(LeetCode 141/142)Linked List Cycle
1、Given a linked list, determine if it has a cycle in it.
2、Given a linked list, return the node where the cycle begins. If there is no cycle, return null.
3、Given a linked list, return the length of the cycle, if there is no cycle, return 0;
题目要求:
1、给一个链表,判断它是否存在环;
2、给一个链表,如果它存在环,请返回环的起点,否则,返回NULL;
3、给一个链表,如果它存在环,请返回环的长度,否则,返回0;
解题思路:
1、判断是否存在环?
方法1:增加一个set容器,遍历链表,将各个结点依次加入Set集合中,如果该节点已存在集合中,说明存在环;如果遍历结束后,发现没有重复的结点,则说明没有环。
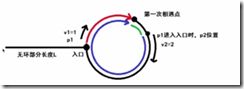
方法2:无需额外空间,设置两个指针p1,p2,从头结点开始,一个走一步,p1=p1->next;,一个走两步,p2=p2->next->next,如果存在环,那么两个指针肯定会相遇;如果走得快的指针p2到达了终点,说明没有环。
2、如何求环的起点和环的长度呢?
设链表起点距离环的起点距离为a,圈长为n,当p1和p2相遇时,相遇点距离环起点距离为b,此时b已绕环走了k圈,则
p1走的距离为a+b;
p2速度为p1的两倍,p2走的距离为2*(a+b);
p2走的距离为a+b+k*n=2*(a+b),从而a+b=k*n
即当p1走a步,p2走(k*n-b)步,当k=1时,则为(n-b)步;
因此如何求环的起点?把p1拉回起点重新出发,p2从相遇点继续走,p1,p2每次均走一步,a步后,p1到达起点,p2也刚好到圈的起点。
如何求环的长度?相遇后,p2再走一圈并统计长度就是圈长。
参考代码:
1、判断是否存在环?
/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * struct ListNode { * int val; * ListNode *next; * ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {} * }; */ class Solution { public: bool hasCycle(ListNode *head) { set<ListNode*> psets; for(ListNode *p=head;p!=NULL;p=p->next){ if(psets.find(p)!=psets.end()) return true; psets.insert(p); } return false; } };
/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * struct ListNode { * int val; * ListNode *next; * ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {} * }; */ class Solution { public: bool hasCycle(ListNode *head) { // if(head==NULL || head->next==NULL) // return false; ListNode *p1=head; ListNode *p2=head; while(p2 && p2->next){ p1=p1->next; p2=p2->next->next; if(p1==p2) return true; } return false; } };
2、求环的起点
/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * struct ListNode { * int val; * ListNode *next; * ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {} * }; */ class Solution { public: ListNode *detectCycle(ListNode *head) { ListNode *p1,*p2; p1=head; p2=head; while(p2 && p2->next){ p1=p1->next; p2=p2->next->next; if(p1==p2){ // p1 points back to head,p2 still stand where they have met // p1,p2 take the same steps // when they meet again, that's where the cycle starts p1=head; while(p1!=p2){ p1=p1->next; p2=p2->next; } return p1; } } return NULL; } };
3、求环的长度
/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * struct ListNode { * int val; * ListNode *next; * ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {} * }; */ class Solution { public: ListNode *detectCycle(ListNode *head) { ListNode *p1,*p2; p1=head; p2=head; while(p2 && p2->next){ p1=p1->next; p2=p2->next->next; if(p1==p2){ // if p2 cycles around,then the length of cycle can be counted ListNode *p=p2->next; int length=1; while(p!=p2){ length++; p2=p2->next; } return length; } } return 0; } };