代码
import math
import random
import numpy as np
from datetime import datetime
from pprint import pprint as p
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# 随机生成一个500个二维 [0,1)平面点
dataset = np.random.rand(500, 2)
# print(dataset)
# 设计一个Canopy类
class Canopy:
def __init__(self, dataset):
self.dataset = dataset
self.t1 = 0
self.t2 = 0
# 设置初始阈值t1 和 t2
def setThreshold(self, t1, t2):
if t1 > t2:
self.t1 = t1
self.t2 = t2
else:
print("t1 needs to be larger than t2!")
# 使用欧式距离进行距离计算
def euclideanDistance(self, vec1, vec2):
return math.sqrt(((vec1 - vec2) ** 2).sum())
# 根据当前dataset的长度随机选择一个下标
def getRandIndex(self):
return np.random.randint(len(self.dataset))
# return random.randint(0, len(self.dataset) - 1)
# 核心算法
def clustering(self):
if self.t1 == 0:
print('Please set the threshold t1 and t2!')
else:
canopies = [] # 用于存放最终归类的结果
while len(self.dataset) != 0:
# 获取一个随机下标
rand_index = self.getRandIndex()
# 随机获取一个中心点,定为P点
current_center = self.dataset[rand_index]
# 初始化P点的canopy类容器
current_center_list = []
# 初始化P点的删除容器
delete_list = []
# 删除随机选择的中心点P
self.dataset = np.delete(self.dataset, rand_index, 0)
for datum_j in range(len(self.dataset)):
datum = self.dataset[datum_j]
# 计算选取的中心点P到每个点之间的距离
distance = self.euclideanDistance(current_center, datum)
if distance < self.t1:
# 若距离小于t1,则将点归入P点的canopy类
current_center_list.append(datum)
if distance < self.t2:
# 若小于t2则归入删除容器
delete_list.append(datum_j)
self.dataset = np.delete(self.dataset, delete_list, 0)
canopies.append((current_center, current_center_list))
return canopies
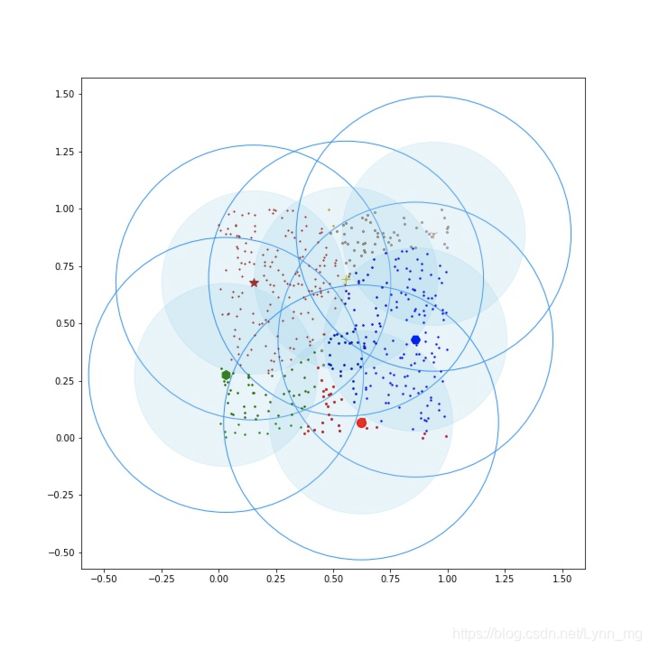
def showCanopy(canopies, dataset, t1, t2):
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(10, 10))
sc = fig.add_subplot(111)
colors = ['brown', 'green', 'blue', 'y', 'r', 'tan', 'dodgerblue', 'deeppink', 'orangered', 'peru', 'blue', 'y', 'r',
'gold', 'dimgray', 'darkorange', 'peru', 'blue', 'y', 'r', 'cyan', 'tan', 'orchid', 'peru', 'blue', 'y', 'r', 'sienna']
markers = ['*', 'h', 'H', '+', 'o', '1', '2', '3', ',', 'v', 'H', '+', '1', '2', '^',
'<', '>', '.', '4', 'H', '+', '1', '2', 's', 'p', 'x', 'D', 'd', '|', '_']
for i in range(len(canopies)):
canopy = canopies[i]
center = canopy[0]
components = canopy[1]
sc.plot(center[0], center[1], marker=markers[i], color=colors[i], markersize=10)
t1_circle = plt.Circle(
xy=(center[0], center[1]), radius=t1, color='dodgerblue', fill=False)
t2_circle = plt.Circle(
xy=(center[0], center[1]), radius=t2, color='skyblue', alpha=0.2)
sc.add_artist(t1_circle)
sc.add_artist(t2_circle)
for component in components:
sc.plot(component[0], component[1], marker=markers[i], color=colors[i], markersize=1.5)
maxvalue = np.amax(dataset)
minvalue = np.amin(dataset)
# print('maxvalue = ', maxvalue)
# print('minvalue = ', minvalue)
# print('t1 = ', t1)
# print('t2 = ', t2)
# print(minvalue - t1, maxvalue + t1)
plt.axis('equal')
plt.xlim((minvalue - t1, maxvalue + t1))
plt.ylim((minvalue - t1, maxvalue + t1))
# plt.axis('scaled')
plt.savefig('Canopy.svg')
plt.show()
def main():
t1 = 0.6
t2 = 0.4
gc =Canopy(dataset)
gc.setThreshold(t1, t2)
canopies = gc.clustering()
print('Get %s initial centers.' % len(canopies))
showCanopy(canopies, dataset, t1, t2)
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
运行结果