手写Spring-SpringMVC
1.知识点
手写SpringMVC之前,我们需要对他的五大组件和执行流程要有一定的了解
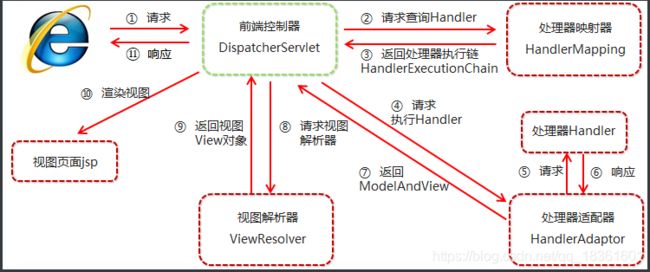
首先我们要知道springmvc的五大组件,如图,分别是
1.前端控制器DispatcherServlet,
2.处理器映射器HandlerMapping
3.处理器适配器HandlerAdaptor
4.处理器Handler
5.视图解析器ViewResolver
SpringMVC执行流程:
当用户请求会经过前端控制器,前端控制器会向处理器映射器查询处理请求的Handler,处理器映射器会返回处理器执行链(包括经过哪些过滤器等),前端控制器再向处理器适配器请求具体执行的Handler处理器,由处理器适配分配具体的处理器处理请求,请求完成会返回ModelAndView给前端控制器,再交由视图解析器,进行页面渲染再响应给用户
2.动手
该篇在上一篇手写IOC的基础上的实现
1.开始我们需要将一些属性封装为对象,所以我们准备好几个实体类
Request: 封装用户请求的请求路径和方法(如GET,POST…)
Param: 维护一个map 存储参数名和参数值
Handler: 定义Controller类的Class类型和方法为属性,即一个Controller类对应一个Handler实体
再定义两个返回数据实体Data和视图实体View
Data:定义返回模型
View:定义视图路径,和数据模型属性
/**
* @description: 实体,请求类中的方法和请求路径和@RequestMapping注解里的方法和路径一致
* @author: cgw
* @date: 2020-12-23
*/
public class Request {
/**
* 请求方法
*/
private String requestMethod;
/**
* 请求路径
*/
private String requestPath;
public Request(String requestMethod, String requestPath) {
this.requestMethod = requestMethod;
this.requestPath = requestPath;
}
public String getRequestMethod() {
return requestMethod;
}
public String getRequestPath() {
return requestPath;
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
int result = 17;
result = 31 * result + requestMethod.hashCode();
result = 31 * result + requestPath.hashCode();
return result;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
if (this == obj) return true;
if (!(obj instanceof Request)) return false;
Request request = (Request) obj;
return request.getRequestPath().equals(this.requestPath) && request.getRequestMethod().equals(this.requestMethod);
}
}
/**
* @description: 用于封装Controller方法的参数
* @author: cgw
* @date: 2020-12-23
*/
public class Param {
private Map<String, Object> paramMap;
public Param() {
}
public Param(Map<String, Object> paramMap) {
this.paramMap = paramMap;
}
public Map<String, Object> getParamMap() {
return paramMap;
}
public boolean isEmpty(){
return MapUtils.isEmpty(paramMap);
}
}
/**
* @description: 实体,封装了Controller的Class对象和Method方法
* @author: cgw
* @date: 2020-12-23
*/
public class Handler {
/**
* Controller 类
*/
private Class<?> controllerClass;
/**
* Controller 方法
*/
private Method controllerMethod;
public Handler(Class<?> controllerClass, Method controllerMethod) {
this.controllerClass = controllerClass;
this.controllerMethod = controllerMethod;
}
public Class<?> getControllerClass() {
return controllerClass;
}
public Method getControllerMethod() {
return controllerMethod;
}
}
/**
* @description: TODO
* @author: cgw
* @date: 2020-12-23
*/
public class View {
/**
* 视图路径
*/
private String path;
/**
* 模型数据
*/
private Map<String, Object> model;
public View(String path) {
this.path = path;
model = new HashMap<String, Object>();
}
public View addModel(String key, Object value) {
model.put(key, value);
return this;
}
public String getPath() {
return path;
}
public Map<String, Object> getModel() {
return model;
}
}
/**
* @description: TODO
* @author: cgw
* @date: 2020-12-23
*/
public class Data {
/**
* 模型数据
*/
private Object model;
public Data(Object model) {
this.model = model;
}
public Object getModel() {
return model;
}
}
2.做好准备工作后,再写我们的核心功能,首先我们提供几个Helper类
ControllerHelper:维护一个Map,key是自定义的Request对象,value是处理器(Handler对象)
RequestHelper:将用户请求中的参数封装为Param对象
HelperLoader:用于集中初始化所有Helper类
/**
* @description: Controller助手类,
* 主要是维护一个map,key为Request对象,value是处理器,
* 该类主要是遍历所有的Controller类,获取请求路径,请求方法(get,post...)封装为Request对象,
* controller的class类型和类的方法封装为Handler处理器对象
* @author: cgw
* @date: 2020-12-23
*/
public final class ControllerHelper {
/**
* REQUEST_MAP为 "请求-处理器" 的映射
*/
private static final Map<Request, Handler> REQUEST_MAP = new HashMap<Request, Handler>();
static {
//遍历所有Controller类
Set<Class<?>> controllerClassSet = ClassHelper.getControllerClassSet();
if (CollectionUtils.isNotEmpty(controllerClassSet)) {
for (Class<?> controllerClass : controllerClassSet) {
//暴力反射获取所有方法
Method[] methods = controllerClass.getDeclaredMethods();
//遍历方法
if (ArrayUtils.isNotEmpty(methods)) {
for (Method method : methods) {
//判断是否带RequestMapping注解
if (method.isAnnotationPresent(RequestMapping.class)) {
RequestMapping requestMapping = method.getAnnotation(RequestMapping.class);
//请求路径
String requestPath = requestMapping.value();
//请求方法
String requestMethod = requestMapping.method().name();
//封装请求和处理器
Request request = new Request(requestMethod, requestPath);
Handler handler = new Handler(controllerClass, method);//具体的控制器方法就是一个handler
REQUEST_MAP.put(request, handler);
}
}
}
}
}
}
/**
* 获取 Handler
*/
public static Handler getHandler(String requestMethod, String requestPath) {
Request request = new Request(requestMethod, requestPath);
return REQUEST_MAP.get(request);
}
}
/**
* @description: 助手类,将请求参数封装到map中
* 前端控制器收到HTTP请求后, 从HTTP中获取请求参数,然后封装到Param(一个存储map的实体)中,key:参数名 value:参数值
* @author: cgw
* @date: 2020-12-23
*/
public final class RequestHelper {
/**
* 获取请求参数
*/
public static Param createParam(HttpServletRequest request) throws IOException {
Map<String, Object> paramMap = new HashMap<>();
Enumeration<String> paramNames = request.getParameterNames();
//没有参数
if (!paramNames.hasMoreElements()) {
return null;
}
//get和post参数都能获取到
while (paramNames.hasMoreElements()) {
String fieldName = paramNames.nextElement();
String fieldValue = request.getParameter(fieldName);
paramMap.put(fieldName, fieldValue);
}
return new Param(paramMap);
}
}
/**
* @description: 助手类,让加载类
* 让类加载更集中,加载一些HELPLoader
* @author: cgw
* @date: 2020-12-24
*/
public final class HelperLoader {
public static void init() {
Class<?>[] classList = {
ClassHelper.class,
BeanHelper.class,
IocHelper.class,
ControllerHelper.class
};
for (Class<?> cls : classList) {
ClassUtil.loadClass(cls.getName());
}
}
}
3.最后就是我们最最核心的前端控制器了,先上代码
/**
* @description: 前端控制器类,首先执行init()方法来加载相关的helper类,每次请求的具体过程
* 每次请求都会执行service()方法,首先将请求封装为Request对象,然后从映射处理器
* (REQUEST_MAP)中获取到处理器,然后从客户端请求中获取Param参数,执行处理器方法
* 判断返回类型是view类型,则跳转,为data类型,则返回json
* @author: cgw
* @date: 2020-12-24
*/
@WebServlet(urlPatterns = "/*", loadOnStartup = 0)
public class DispatcherServlet extends HttpServlet {
@Override
public void init(ServletConfig servletConfig) throws ServletException {
//初始化相关的helper类
HelperLoader.init();
//获取ServletContext对象, 用于注册Servlet
ServletContext servletContext = servletConfig.getServletContext();
//注册处理jsp和静态资源的servlet
registerServlet(servletContext);
}
/**
* DefaultServlet和JspServlet都是由Web容器创建
* org.apache.catalina.servlets.DefaultServlet
* org.apache.jasper.servlet.JspServlet
*/
private void registerServlet(ServletContext servletContext) {
//动态注册处理JSP的Servlet
ServletRegistration jspServlet = servletContext.getServletRegistration("jsp");
jspServlet.addMapping(ConfigHelper.getAppJspPath() + "*");
//动态注册处理静态资源的默认Servlet
ServletRegistration defaultServlet = servletContext.getServletRegistration("default");
defaultServlet.addMapping("/favicon.ico"); //网站头像
defaultServlet.addMapping(ConfigHelper.getAppAssetPath() + "*");
}
@Override
public void service(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
String requestMethod = request.getMethod().toUpperCase();
String requestPath = request.getPathInfo();
//这里根据Tomcat的配置路径有两种情况, 一种是 "/userList", 另一种是 "/context地址/userList".
String[] splits = requestPath.split("/");
if (splits.length > 2) {
requestPath = "/" + splits[2];
}
//根据请求获取处理器(这里类似于SpringMVC中的映射处理器)
Handler handler = ControllerHelper.getHandler(requestMethod, requestPath);
if (handler != null) {
Class<?> controllerClass = handler.getControllerClass();//获取Controller类的Class类型
Object controllerBean = BeanHelper.getBean(controllerClass);//根据Class类型获取具体的实例对象
//初始化参数
Param param = RequestHelper.createParam(request);
//调用与请求对应的方法(这里类似于SpringMVC中的处理器适配器)
Object result;
Method actionMethod = handler.getControllerMethod();
//通过反射,使用具体的bean执行具体的方法(类似于处理器适配器交由具体的处理器处理)
if (param == null || param.isEmpty()) {
result = ReflectionUtil.invokeMethod(controllerBean, actionMethod);
} else {
result = ReflectionUtil.invokeMethod(controllerBean, actionMethod, param);
}
//跳转页面或返回json数据(这里类似于SpringMVC中的视图解析器)
if (result instanceof View) {
handleViewResult((View) result, request, response);
} else if (result instanceof Data) {
handleDataResult((Data) result, response);
}
}
}
/**
* 跳转页面
*/
private void handleViewResult(View view, HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws IOException, ServletException {
String path = view.getPath();
if (StringUtils.isNotEmpty(path)) {
if (path.startsWith("/")) {
//重定向
response.sendRedirect(request.getContextPath() + path);
} else {
//请求转发
Map<String, Object> model = view.getModel();
for (Map.Entry<String, Object> entry : model.entrySet()) {
request.setAttribute(entry.getKey(), entry.getValue());
}
request.getRequestDispatcher(ConfigHelper.getAppJspPath() + path).forward(request, response);
}
}
}
/**
* 返回JSON数据
*/
private void handleDataResult(Data data, HttpServletResponse response) throws IOException {
Object model = data.getModel();
if (model != null) {
response.setContentType("application/json");
response.setCharacterEncoding("UTF-8");
PrintWriter writer = response.getWriter();
String json = JSON.toJSON(model).toString();
writer.write(json);
writer.flush();
writer.close();
}
}
}
前端控制器实际上是一个Servlet,这里配置拦截所有请求,根据Servlet的生命周期我们知道Servlet先执行init()方法,在init()方法中我们先统一初始化所有的Helper类,动态注册处理JSP的Servlet和动态注册处理静态资源的默认Servlet.当每次请求访问我们的前端控制器的时候,都会执行我们的Service()方法,在Service()方法中,首先获取请求方法和请求路径,然后找到具体处理的处理器,即要执行我们的Controller类中的方法,我们需要获取到处理器具体实例对象,再封装请求参数,最后使用反射执行具体方法.根据返回类型决定跳转视图还是返回数据.
总结:总而言之,根据执行流程我们能大致清楚springmvc在请求中做了哪些事情,在本案例中我们能比较清晰的明白springmvc实现的方式方法,感受到spring框架帮我们做了哪些事情,通过本文,使我在使用springmvc的时候,将更得心应手.
本文学习参考总结至手写springmvc