前言
本人作为左程云的学生,现将课程上的morris遍历内容进行归纳整理,java版本代码均为左老师课上代码,c++代码为本人直接改写,并均通过leetcode测试。
什么是morris遍历
morris遍历是利用二叉树本身空闲出来的指针(n个节点的二叉树有n+1个指针空闲)来作为辅助变量完成二叉树的遍历的一种方法。Morris遍历法能以O(1)的空间复杂度和O(n)的时间复杂度实现二叉树的三种遍历,其中不使用栈或额外空间。
morris遍历流程
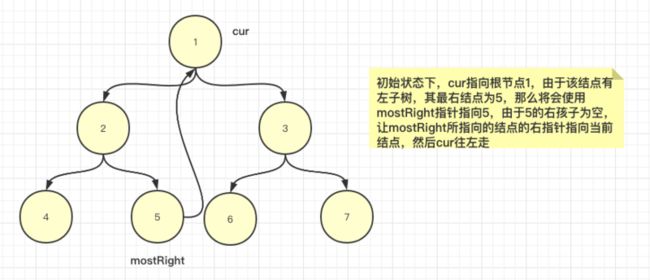
1、我们使用cur指针指向当前结点,mostRight指针指向cur左子树的最右结点,也即是cur的前驱结点
2、如果当前结点没有左子树,我们让cur往右走
3、如果有左子树,那么找到其左子树的最右结点(原树中的最右结点,而不是修改过指针的最右结点,看到后面就清楚了),并使用mostRight保存。
3.1、如果mostRight的右指针为空,(说明此时是第一次来到cur所指向结点),让mostRight的右指针指向cur,然后让cur往左走。
3.2、如果mostRight的右指针不为空,(说明此时是第二次来到cur所指向结点),让mostRight的右指针重新置为null,然后cur往右走
4、如果当前结点为空,遍历停止(回退过程合并到往右走了)。morris遍历图解:
morris序
在进行morris遍历的时候每次遍历都访问该节点所获得的访问顺序就是morris序。在上述例子中的morris如下
1 2 4 2 5 1 3 6 3 7
可以看到有的节点访问了两次有的节点只访问了一次,根据这个特点我们可以推导出morris的前序,中序和后序序列,并且这里得记住一个特点就是,只有有左孩子的节点才会被访问两次,没有左孩子的只会访问一次。
morris序的代码实现
java版本
public static class Node {
public int value;
Node left;
Node right;
public Node(int data) {
this.value = data;
}
}
public static void morris(Node head) {
if (head == null) {
return;
}
Node cur = head;
Node mostRight = null;
while (cur != null) {
mostRight = cur.left;
if (mostRight != null) { // 有左树的情况下
// 找到cur左树上,真实的最右
while (mostRight.right != null && mostRight.right != cur) {
mostRight = mostRight.right;
}
// 从while中出来,mostRight一定是cur左树上的最右节点
// mostRight
if (mostRight.right == null) {// 第一次来到cur结点
mostRight.right = cur;
cur = cur.left;
continue;
} else { // mostRight.right != null -> mostRight.right == cur
mostRight.right = null;
}
}
// 没有左子树或者第二次来到cur结点
cur = cur.right;
}
}
c++版本
struct TreeNode {
int val;
TreeNode *left;
TreeNode *right;
TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
};
void morris(TreeNode* root){
if(!root) return;
TreeNode* cur=root;
TreeNode* mostRight;
while(cur){
mostRight = cur->left;
if(mostRight){
// 有左子树
while(mostRight->right&&mostRight->right!=cur){
// 只要有右孩子并且右孩子不是当前结点
mostRight = mostRight->right;
}
if(!mostRight->right){
// mostRight的右孩子为空,说明是第一次访问cur
mostRight->right = cur;
cur = cur->left;
continue;
}else{
// mostRight的右孩子为cur,说明是第二次来到cur
mostRight->right = nullptr;
}
}
// 没有左子树或者第二次来到cur结点
cur = cur->right;
}
}
morris先序遍历
先序遍历就是在morris遍历的时候在第一次遍历当前结点的时候进行输出即可,这里直接给出代码,会发现改动的地方就2处
java版本
public static void morrisPre(Node head) {
if (head == null) {
return;
}
Node cur1 = head;
Node cur2 = null;
while (cur1 != null) {
cur2 = cur1.left;
if (cur2 != null) {
while (cur2.right != null && cur2.right != cur1) {
cur2 = cur2.right;
}
if (cur2.right == null) {
cur2.right = cur1;
System.out.print(cur1.value + " ");
cur1 = cur1.left;
continue;
} else {
cur2.right = null;
}
} else {
System.out.print(cur1.value + " ");
}
cur1 = cur1.right;
}
System.out.println();
}c++版本
vector result;// 保存先序遍历
void morris(TreeNode* root){
if(!root) return;
TreeNode* cur=root;
TreeNode* mostRight;
while(cur){
mostRight = cur->left;
if(mostRight){
// 有左子树
while(mostRight->right&&mostRight->right!=cur){
// 只要有右孩子并且右孩子不是当前结点
mostRight = mostRight->right;
}
if(!mostRight->right){
// mostRight的右孩子为空,说明是第一次访问cur
result.push_back(cur->val);
mostRight->right = cur;
cur = cur->left;
continue;
}else{
// mostRight的右孩子为cur,说明是第二次来到cur
mostRight->right = nullptr;
}
}else{
// 没有左子树,只会遍历一次,直接访问
result.push_back(cur->val);
}
// 没有左子树或者第二次来到cur结点
cur = cur->right;
}
}
morris中序遍历
中序遍历就是在morris遍历的时候在第二次遍历当前结点的时候进行输出即可,这里同样直接给出代码,需要修改的地方就一处。
java版本
public static void morrisIn(Node head) {
if (head == null) {
return;
}
Node cur = head;
Node mostRight = null;
while (cur != null) {
mostRight = cur.left;
if (mostRight != null) {
while (mostRight.right != null && mostRight.right != cur) {
mostRight = mostRight.right;
}
if (mostRight.right == null) {
mostRight.right = cur;
cur = cur.left;
continue;
} else {
mostRight.right = null;
}
}
System.out.print(cur.value + " ");
cur = cur.right;
}
System.out.println();
}c++版本
vector result;// 保存中序遍历结果
void morris(TreeNode* root){
if(!root) return;
TreeNode* cur=root;
TreeNode* mostRight;
while(cur){
mostRight = cur->left;
if(mostRight){
// 有左子树
while(mostRight->right&&mostRight->right!=cur){
// 只要有右孩子并且右孩子不是当前结点
mostRight = mostRight->right;
}
if(!mostRight->right){
// mostRight的右孩子为空,说明是第一次访问cur
mostRight->right = cur;
cur = cur->left;
continue;
}else{
// mostRight的右孩子为cur,说明是第二次来到cur
mostRight->right = nullptr;
}
}
// 没有左子树或者第二次来到cur结点
result.push_back(cur->val);
cur = cur->right;
}
}
morris后序遍历
后序遍历的处理有点复杂,因为没有哪个节点是遍历3次的,但是一样可以利用遍历2次的节点来处理,我们使用的方法时在第二次来到当前节点时,将该节点的左子树的右边界进行逆序输出,直到左右有左子树的节点的左子树右边界均输出完毕,最后再把根节点的右边边界进行逆序输出即可。说起来感觉有点抽象,看下面的例子就好。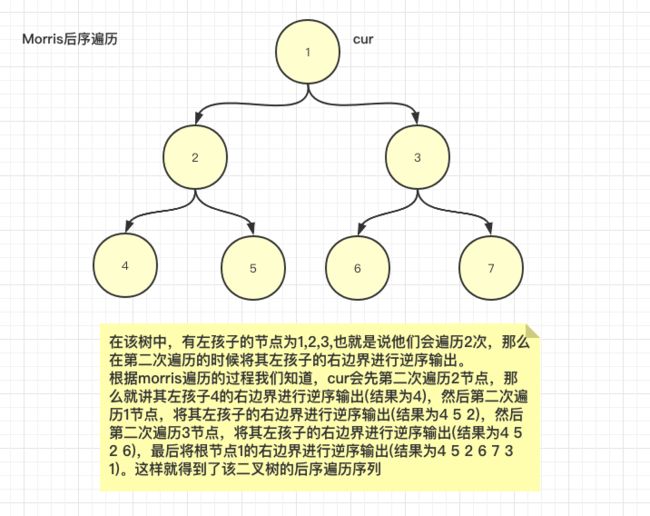
那么现在就只剩下一个问题了,morris遍历是一个时间复杂度为O(n),空间复杂度为O(1)的算法,如何原地逆置任意节点的左子树的右边界呢?
答案是单链表逆置,我们在每一次需要逆序输出右边界的时候就使用单链表逆置的方法将右边界节点逆置,然后再从尾往前输出就好,输出完毕后再逆置还原。java版本
public static void morrisPos(Node head) {
if (head == null) {
return;
}
Node cur = head;
Node mostRight = null;
while (cur != null) {
mostRight = cur.left;
if (mostRight != null) {
while (mostRight.right != null && mostRight.right != cur) {
mostRight = mostRight.right;
}
if (mostRight.right == null) {
mostRight.right = cur;
cur = cur.left;
continue;
} else {
mostRight.right = null;
printEdge(cur.left);
}
}
cur = cur.right;
}
printEdge(head);
System.out.println();
}
public static void printEdge(Node head) {
Node tail = reverseEdge(head);
Node cur = tail;
while (cur != null) {
System.out.print(cur.value + " ");
cur = cur.right;
}
reverseEdge(tail);
}
public static Node reverseEdge(Node from) {
Node pre = null;
Node next = null;
while (from != null) {
next = from.right;
from.right = pre;
pre = from;
from = next;
}
return pre;
}c++版本
struct TreeNode {
int val;
TreeNode *left;
TreeNode *right;
TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
};
vector result;
TreeNode* reverseEdge(TreeNode* root){
TreeNode* pre = nullptr;
TreeNode* next = nullptr;
while(root){
next = root->right;
root->right = pre;
pre = root;
root = next;
}
return pre;
}
void printRightEdge(TreeNode* root){
TreeNode* tail = reverseEdge(root);// 获得逆置后的尾结点
TreeNode* cur = tail;//暂存尾结点作为工作节点,最后得重新逆置tail还原
while(cur){
result.push_back(cur->val);
cur = cur->right;
}
reverseEdge(tail);
}
void morris(TreeNode* root){
if(!root) return;
TreeNode* cur = root;
TreeNode* mostRight = nullptr;
while(cur){
mostRight = cur->left;
if(mostRight){
while(mostRight->right&&mostRight->right!=cur){
mostRight = mostRight->right;
}
if(!mostRight->right){
// 第一次遍历cur节点
mostRight->right = cur;
cur = cur->left;
continue;
}else{
mostRight->right = nullptr;
printRightEdge(cur->left);
}
}
// 没有左孩子或者第二次遍历到cur节点
cur = cur->right;
}
// 最后处理根节点的右边界
printRightEdge(root);
}