JavaWeb工程中web.xml基本配置
一.理论准备
先说下我记得xml规则,必须有且只有一个根节点,大小写敏感,标签不嵌套,必须配对。
web.xml是不是必须的呢?不是的,只要你不用到里面的配置信息就好了,不过在大型web工程下使用该文件是很方便的,若是没有也会很复杂。
那么web.xml能做的所有事情都有那些?其实,web.xml的模式(Schema)文件中定义了多少种标签元素,web.xml中就可以出现它的模式文件所定义的标签元素,它就能拥有定义出来的那些功能。web.xml的模式文件是由Sun公司定义的,每个web.xml文件的根元素<web-app>中,都必须标明这个web.xml使用的是哪个模式文件。
来看个例子:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<web-app xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee" xmlns:web="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_2_5.xsd" xsi:schemaLocation="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_2_5.xsd" id="WebApp_ID" version="2.5">
<display-name>db</display-name>
<welcome-file-list>
<welcome-file>index.html</welcome-file>
<welcome-file>index.htm</welcome-file>
<welcome-file>index.jsp</welcome-file>
<welcome-file>default.html</welcome-file>
<welcome-file>default.htm</welcome-file>
<welcome-file>default.jsp</welcome-file>
</welcome-file-list>
</web-app>
二.标签元素
- 指定欢迎页面
<welcome-file-list>
<welcome-file>index.jsp</welcome-file>
<welcome-file>index1.jsp</welcome-file>
</welcome-file-list>
上面的例子指定了2个欢迎页面,显示时按顺序从第一个找起,如果第一个存在,就显示第一个,后面的不起作用。如果第一个不存在,就找第二个,以此类推。
关于欢迎页面:访问一个网站时,默认看到的第一个页面就叫欢迎页,一般情况下是由首页来充当欢迎页的。一般情况下,我们会在web.xml中指定欢迎页。但web.xml并不是一个Web的必要文件,没有web.xml,网站仍然是可以正常工作的。只不过网站的功能复杂起来后,web.xml的确有非常大用处,所以,默认创建的动态web工程在WEB-INF文件夹下面都有一个web.xml文件。
对于tomcat来说,当你只指定一个web的根名,没有指定具体页面,去访问时一个web时,如果web.xml文件中配置了欢迎页,那么就返回指定的那个页面作为欢迎页,而在文中没有web.xml文件,或虽然有web.xml,但web.xml也没指定欢迎页的情况下,它默认先查找index.html文件,如果找到了,就把index.html作为欢迎页还回给浏览器。如果没找到index.html,tomcat就去找index.jsp。找到index.jsp就把它作为欢迎页面返回。而如果index.html和index.jsp都没找到,又没有用web.xml文件指定欢迎页面,那此时tomcat就不知道该返回哪个文件了,它就显示The requested resource (/XXX) is not available(我就出现过这个问题)的页面。其中XXX表示web的根名。但如果你指定了具体页面,是可以正常访问的。
- 命名与定制URL
<servlet>
<servlet-name>servlet1</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>net.test.TestServlet</servlet-class>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>servlet1</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>*.do</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
url-pattern的意思是所有的.do文件都会经过TestServlet处理。
- 定制初始化参数
<servlet>
<servlet-name>servlet1</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>net.test.TestServlet</servlet-class>
<init-param>
<param-name>userName</param-name>
<param-value>Tommy</param-value>
</init-param>
<init-param>
<param-name>E-mail</param-name>
<param-value>[email protected]</param-value>
</init-param>
</servlet>
经过上面的配置,在servlet中能够调用getServletConfig().getInitParameter("param1")获得参数名对应的值。
//上下文参数:声明应用范围内的初始化参数。
<context-param>
<param-name>ContextParameter</para-name>
<param-value>test</param-value>
<description>It is a test parameter.</description>
</context-param>
//在servlet里面可以通过getServletContext().getInitParameter("context/param")
得到
- 指定错误处理页面,可以通过“异常类型”或“错误码”来指定错误处理页面。
<error-page>
<error-code>404</error-code>
<location>/error404.jsp</location>
</error-page>
-----------------------------
<error-page>
<exception-type>java.lang.Exception<exception-type>
<location>/exception.jsp<location>
</error-page>
<error-page>
<exception-type>java.lang.NullException</exception-type>
<location>/error.jsp</location>
</error-page>
- 设置过滤器:比如设置一个编码过滤器,过滤所有资源
<filter>
<filter-name>XXXCharaSetFilter</filter-name>
<filter-class>net.test.CharSetFilter</filter-class>
</filter>
<filter-mapping>
<filter-name>XXXCharaSetFilter</filter-name>
<url-pattern>/*</url-pattern>
</filter-mapping>
6.设置监听器
web.xml中的<listener></listener>有什么用? 没别的用处!就是配置监听类的~,它能捕捉到服务器的启动和停止! 在启动和停止触发里面的方法做相应的操作! 它必须在web.xml 中配置才能使用! web.xml 中listener元素不是只能有一个,有多个时按顺序执行。
如何在web.xml向listener中传参数 ?
<listener>
<listener-class>监听器类的完整路径</listener-class>
</listener>
监听器中不能够写初始化参数; 可通过另个的途径达到初始化参数的效果: 1.写一个properties文件,在文件里写好初始化参数值, 2.在监听器中可以通得到properties文件中的值(写在静态块中)。
- 设置会话(Session)过期时间,其中时间以分钟为单位
<session-config>
<session-timeout>60</session-timeout>
</session-config>
除了这些标签元素之外,还可以往web.xml中添加那些标签元素呢,那些标签元素都能起什么作用呢?我们只要去查看web.xml的模式文件就能知道。直接看模式文件看不懂,可以找一些中文教程来看看。
三.遗留问题
- 在项目中总会遇到一些关于加载的优先级问题,近期也同样遇到过类似的,所以自己查找资 料总结了下,下面有些是转载其他人的,毕竟人家写的不错,自己也就不重复造轮子了,只 是略加点了自己的修饰。 首先可以肯定的是,加载顺序与它们在 web.xml 文件中的先后顺序无关。即不会 因为 filter 写在 listener 的前面而会先加载 filter。最终得出的结论是:listener -> filter -> servlet 。<session-config></session-config> 如果某个会话在一定时间内未被访问,服务器可 以抛弃它以节省内存。可通过使用HttpSession的setMaxInactiveInterval方法明确设置单个会话对 象的超时值,或者可利用session-config元素制定缺省超时值。
- <welcome-file-list></welcome-file-list> 指示服务器在收到引用一个目录名而不是 文件名的URL时,使用哪个文件。
- web.xml中怎么配置url-pattern? 首先要知道 web.xml 中url-pattern的作用,他是给外部提供的一个访问DoGetDemo类的接口,你可以自己随意定义,然后在IE里面写入这个配置内容。 可以看我给你写的一个例子图片,应该一下就看懂的,用 SimpleHello.java 为例,看图片,访问的时候,可以输入下面的网址 http://192.168.0.67:8888/book/hello 这样,服务器就可以通过 <url-pattern>/hello</url-pattern> 找到ch06.SimpleHello类,因此你的<url-pattern></url-pattern> 里面的内容可以自己定义。然后在应用目录下访问这个servlet 。
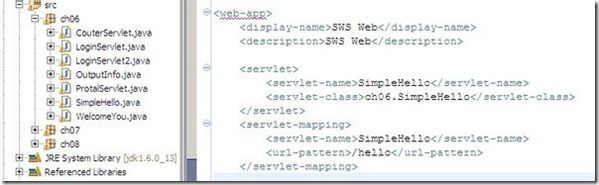
- web.xml中既然有url-pattern为什么还需要servlet-class呢?url-pattern是表明什么格式的的url进入这个servlet ,servlet-class 是表明哪个java类来处理这个请求 ,一个请求过来,先到servlet-mapping中去根据请求的url寻找这个url所对应的url-pattern,找到url-pattern后找到了servlet-name, 然后根据servlet-name和servlet中的servlet-name对应找到其所对应的servlet-class,具体的业务逻辑就写在来servlet-class对应的java类中了!
四.参考资料
csdn:http://blog.csdn.net/shanliangliuxing/article/details/7458492
百度知道