df373e5710c6a
├── 93
│ └── 31
│ └── 2b3c006ae7de6f499050603ab7d93193
└── ea
└── 23
注意:对于动态内容,一般情况下,需要开发自行定义需要缓存哪些页面;因为某些动态页面是需要不停的更新的,如果缓存后,用户访问的可能是旧的数据。
10. Nginx 静态资源压缩
Nginx的ngx_http_gzip_module模块提供了静态资源压缩功能。
该模块的相关指令可参照官方文档查阅
10.1 静态资源类型
静态资源指的非服务器动态运行生成的相关文件;比如常见的动态文件有.php,.jsp等后缀结尾的;
静态资源可以概括一下积累:
| 类型 | 种类 |
|---|---|
| 浏览器端渲染 | HTML、CSS、JS |
| 图片 | JPEG、GIF、PNG |
| 音频 | FLV、MP3、Mp4 |
| 文件 | TXT、XML、其他文本类型的文件 |
10.2 静态资源压缩场景
Nginx在作为静态web服务器时,为了传输高效及节省服务器带宽、降低I/O、减少网络带宽、提高服务器并发性能等,那么有必要启用静态资源压缩功能。
10.3 配置案例
ngx_http_gzip_module模块中的相关指令可以放在http、server、location的上下文中,这里按这3个配置并提供不同业务需求。
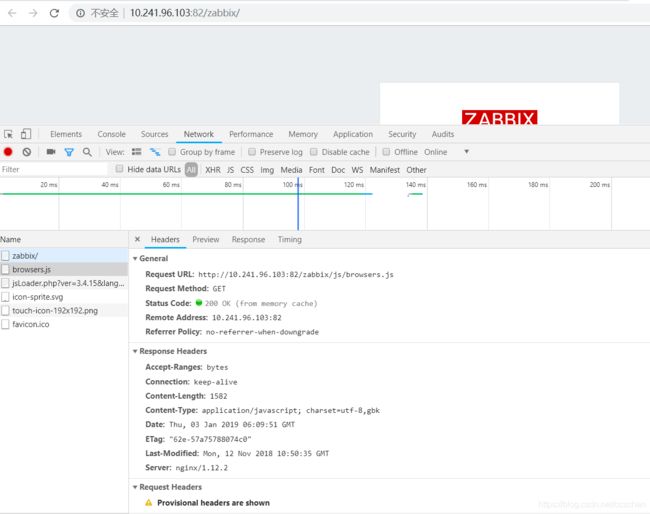
对于我们所代理的zabbix服务器,现在是没有配置gzip压缩功能的,如下图
10.3.1 全局压缩案例
这里的全局指的是在http中配置gzip等指令,在http同配置的gzip为server/location提供默认压缩配置。
示例配置如下:
[root@lbserver ~]# cat /etc/nginx/nginx.conf
...
http {
...
gzip on;
gzip_http_version 1.1;
gzip_buffers 16 8k;
gzip_comp_level 1;
gzip_min_length 1024;
gzip_proxied any;
gzip_vary on;
gzip_disable "MSIE[1-6]\.(?!.*SV1)";
gzip_types text/plain application/json application/javascript application/x-javascript application/css application/xml application/xml+rss text/javascript text/css application/x-httpd-php image/jpeg image/jpg image/gif image/png image/svg+xml;
server {
listen 82;
server_name localhost;
location / {
proxy_pass http://10.241.96.121;
proxy_set_header Host $host;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
proxy_cache mycache;
proxy_cache_valid 200 1h;
proxy_cache_valid 301 302 10m;
proxy_cache_valid any 1m;
proxy_cache_use_stale error timeout invalid_header updating http_500 http_502 http_503 http_504;
proxy_connect_timeout 30s;
proxy_send_timeout 30s;
proxy_read_timeout 30s;
}
}
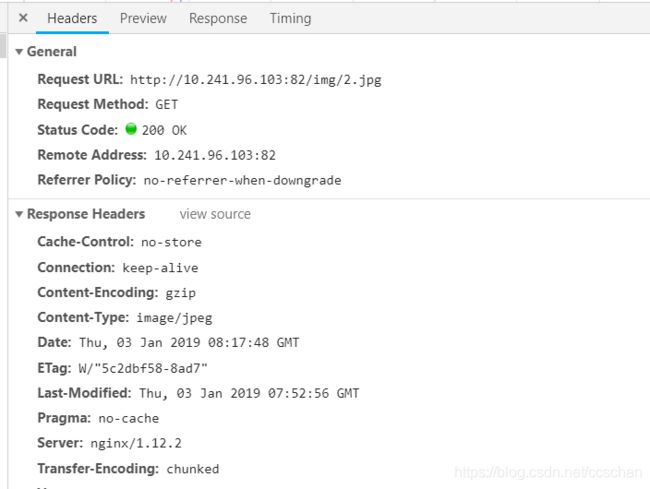
访问测试
10.3.2 图片压缩案例
我们将gzip指令配置到指定图片目录的location
示例配置如下:
location ~ .*\.(jpg|gif|png)$ {
gzip on;
gzip_http_version 1.1;
gzip_comp_level 2;
gzip_types text/plain application/json application/javascript application/x-javascript application/css application/xml application/xml+rss text/javascript text/css application/x-httpd-php image/jpeg image/jpg image/gif image/png image/svg+xml;
root /data/images;
}
10.3.3 文件压缩案例
我们将gzip指令配置到指定图片目录的location
示例配置如下:
location ~ .*\.(txt|xml)$ {
gzip on;
gzip_http_version 1.1;
gzip_comp_level 1;
gzip_types text/plain application/json application/javascript application/x-javascript application/css application/xml application/xml+rss text/javascript text/css application/x-httpd-php image/jpeg image/jpg image/gif image/png image/svg+xml;
root /data/htdocs;
由此,我们可以对不同的location/server配置不同的压缩等级、压缩是否开启等不同的方案。
11. Nginx 静态资源浏览器缓存
Nginx的ngx_http_headers_module模块提供设置静态资源浏览器缓存的功能。
该模块的相关指令可参照官方文档查阅
在HTTP协议中,定义了静态文件的缓存机制,如Expires,Cache-control等;如果在Nginx配置中同时定义了Expires和Cache-control,则以Cache-control定义的生效,因为Cache-control的优先级高于expires
浏览器有缓存:浏览器请求 -> 无缓存 -> 请求web服务器 -> 收到响应 -> 缓存
浏览器无缓存:浏览器请求 -> 有缓存 -> 校验是否过期 -> 确认是否有更新 -> 呈现
1)使用expire指令配置静态资源浏览器缓存
示例配置:
location ~ .*\.(js|css|html)$ {
root /data/htdocs;
expires 1h;
}
location ~ .*\.(jpg|gif|png)$ {
root /data/htdocs;
expires 7d;
}
访问测试
2)使用expire指令配置静态资源浏览器不缓存
示例配置
location ~ .*\.(js|css|html)$ {
root /data/htdocs;
expires 1h;
}
location ~ .*\.(jpg|gif|png)$ {
root /data/htdocs;
expires -1;
}
访问测试
2)使用add_header Cache-control配置静态资源不被浏览器缓存
这种方式同样适用于开发代码还在测试环境测试阶段时使用,希望静态文件不被缓存。
[root@lbserver ~]# tree /data/htdocs/
/data/htdocs/
├── images
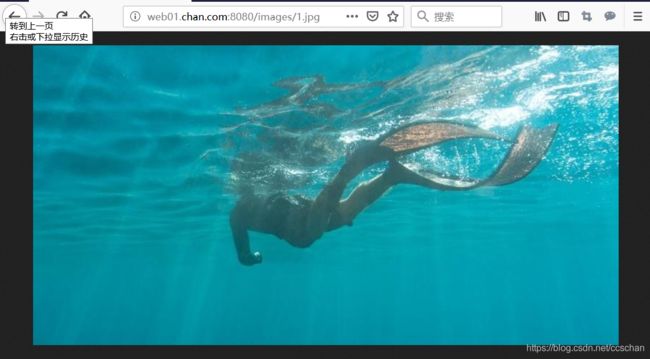
│ └── 1.jpg
└── img
└── 2.jpg
## 配置/images目录下的图片缓存,加入if配置/img目录下的图片不缓存
location ^~ /img/ {
root /data/htdocs;
add_header Cache-control "no-store";
add_header Pragma no-cache;
}
location ~* \.(png|gif|jpg|jpeg)$ {
expires 1h;
root /data/htdocs;
}
访问测试
/images/1.jpg缓存
/img/2.jpg不缓存
参考:
阿里云缓存策略帮助手册
Nginx静态资源缓存
12. Nginx 七层负载均衡
Nginx的ngx_http_upstream_module模块提供了七层负载均衡的功能。该模块用于将多个服务器定义成服务器组,由proxy_pass,fastcgi_pass等指令进行引用;
该模块的相关指令可参照官方文档查阅