一、前言
在 Java 集合(一)中我们已经讲了 Collection 集合接口、Iterator 迭代器和泛型,今天我们来讲 Set 集合、List 集合 和 Collections 工具类。
二、Set 集合
Set 接口继承自 Collection 接口,它与 Collection 接口中的方法基本一致,并没有对 Collection 接口进行功能上的扩展,只是比 Collection 接口更加严格了,与 List 集合不同的是,Set 集合不允许存储重复的元素,而且 Set 集合是没有索引的。
Set 集合有多个子类,这里我们介绍其中的 HashSet 与 LinkedHashSet 这两个集合。
Set 集合取出元素的方式可以采用:迭代器、增强 for。
2.1、HashSet 集合
HashSet 集合实现了 Set 接口,首先 Set 集合有的特点它都有,同时它还有以下特点:
- 是一个无序的集合,存储元素和取出元素的顺序有可能不一致。
- 底层是一个哈希表结构,查询的速度非常的快。
HashSet 集合代码演示如下所示:
public class SetDemo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Set set = new HashSet<>();
// 使用 add() 方法添加元素
set.add(1);
set.add(3);
set.add(2);
set.add(1);
// 使用迭代器遍历集合
Iterator iterator = set.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
System.out.println(iterator.next());
}
// 使用增强 for 循环遍历
for (Integer integer : set) {
System.out.println(integer);
}
}
} 2.2、哈希值
哈希值是一个十进制的整数,由系统随机给出,实际上就是对象的地址值,是一个逻辑地址,是模拟出来的地址,不是数据实际存储的物理地址。在 Object 类有一个方法 hashCode(),可以获取对象的哈希值。
hashCode() 方法源码如下:(native 代表该方法调用的是本地操作系统的方法)
public native int hashCode();toString() 的源码如下:
public String toString() {
return getClass().getName() + "@" + Integer.toHexString(hashCode());
}可以看出 toString() 也调用了 hashCode() 并将其转化为十六进制。
哈希值代码演示如下所示:
public class Person extends Object {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Person p1 = new Person();
int h1 = p1.hashCode();
System.out.println(h1); // 1163157884
Person p2 = new Person();
int h2 = p2.hashCode();
System.out.println(h2); // 1956725890
/**
* toString() 的源码
* public String toString() {
* return getClass().getName() + "@" + Integer.toHexString(hashCode());
* }
*/
System.out.println(p1); // com.zjgsu.Set.Person@4554617c
System.out.println(p2); // com.zjgsu.Set.Person@74a14482
/**
* String 类的哈希值
* String 类重写了 hashCode() 所以下面两个哈希值是一样的
*/
String s1 = new String("abc");
String s2 = new String("abc");
System.out.println(s1.hashCode());
System.out.println(s2.hashCode());
}
}2.3、哈希表
在 JDK1.8 之前哈希表 =数组 + 链表,但是在JDK1.8之后,哈希表 = 数组 + 链表 + 红黑树(提高查询效率)。具体如下图所示: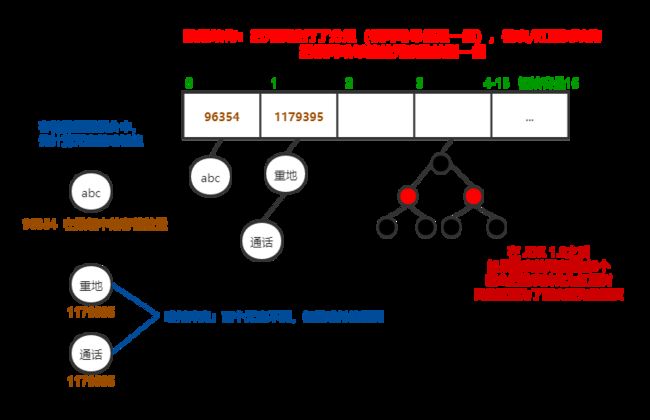
2.4、Set 集合存储元素不重复的原理
我们先来执行以下下面的代码:
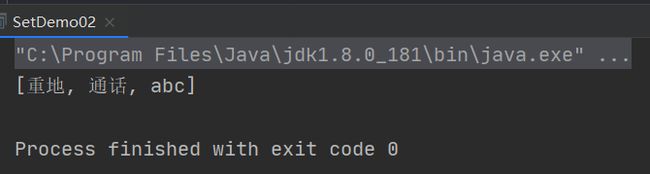
public class SetDemo02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashSet set = new HashSet ();
String s1 = new String("abc");
String s2 = new String("abc");
set.add(s1);
set.add(s2);
set.add("重地");
set.add("通话");
set.add("abc");
System.out.println(set); // [重地, 通话, abc]
}
} 我们根据代码来分析一下:
- HashSet
set = new HashSet ():现在我们已经知道hashSet 底层是一个哈希表,所以这句代码会创建一个哈希表。 - set.add(s1):add() 方法会调用 s1 的 hashCode() 方法。计算字符串 “abc” 的哈希值,哈希值是 96354,在集合中找有没有 96354 这个哈希值的元素,发现没有,就把 s1 存储到集合中。
- set.add(s2):add() 方法会调用 s2 的 hashCode() 方法。计算字符串 “abc” 的哈希值,哈希值是 96354,在集合中找有没有 96354 这个哈希值的元素,发现有(哈希冲突),s2 会调用 equals() 方法和哈希值相同的元素进行比较,s2.equals(s1) 返回 true,两个元素相同,就不会把 s2 存储到集合中。
- set.add("重地");:add() 方法会调用 "重地" 的 hashCode() 方法。计算字符串 “重地” 的哈希值,哈希值是 1179395,在集合中找有没有 1179395 这个哈希值的元素,发现 没有,就把"重地"存储到集合中。
- set.add("通话");:add() 方法会调用 "通话" 的 hashCode() 方法。计算字符串 “通话” 的哈希值,哈希值是 1179395,在集合中找有没有 1179395 这个哈希值的元素,发现有(哈希冲突),"通话" 会调用 equals() 方法和哈希值相同的元素进行比较,"通话".equals("重地") 返回 false,两个元素不同,就把"通话"存储到集合中。
最后哈希表中的元素如下所示:
通过上述步骤的分析,已经很明了的说明了 Set 集合元素不重复的原理,前提就是存储的元素必须重写 hashCode() 方法 和 equals() 方法。
2.5、HashSet 集合存储自定义类型元素
给 HashSet 中存放自定义类型元素时,需要重写对象中的hashCode() 方法和 equals() 方法,建立自己的比较方式,才能保证 HashSet 集合中的对象唯一。我们来看个例子,如下所示:
public class Student {
private String name;
private int age;
public Student() {
}
public Student(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
'}';
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashSet set = new HashSet<>();
Student s1 = new Student("张三", 18);
Student s2 = new Student("张三", 18);
Student s3 = new Student("张三", 30);
System.out.println(s1.hashCode());
System.out.println(s2.hashCode());
System.out.println(s3.hashCode());
set.add(s1);
set.add(s2);
set.add(s3);
System.out.println(set);
}
} 打印结果如下所示: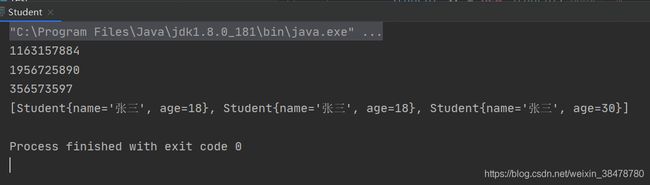
可以看到,如果没有重写 hashCode() 方法 和 equals() 方法,那么三个人是都会打印出来的,因为这时候他们的哈希值是不同的。
给 Student 类重写 hashCode() 方法和 equals() 方法,具体如下所示:
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return Objects.hash(name, age);
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (this == o) return true;
if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) return false;
Student student = (Student) o;
return age == student.age &&
Objects.equals(name, student.name);
}打印结果如下所示: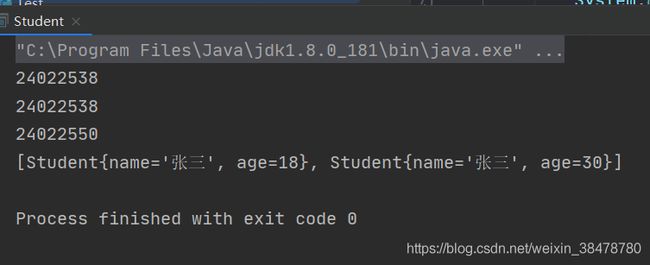
可以看到,重写了 hashCode() 方法 和 equals() 方法之后,就把重复的 Student 对象去掉了。
2.6、LinkedHashSet 集合
我们知道 HashSet 保证元素唯一,可是元素存放进去是没有顺序的,那么我们要保证有序,怎么办呢?在 HashSet 下面有一个子类 LinkedHashSet,它是链表和哈希表组合的一个数据存储结构,它多了一条链表用来记录元素的存储顺序,所以 LinkedHashSet 是有序的。
LinkedHashSet 集合代码演示如下所示:
public class LinkedHashSetDemo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashSet set = new HashSet<>();
set.add("abc");
set.add("www");
set.add("zz");
set.add("qq");
set.add("it");
System.out.println(set);
LinkedHashSet linkedSet = new LinkedHashSet<>();
linkedSet.add("abc");
linkedSet.add("www");
linkedSet.add("zz");
linkedSet.add("qq");
linkedSet.add("it");
System.out.println(linkedSet);
}
} 三、List 集合
3.1、List 接口介绍
List 接口继承自 Collection 接口,我们会将实现了 List 接口的对象称为 List 集合。在 List 集合中允许出现重复的元素,所有的元素是以一种线性的方式进行存储的,在程序中可以通过索引来访问集合中的指定元素。另外,List 集合还有一个特点就是元素有序,即元素的存储和取出顺序一致。
3.2、List 接口常用方法
List 不但继承了 Collection 接口的全部方法,而且还增加了一些根据元素索引来操作集合的特有方法,如下:
- public void add(int index, E element):将指定的元素添加到指定位置上。
- public E get(int index):返回集合中指定位置的元素。
- public E remove(int index):将指定位置上的元素移除并返回该元素。
- public E set(int index, E element):用指定元素替换集合中指定位置的元素,并返回被替换的元素。
List 接口常用方法代码演示如下所示:
public class ListDemo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建一个 List 集合对象
List list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add("a");
list.add("b");
list.add("c");
list.add("d");
list.add("a");
System.out.println(list);
// public void add(int index, E element)
// 在 c 和 d 之间添加一个 Test
list.add(3, "Test");
System.out.println(list);
// public E remove(int index)
// 移除 c 元素
String removeE = list.remove(2);
System.out.println(removeE);
System.out.println(list);
// public E set(int index, E element)
// 把最后一个 a 替换成 A
String setE = list.set(4, "A");
System.out.println(setE);
System.out.println(list);
// public E get(int index)
// List 集合遍历有三种方式
// 1、使用普通 for 循环
for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) {
System.out.print(list.get(i) + ", ");
}
System.out.println("\n");
System.out.println("----------------------------分割线--------------------------");
// 2、使用迭代器循环
Iterator iterator = list.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
System.out.print(iterator.next() + ", ");
}
System.out.println("\n");
System.out.println("----------------------------分割线--------------------------");
// 3、使用增强 for 循环
for (String s : list) {
System.out.print(s + ", ");
}
}
} $\\color{red}{注意}$:操作索引的时候一定要放置索引越界异常。
3.3、List 接口的子类
3.3.1、ArrayList 集合
ArrayList 集合的底层数据结构是数组结构,其特点是元素增删慢,查询快,由于日常开发中使用最多的功能就算查询数据,所以 ArrayList 是最常用的集合。但是呢,我们不能再开发中随意的使用 ArrayList 完成任何需求,只有当 ArrayList 适合我们的开发需求时(查询多,增删少),我们才去使用它。
3.3.2、LinkedList 集合
LinkedList 集合的底层数据结构是链表结构,其特点是元素增删快,查询慢,但是链表结构的首尾元素查找速度跟数组的查找是一样快的,所以 LinkedList 中包含了大量操作首尾元素的方法。所以当我们需要实现的需求增删操作很多,查询很少或者查询很多但都是查询手尾的时候,我们就可以使用 LinkedList 集合。
LinkedList 集合操作首尾元素方法代码演示如下所示:
public class LinkedListDemo02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// show01();
// show02();
show03();
}
// 增加元素
private static void show01() {
// 创建LinkedList集合对象
LinkedList linkedList = new LinkedList<>();
linkedList.add("a");
linkedList.add("b");
linkedList.add("c");
System.out.println(linkedList);
// addFirst()
linkedList.addFirst("www");
System.out.println(linkedList);
// push() 等效于 addFirst()
linkedList.push("ccc");
System.out.println(linkedList);
// addLast() 等效于 add()
linkedList.addLast("com");
System.out.println(linkedList);
}
// 获取元素
private static void show02() {
// 创建LinkedList集合对象
LinkedList linkedList = new LinkedList<>();
linkedList.add("a");
linkedList.add("b");
linkedList.add("c");
System.out.println(linkedList);
if (!linkedList.isEmpty()) {
String first = linkedList.getFirst();
System.out.println(first);
String last = linkedList.getLast();
System.out.println(last);
}
}
// 移除元素
private static void show03() {
// 创建LinkedList集合对象
LinkedList linkedList = new LinkedList<>();
linkedList.add("a");
linkedList.add("b");
linkedList.add("c");
System.out.println(linkedList);
// pop() 相当于 removeFirst()
String first = linkedList.removeFirst();
System.out.println(first);
String last = linkedList.removeLast();
System.out.println(last);
System.out.println(linkedList);
}
} 3.3.3、Vector 集合
Vector 集合的底层数据结构也是数组结构,但是与List和LinkedList 不同的是,Vector 集合是单线程的,速度慢,目前已经被 ArrayList 所取代。
四、Collections 集合工具类
4.1、常用功能
Collections 是集合工具类,用来对集合进行操作,部分方法如下:
- public static <泛型> boolean addAll(Collections
, c, T...elements) :往集合中添加一些元素。 - public static void shuffle(List list):打乱集合顺序。
- public static <泛型> void sort(List list):将集合中元素按照默认规则排序。
- public static <泛型> void sort(List list, Comparator):将集合中元素按照指定规则排序。
4.2、sort(List list) 方法
sort(List list) 方法的使用前提是被排序的集合里面存储的元素必须实现 Comparable 接口,并重写接口中的 compareTo() 方法定义排序的规则。
sort(List list) 方法代码演示如下所示:
public class CollectionsDemo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add(new Student("张三", 18));
list.add(new Student("李四", 20));
list.add(new Student("王五", 15));
System.out.println(list);
Collections.sort(list);
System.out.println(list);
}
static class Student implements Comparable {
private String name;
private int age;
public Student() {
}
public Student(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
'}';
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Student o) {
// 自定义比较规则
// 比较两个人的年龄
return this.getAge() - o.getAge(); // 按照年龄升序
//return o.getAge() - this.getAge(); // 按照年龄降序
}
}
} 4.3、sort(list, Comparator) 方法
Comparator 和 Comparable 的区别:
- Comparable 是排序接口,若一个类实现了 Comparable 接口,就意味着“该类支持排序”。
- Comparator 是比较器,我们若需要控制某个类的次序,可以建立一个“该类的比较器”来进行排序。
- Comparable 相当于“内部比较器”,而 Comparator 相当于“外部比较器”。
一个对象不支持自己和自己比较(没有实现Comparable接口),但是又想对两个对象进行比较
sort(list, Comparator) 方法代码演示如下所示:
public class ComparatorDemo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add(1);
list.add(3);
list.add(2);
System.out.println(list);
Collections.sort(list, new Comparator() {
// 重写比较的规则
@Override
public int compare(Integer o1, Integer o2) {
return o1 - o2; // 升序
//return o2 - o1; // 降序
}
});
System.out.println(list);
ArrayList list2 = new ArrayList<>();
list2.add(new CollectionsDemo01.Student("张三", 18));
list2.add(new CollectionsDemo01.Student("李四", 20));
list2.add(new CollectionsDemo01.Student("b王五", 15));
list2.add(new CollectionsDemo01.Student("a李六", 15));
System.out.println(list2);
Collections.sort(list2, new Comparator() {
@Override
public int compare(CollectionsDemo01.Student o1, CollectionsDemo01.Student o2) {
int result = o1.getAge() - o2.getAge();
// 如果两个人的年龄是一样的,就用姓名的第一字比较规则
if (result == 0) {
return o1.getName().charAt(0) - o2.getName().charAt(0);
}
return result;
}
});
System.out.println(list2);
}
static class Student {
private String name;
private int age;
public Student() {
}
public Student(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
'}';
}
}
} 五、小结
集合第二部分中我们讲了 List 集合、 Set 集合和 Collections 集合工具类,下一节我们讲 Map 集合和一个综合案例。
六、源码
文章中用到的所有源码已上传至 github,有需要的可以去下载。