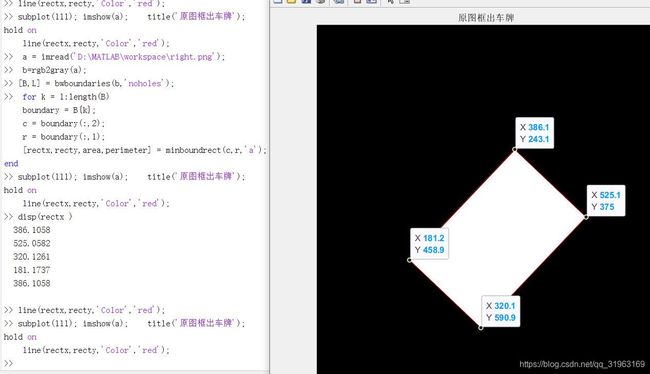
matlab求最小外接斜矩形minboundrect方法
最近在做课程大作业时看到opencv函数cv2.minAreaRect(),
但是想用matlab实现,于是查到了John D’Errico写的matlab实现求最小外接斜矩形函数。(代码贴在最后,仅供学习使用)
[rectx,recty,area,perimeter] = minboundrect(c,r,‘a’)
其中a表示以面积最小、如果是p的话则是以边长最小
这里有个问题,用minboundrect函数求得的四个点顺序是什么?
于是做了两张图验证了一下

放上结果:
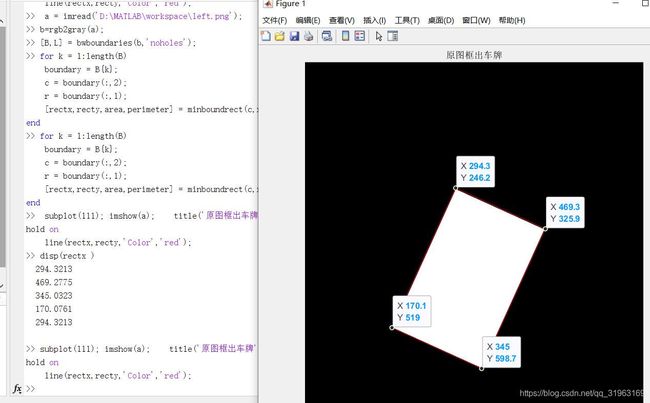
可以得到minboundrect函数得到的结果(rectx,recty)是从最上边的点开始,按照顺时针方向索引。
minboundrect代码
function [rectx,recty,area,perimeter] = minboundrect(x,y,metric)
% minboundrect: Compute the minimal bounding rectangle of points in the plane
% usage: [rectx,recty,area,perimeter] = minboundrect(x,y,metric)
%
% arguments: (input)
% x,y - vectors of points, describing points in the plane as
% (x,y) pairs. x and y must be the same lengths.
%
% metric - (OPTIONAL) - single letter character flag which
% denotes the use of minimal area or perimeter as the
% metric to be minimized. metric may be either 'a' or 'p',
% capitalization is ignored. Any other contraction of 'area'
% or 'perimeter' is also accepted.
%
% DEFAULT: 'a' ('area')
%
% arguments: (output)
% rectx,recty - 5x1 vectors of points that define the minimal
% bounding rectangle.
%
% area - (scalar) area of the minimal rect itself.
%
% perimeter - (scalar) perimeter of the minimal rect as found
%
%
% Note: For those individuals who would prefer the rect with minimum
% perimeter or area, careful testing convinces me that the minimum area
% rect was generally also the minimum perimeter rect on most problems
% (with one class of exceptions). This same testing appeared to verify my
% assumption that the minimum area rect must always contain at least
% one edge of the convex hull. The exception I refer to above is for
% problems when the convex hull is composed of only a few points,
% most likely exactly 3. Here one may see differences between the
% two metrics. My thanks to Roger Stafford for pointing out this
% class of counter-examples.
%
% Thanks are also due to Roger for pointing out a proof that the
% bounding rect must always contain an edge of the convex hull, in
% both the minimal perimeter and area cases.
%
%
% Example usage:
% x = rand(50000,1);
% y = rand(50000,1);
% tic,[rx,ry,area] = minboundrect(x,y);toc
%
% Elapsed time is 0.105754 seconds.
%
% [rx,ry]
% ans =
% 0.99994 -4.2515e-06
% 0.99998 0.99999
% 2.6441e-05 1
% -5.1673e-06 2.7356e-05
% 0.99994 -4.2515e-06
%
% area
% area =
% 0.99994
%
%
% See also: minboundcircle, minboundtri, minboundsphere
%
%
% Author: John D'Errico
% E-mail: woodchips@rochester.rr.com
% Release: 3.0
% Release date: 3/7/07
% default for metric
if (nargin<3) || isempty(metric)
metric = 'a';
elseif ~ischar(metric)
error 'metric must be a character flag if it is supplied.'
else
% check for 'a' or 'p'
metric = lower(metric(:)');
ind = strmatch(metric,{
'area','perimeter'});
if isempty(ind)
error 'metric does not match either ''area'' or ''perimeter'''
end
% just keep the first letter.
metric = metric(1);
end
% preprocess data
x=x(:);
y=y(:);
% not many error checks to worry about
n = length(x);
if n~=length(y)
error 'x and y must be the same sizes'
end
% start out with the convex hull of the points to
% reduce the problem dramatically. Note that any
% points in the interior of the convex hull are
% never needed, so we drop them.
if n>3
edges = convhull(x,y);
%edges = convhull(x,y,{
'Qt'}); % 'Pp' will silence the warnings
% exclude those points inside the hull as not relevant
% also sorts the points into their convex hull as a
% closed polygon
x = x(edges);
y = y(edges);
% probably fewer points now, unless the points are fully convex
nedges = length(x) - 1;
elseif n>1
% n must be 2 or 3
nedges = n;
x(end+1) = x(1);
y(end+1) = y(1);
else
% n must be 0 or 1
nedges = n;
end
% now we must find the bounding rectangle of those
% that remain.
% special case small numbers of points. If we trip any
% of these cases, then we are done, so return.
switch nedges
case 0
% empty begets empty
rectx = [];
recty = [];
area = [];
perimeter = [];
return
case 1
% with one point, the rect is simple.
rectx = repmat(x,1,5);
recty = repmat(y,1,5);
area = 0;
perimeter = 0;
return
case 2
% only two points. also simple.
rectx = x([1 2 2 1 1]);
recty = y([1 2 2 1 1]);
area = 0;
perimeter = 2*sqrt(diff(x).^2 + diff(y).^2);
return
end
% 3 or more points.
% will need a 2x2 rotation matrix through an angle theta
Rmat = @(theta) [cos(theta) sin(theta);-sin(theta) cos(theta)];
% get the angle of each edge of the hull polygon.
ind = 1:(length(x)-1);
edgeangles = atan2(y(ind+1) - y(ind),x(ind+1) - x(ind));
% move the angle into the first quadrant.
edgeangles = unique(mod(edgeangles,pi/2));
% now just check each edge of the hull
nang = length(edgeangles);
area = inf;
perimeter = inf;
met = inf;
xy = [x,y];
for i = 1:nang
% rotate the data through -theta
rot = Rmat(-edgeangles(i));
xyr = xy*rot;
xymin = min(xyr,[],1);
xymax = max(xyr,[],1);
% The area is simple, as is the perimeter
A_i = prod(xymax - xymin);
P_i = 2*sum(xymax-xymin);
if metric=='a'
M_i = A_i;
else
M_i = P_i;
end
% new metric value for the current interval. Is it better?
if M_i<met
% keep this one
met = M_i;
area = A_i;
perimeter = P_i;
rect = [xymin;[xymax(1),xymin(2)];xymax;[xymin(1),xymax(2)];xymin];
rect = rect*rot';
rectx = rect(:,1);
recty = rect(:,2);
end
end
% get the final rect
% all done
end % mainline end
代码仅供学习