基于感知机的人名-性别预测系统 —— Python实现
文章目录
- 一. 感知机基础知识:
-
- 1. 模型结构:
- 2. 训练数据:
- 3. 损失函数:
- 4. 学习算法:
- 二. 项目实践
-
- 1. 特征函数:
- 2. 核心代码介绍:
- 3. 模型评价:
- 4. 完整代码:
一. 感知机基础知识:
如上图所示,感知机模型是一个线性二分类模型,可以将线性可分的特征向量映射为+1 / -1的二值分类结果。下面具体介绍此过程:
1. 模型结构:
设输入与输出:
χ ⊆ R n , γ ⊆ { + 1 , − 1 } ; \chi \subseteq \mathbb R^n,\gamma\subseteq \{+1,-1\}; χ⊆Rn,γ⊆{ +1,−1};
x ∈ χ , y ∈ γ ; x\in \chi,y \in \gamma ; x∈χ,y∈γ;
则感知机模型表示为:
y = f ( x ) = s i g n ( w x + b ) , y = f(x)=sign(wx+b), y=f(x)=sign(wx+b),
其中 w ∈ R n , b ∈ R ; w\in\mathbb R^n,b\in\mathbb R; w∈Rn,b∈R;
s i g n ( x ) = { 1 , x ⩾ 0 − 1 , x < 0 sign(x) = \begin{cases} 1, & x \geqslant0 \\ -1, & x<0 \end{cases} sign(x)={ 1,−1,x⩾0x<0
2. 训练数据:
此模型需要的训练数据为 T = { ( x 1 , y 1 ) , ( x 2 , y 2 ) , . . . . . . ( x N , y N ) } , T = \{(x_1,y_1),(x_2,y_2),. . . . . . (x_N,y_N)\}, T={ (x1,y1),(x2,y2),......(xN,yN)},
其中 x i ∈ χ , y i ∈ γ ; x_i\in\chi,y_i\in\gamma; xi∈χ,yi∈γ;
3. 损失函数:
我们使用误分类点到超平面的距离构造损失函数:
设 x 0 ∈ R n x_0\in\mathbb R^n x0∈Rn为误分类点,
感知机定义的超平面为 S : w x + b = 0 , S:wx+b=0, S:wx+b=0,
则此误分类点到超平面的距离为:
1 ∣ ∣ w ∣ ∣ ∣ w x 0 + b ∣ \dfrac{1}{||w||}|wx_0+b| ∣∣w∣∣1∣wx0+b∣,其中 ∣ ∣ w ∣ ∣ ||w|| ∣∣w∣∣为权重的 L 2 L_2 L2范数。
对于误分类点 x i ∈ M , x_i \in M, xi∈M,有
− y i ( w x i + b ) > 0 , -y_i(wx_i+b)>0, −yi(wxi+b)>0,
忽略 l 2 l_2 l2范数,则损失函数定义为
L ( w , b ) = − ∑ x i ∈ M y i ( w x i + b ) , L(w,b)=-\sum_{x_i\in M}^{}y_i(wx_i+b), L(w,b)=−∑xi∈Myi(wxi+b),
我们的学习目标就是求得 w , b , w,b, w,b,有
m i n w , b L ( w , b ) 。 min_{w,b}L(w,b)。 minw,bL(w,b)。
4. 学习算法:
感知机的学习采用梯度下降法,学习的目的是让模型在训练集上没有误分类点,具体的权重和偏执的更新为:
w : = w + α y i x i w := w+\alpha y_ix_i w:=w+αyixi
b : = b + α y i b := b + \alpha y_i b:=b+αyi
二. 项目实践
1. 特征函数:
当我们想要在一个数据集上采用感知机算法来实现二分类时,我们首先需要考虑的是将数据转化为特征向量,这一过程的实现需要一系列的特征函数,每一个特征函数考量数据是否有相应的特征,并将数据的该特征转化为数值。这一系列的特征函数的作用结果就使得数据转化为了特征向量,也就是说N个特征函数可以提取N个特征,形成N维特征向量。
对于线性不可分的数据集,例如异或关系产生的数据,感知机算法是无效的。但在实际中,我们很难知道一个数据集是否是线性可分的,特别是往往我们无法直观理解数据的特征向量。为了解决感知机算法只能处理线性可分的数据,最简单的方法就是尽量提高特征向量的维度,维度越高,特征向量越可能是线性可分的。
具体到我们的项目中,数据集中包含120000个数据,截取一部分如下:
1,闳家,1
2,玉璎,0
3,于邺,1
4,越英,0
5,蕴萱,0
6,子颀,0
7,靖曦,0
8,鲁莱,1
9,永远,1
10,红孙,1
我们采用的方法是统计名字(除去姓氏)中所有出现的字符形成一个字符表,将此字符表作为特征模板,对于某个名字,当其中出现了字符表中的某个字符时,我们将模板中的该位置标记为1,其它位置标记为0,经过这样的处理后特征模板转化为了特征向量。
我们在实践过程中将100000个数据作为训练集、20000个数据作为测试集,训练集中统计得到的字符集包含5276个字符,也就是说我们的特征向量的维度为5276。
同时,选择此种构造特征向量的方式也有其它好处:存储特征向量时,由于特征向量是十分稀疏的多热向量,所以我们只需存储那些值为1的点即可,而通常值为1的点的数量不会超过2,这样可以大大节省存储空间与运算时间。
2. 核心代码介绍:
3. 模型评价:
当我们不进行训练,只使用权重为0.01、偏置值为0.5的模型进行测试时,准确率为55%。
当世代为4、学习率为0.25时,模型预测的准确率接近80%。
对于这样的结果,考量数据集本身的问题,会发现一些数据的标签明显有问题,同时数据中的名字大多是两个字,对一个字的名字的预测准确率较低。实际上,对于生活中的常见名字,此模型的预测准确率还是比较高的。
4. 完整代码:
import json
import numpy as np
class MyModel(object):
def __init__(self):
self.orginal_path = r'train.txt'
self.data_path = r'clear_train.json'
self.test_data = r'clear_test.json'
self.slot = r'slot.json'
self.feature_vectors = r'feature_vectors.json'
self.label = r'label.json'
self.w = r'model_w.json'
self.b = r'model_b.json'
self.slotNum = 5276
def clear_orginal_data(self):
data = []
flag = 0
with open(self.orginal_path,'r',encoding='utf-8') as f_obj:
for line in f_obj:
if flag >= 100000:
break
now_data = line.strip().split(',')[1:]
if now_data[1] == '0':
now_data[1] = -1
else:
now_data[1] = 1
data.append(now_data)
flag += 1
print(len(data))
print(data[0])
print(data[len(data) - 1])
input()
with open(self.data_path,'w') as f_obj:
f_obj.write(json.dumps(data))
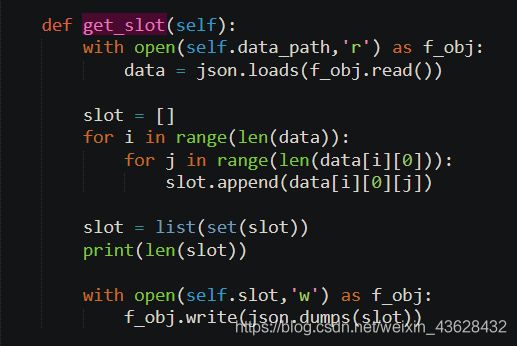
def get_slot(self):
with open(self.data_path,'r') as f_obj:
data = json.loads(f_obj.read())
slot = []
for i in range(len(data)):
for j in range(len(data[i][0])):
slot.append(data[i][0][j])
slot = list(set(slot))
print(len(slot))
with open(self.slot,'w') as f_obj:
f_obj.write(json.dumps(slot))
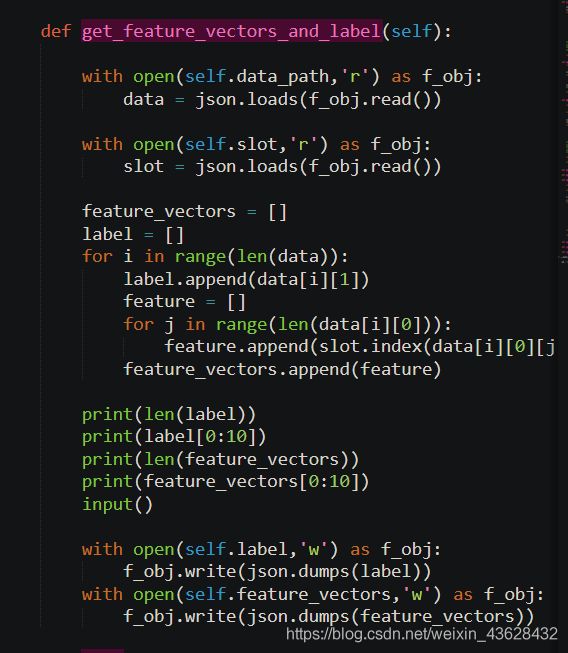
def get_feature_vectors_and_label(self):
with open(self.data_path,'r') as f_obj:
data = json.loads(f_obj.read())
with open(self.slot,'r') as f_obj:
slot = json.loads(f_obj.read())
feature_vectors = []
label = []
for i in range(len(data)):
label.append(data[i][1])
feature = []
for j in range(len(data[i][0])):
feature.append(slot.index(data[i][0][j]))
feature_vectors.append(feature)
print(len(label))
print(label[0:10])
print(len(feature_vectors))
print(feature_vectors[0:10])
input()
with open(self.label,'w') as f_obj:
f_obj.write(json.dumps(label))
with open(self.feature_vectors,'w') as f_obj:
f_obj.write(json.dumps(feature_vectors))
def sign(self,x):
if x >= 0:
return 1
else:
return -1
def perceptron(self,w,x,b):
w = np.array(w)
x = np.array(x)
return self.sign(np.dot(w,x) + b)
def train(self,epoch=4,alpha=0.25):
with open(self.label,'r') as f_obj:
label = json.loads(f_obj.read())
with open(self.feature_vectors,'r') as f_obj:
feature_vectors = json.loads(f_obj.read())
b = 0.5
w = np.ones(self.slotNum,float) * 0.001
for e in range(epoch):
for i in range(len(label)):
y_i = label[i]
x_i = np.zeros(self.slotNum,float)
for j in range(len(feature_vectors[i])):
x_i[feature_vectors[i][j]] = 1
if self.perceptron(w,x_i,b) * y_i <= 0:
w = w + alpha * y_i * x_i
b = b + alpha * y_i
with open(self.w,'w') as f_obj:
f_obj.write(json.dumps(list(w)))
with open(self.b,'w') as f_obj:
f_obj.write(json.dumps(b))
def pred(self,name):
with open(self.slot,'r') as f_obj:
slot = json.loads(f_obj.read())
with open(self.w,'r') as f_obj:
w = json.loads(f_obj.read())
with open(self.b,'r') as f_obj:
b = json.loads(f_obj.read())
x = np.zeros(self.slotNum,float)
for i in range(len(name)):
if i == 0:
continue
try:
x[slot.index(name[i])] = 1
except:
print('字库中无{}字'.format(name[i]))
result = self.perceptron(w,x,b)
if result == 1:
return '男'
else:
return '女'
def clear_test_data(self):
data = []
flag = 0
with open(self.orginal_path,'r',encoding='utf-8') as f_obj:
for line in f_obj:
if flag >= 100000:
now_data = line.strip().split(',')[1:]
if now_data[1] == '0':
now_data[1] = -1
else:
now_data[1] = 1
data.append(now_data)
flag += 1
print(len(data))
print(data[0:10])
input()
with open(self.test_data,'w') as f_obj:
f_obj.write(json.dumps(data))
def test(self):
with open(self.slot,'r') as f_obj:
slot = json.loads(f_obj.read())
with open(self.w,'r') as f_obj:
w = json.loads(f_obj.read())
with open(self.b,'r') as f_obj:
b = json.loads(f_obj.read())
with open(self.test_data,'r') as f_obj:
data = json.loads(f_obj.read())
feature_vectors = []
label = []
no = []
error = 0
for i in range(len(data)):
feature = []
flag = 0
for j in range(len(data[i][0])):
try:
feature.append(slot.index(data[i][0][j]))
except:
error += 1
flag = 1
break
if flag == 0:
feature_vectors.append(feature)
label.append(data[i][1])
all_simple_num = len(label)
success_num = 0
for i in range(len(label)):
x_i = np.zeros(self.slotNum,float)
for j in range(len(feature_vectors[i])):
x_i[feature_vectors[i][j]] = 1
if (label[i] == self.perceptron(w,x_i,b)):
success_num += 1
print(success_num / all_simple_num)