_init方法
new Vue()会执行Vue构造函数的_init方法,_init方法被initMixin中扩展的,src\core\instance\init.js
export function initMixin (Vue: Class) {
Vue.prototype._init = function (options?: Object) {
const vm: Component = this
// a uid
vm._uid = uid++
let startTag, endTag
/* istanbul ignore if */
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' && config.performance && mark) {
startTag = `vue-perf-start:${vm._uid}`
endTag = `vue-perf-end:${vm._uid}`
mark(startTag)
}
// a flag to avoid this being observed
vm._isVue = true
// 合并配置
if (options && options._isComponent) {
// optimize internal component instantiation
// since dynamic options merging is pretty slow, and none of the
// internal component options needs special treatment.
initInternalComponent(vm, options)
} else {
vm.$options = mergeOptions(
resolveConstructorOptions(vm.constructor),
options || {},
vm
)
}
/* istanbul ignore else */
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production') {
initProxy(vm)
} else {
vm._renderProxy = vm
}
// expose real self
vm._self = vm
// vue实例vm扩展
// 生命周期
initLifecycle(vm)
// 事件
initEvents(vm)
// 渲染
// createElement也就是我们手写render函数的参数h
// slots
initRender(vm)
// 第一个生命周期
// data,props还没有
callHook(vm, 'beforeCreate')
// inject 的实现,在provide之前
initInjections(vm) // resolve injections before data/props
// props,data,computed,methods都在这里,需要重点看,所以beforCreate钩子函数中无法读取props和data的变量
initState(vm)
// provide 的实现
initProvide(vm) // resolve provide after data/props
// 第二个生命周期,这是可以获取到data,props,computed,methods
// 所有的生命周期函数都是调用的callHook函数
callHook(vm, 'created')
/* istanbul ignore if */
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' && config.performance && mark) {
vm._name = formatComponentName(vm, false)
mark(endTag)
measure(`vue ${vm._name} init`, startTag, endTag)
}
// 如果有el,则调用$mount
if (vm.$options.el) {
vm.$mount(vm.$options.el)
}
}
} _init方法主要做的就是合并配置,初始化生命周期,初始化事件中心,初始化渲染,初始化 data、props、computed、watcher 等等
挂载$mount
如果实例化的时候提供了el属性,就执行vm.$mount(vm.$options.el),如果没有提供就执行new Vue().$mount('#app'),$mount方法定义在src\platforms\web\runtime\index.js
// 这是web环境,如果是服务端渲染为noop(空函数),否则为patch
Vue.prototype.__patch__ = inBrowser ? patch : noop
// public mount method
Vue.prototype.$mount = function (
el?: string | Element,
hydrating?: boolean
): Component {
el = el && inBrowser ? query(el) : undefined
return mountComponent(this, el, hydrating)
}最终调用的是mountComponent,定义在src\core\instance\lifecycle.js
// 此方法核心就是先实例化一个渲染Watcher,在它的回调函数中会调用 updateComponent 方法,
// 在此方法中调用 vm._render 方法先生成虚拟 Node,最终调用 vm._update 更新 DOM
export function mountComponent (
vm: Component,
el: ?Element,
hydrating?: boolean
): Component {
vm.$el = el
if (!vm.$options.render) {
vm.$options.render = createEmptyVNode
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production') {
/* istanbul ignore if */
if ((vm.$options.template && vm.$options.template.charAt(0) !== '#') ||
vm.$options.el || el) {
warn(
'You are using the runtime-only build of Vue where the template ' +
'compiler is not available. Either pre-compile the templates into ' +
'render functions, or use the compiler-included build.',
vm
)
} else {
warn(
'Failed to mount component: template or render function not defined.',
vm
)
}
}
}
// 调用beforeMount生命周期函数
callHook(vm, 'beforeMount')
let updateComponent
/* istanbul ignore if */
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' && config.performance && mark) {
updateComponent = () => {
const name = vm._name
const id = vm._uid
const startTag = `vue-perf-start:${id}`
const endTag = `vue-perf-end:${id}`
mark(startTag)
// vm._render 最终是通过执行 createElement 方法并返回的是 vnode
// 调用vm._render()生成虚拟dom,vm._render()调用vm.$options.render函数
const vnode = vm._render()
mark(endTag)
measure(`vue ${name} render`, startTag, endTag)
mark(startTag)
// 调用vm._update更新dom
vm._update(vnode, hydrating)
mark(endTag)
measure(`vue ${name} patch`, startTag, endTag)
}
} else {
updateComponent = () => {
vm._update(vm._render(), hydrating)
}
}
// we set this to vm._watcher inside the watcher's constructor
// since the watcher's initial patch may call $forceUpdate (e.g. inside child
// component's mounted hook), which relies on vm._watcher being already defined
// Watcher做什么用?
// Watcher 在这里起到两个作用,一个是初始化的时候会执行回调函数updateComponent
// 另一个是当 vm 实例中的监测的数据发生变化的时候执行回调函数
new Watcher(vm, updateComponent, noop, {
before () {
if (vm._isMounted && !vm._isDestroyed) {
callHook(vm, 'beforeUpdate')
}
}
}, true /* isRenderWatcher */)
hydrating = false
// manually mounted instance, call mounted on self
// mounted is called for render-created child components in its inserted hook
// vm.$vnode指的是父组件虚拟dom
if (vm.$vnode == null) {
vm._isMounted = true
// 调用mounted生命周期函数
callHook(vm, 'mounted')
}
return vm
}mountComponent方法有三个核心:vm._render(), vm._update(),new Watcher()。renderMixin函数在Vue的原型上挂载了_render方法,src\core\instance\render.js
export function renderMixin (Vue: Class) {
// install runtime convenience helpers
installRenderHelpers(Vue.prototype)
Vue.prototype.$nextTick = function (fn: Function) {
return nextTick(fn, this)
}
// 虚拟dom
Vue.prototype._render = function (): VNode {
const vm: Component = this
const { render, _parentVnode } = vm.$options
...
let vnode
// 渲染函数是实例私有的,有一个参数createElement,createElement就是vm.$createElement,它的定义是在执行initRender时
// render就是vm.option.render,接受vm.$createElement(别名为h)作为参数:render: h => h(App)
// vm.$createElement在initRender中定义
vnode = render.call(vm._renderProxy, vm.$createElement)
..
vnode = createEmptyVNode()
}
// set parent
// _parentVnode就是vm.$vnode
vnode.parent = _parentVnode
return vnode
}
} vm_render()最终调用vm.$options.render,并且传递了vm.$createElemnt,定义在initRender()中。render函数的返回是createElemnt方法生成的vnode,通过new VNode()生产vnode。
vm._update放在执行lifecycleMixin()是挂载到Vue原型上的,src\core\instance\lifecycle.js
// 此方法核心时调用了vm.__patch__方法(src/platforms/web/runtime/index.js)
Vue.prototype._update = function (vnode: VNode, hydrating?: boolean) {
const vm: Component = this
const prevEl = vm.$el
const prevVnode = vm._vnode
const restoreActiveInstance = setActiveInstance(vm)
vm._vnode = vnode
// Vue.prototype.__patch__ is injected in entry points
// based on the rendering backend used.
if (!prevVnode) {
// initial render
vm.$el = vm.__patch__(vm.$el, vnode, hydrating, false /* removeOnly */)
} else {
// updates
vm.$el = vm.__patch__(prevVnode, vnode)
}
restoreActiveInstance()
// update __vue__ reference
if (prevEl) {
prevEl.__vue__ = null
}
if (vm.$el) {
vm.$el.__vue__ = vm
}
// if parent is an HOC, update its $el as well
if (vm.$vnode && vm.$parent && vm.$vnode === vm.$parent._vnode) {
vm.$parent.$el = vm.$el
}
// updated hook is called by the scheduler to ensure that children are
// updated in a parent's updated hook.
}最终调用vm.__patch__方法,定义在__patch__方法调用了createPatchFunction,src\core\vdom\patch.js
return function patch (oldVnode, vnode, hydrating, removeOnly) {
if (isUndef(vnode)) {
if (isDef(oldVnode)) invokeDestroyHook(oldVnode)
return
}
let isInitialPatch = false
const insertedVnodeQueue = []
if (isUndef(oldVnode)) {
// empty mount (likely as component), create new root element
isInitialPatch = true
createElm(vnode, insertedVnodeQueue)
} else {
const isRealElement = isDef(oldVnode.nodeType)
if (!isRealElement && sameVnode(oldVnode, vnode)) {
// patch existing root node
patchVnode(oldVnode, vnode, insertedVnodeQueue, null, null, removeOnly)
} else {
if (isRealElement) {
// mounting to a real element
// check if this is server-rendered content and if we can perform
// a successful hydration.
if (oldVnode.nodeType === 1 && oldVnode.hasAttribute(SSR_ATTR)) {
oldVnode.removeAttribute(SSR_ATTR)
hydrating = true
}
if (isTrue(hydrating)) {
if (hydrate(oldVnode, vnode, insertedVnodeQueue)) {
invokeInsertHook(vnode, insertedVnodeQueue, true)
return oldVnode
} else if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production') {
warn(
'The client-side rendered virtual DOM tree is not matching ' +
'server-rendered content. This is likely caused by incorrect ' +
'HTML markup, for example nesting block-level elements inside ' +
', or missing
. Bailing hydration and performing ' +
'full client-side render.'
)
}
}
// either not server-rendered, or hydration failed.
// create an empty node and replace it
oldVnode = emptyNodeAt(oldVnode)
}
// replacing existing element
const oldElm = oldVnode.elm
const parentElm = nodeOps.parentNode(oldElm)
// create new node
createElm(
vnode,
insertedVnodeQueue,
// extremely rare edge case: do not insert if old element is in a
// leaving transition. Only happens when combining transition +
// keep-alive + HOCs. (#4590)
oldElm._leaveCb ? null : parentElm,
nodeOps.nextSibling(oldElm)
)
// update parent placeholder node element, recursively
if (isDef(vnode.parent)) {
let ancestor = vnode.parent
const patchable = isPatchable(vnode)
while (ancestor) {
for (let i = 0; i < cbs.destroy.length; ++i) {
cbs.destroy[i](ancestor)
}
ancestor.elm = vnode.elm
if (patchable) {
for (let i = 0; i < cbs.create.length; ++i) {
cbs.create[i](emptyNode, ancestor)
}
// #6513
// invoke insert hooks that may have been merged by create hooks.
// e.g. for directives that uses the "inserted" hook.
const insert = ancestor.data.hook.insert
if (insert.merged) {
// start at index 1 to avoid re-invoking component mounted hook
for (let i = 1; i < insert.fns.length; i++) {
insert.fns[i]()
}
}
} else {
registerRef(ancestor)
}
ancestor = ancestor.parent
}
}
// destroy old node
if (isDef(parentElm)) {
removeVnodes([oldVnode], 0, 0)
} else if (isDef(oldVnode.tag)) {
invokeDestroyHook(oldVnode)
}
}
}
invokeInsertHook(vnode, insertedVnodeQueue, isInitialPatch)
return vnode.elm
}
path方法核心是调用createElm方法,createElm调用insert,insert方法将vnode通过原生方法appendChild插入到app标签中,实际上整个过程就是递归创建了一个完整的 DOM 树并插入到 #app父级标签上
有这样一个列子
var app = new Vue({
el: '#app',
render: function (createElement) {
return createElement('div', {
attrs: {
id: 'app'
},
}, this.message)
},
data: {
message: 'Hello Vue!'
}
})
new Vue的完整流程
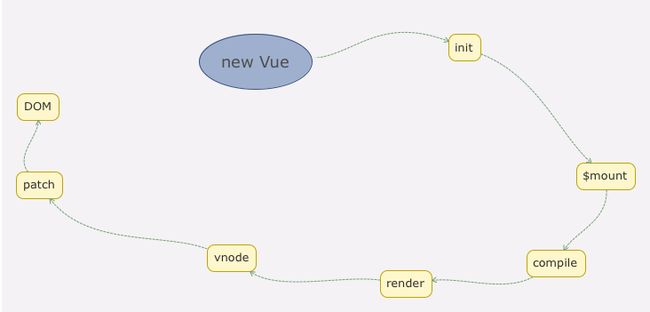
你可能感兴趣的:(vue.js,前端)