Set--HashSet&&TreeSet
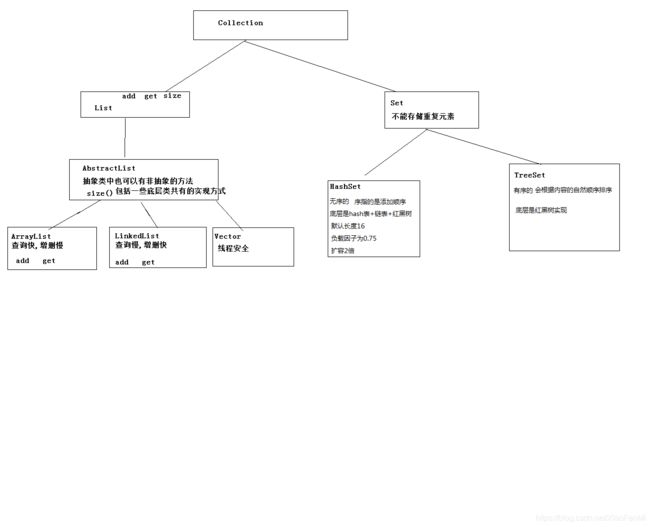
Set
Set不能存储重复元素
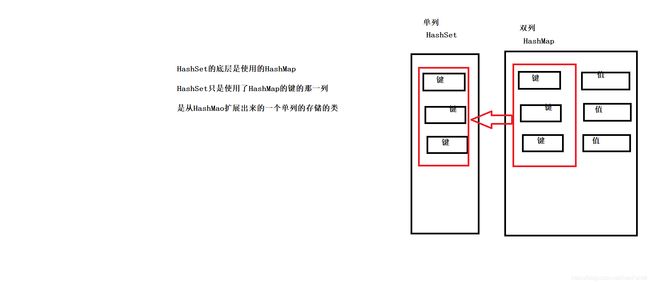
HashSet
HashSet无序存储
public class HashSetDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashSet h = new HashSet();
h.add("a");
h.add("b");
h.add("a");
h.add("w");
h.add("s");
h.add("f");
h.add("d");
h.add("e");
h.add("h");
h.add("j");
h.add("k");
h.add("n");
h.add("m");
h.add("v");
System.out.println(h);
}
/*
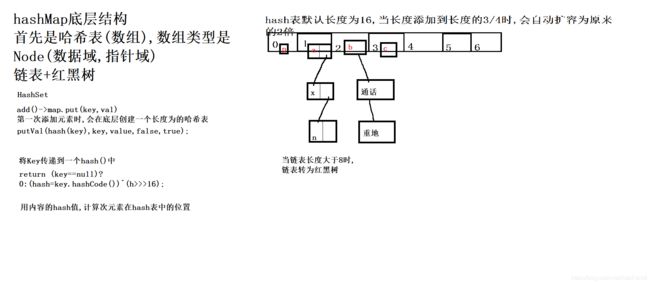
1.哈希结构的底层是如何存储数据的
哈希表本职业是数组
2.HashSet是如何去除重复元素的
先用元素的哈希值比较(快),但是内容不同,hash值可能相同
hash相同时,在使用equals()方法判断内容是否相等(安全可靠,效率低)
双保险:保证效率,有保证了安全
*/
}
HashSet去重
先用元素的哈希值比较(快),但是内容不同,hash值可能相同
hash相同时,在使用equals()方法判断内容是否相等(安全可靠,效率低)
hash值怎么来:调用hashCode()方法
两种情况:
1.类中已经重写hashCode(),例如String类,根据内容计算hash值
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashSet<String> h= new HashSet<>();
h.add("a");
h.add("c");
h.add("b");
h.add("a");
System.out.println(h);
}
2.类中没有重写hashCode(),调用Object类中的hashCode()
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashSet<Student> h= new HashSet<>();
Student s1= new Student(10,"我丢");
Student s2= new Student(11,"通话");
Student s3= new Student(11,"重地");
Student s4= new Student(10,"我丢");
System.out.println(s1.hashCode());
System.out.println(s2.hashCode());
System.out.println(s3.hashCode());
System.out.println(s4.hashCode());
h.add(s1);
h.add(s2);
h.add(s3);
h.add(s4);
System.out.println(h);
}
public class Student implements Comparable<Student>{
private int num;
private String use;
public Student(int num, String use) {
this.num = num;
this.use = use;
}
//自己类中重写hashCode(),根据内容计算hash值
//当hash值相同时,调用equals,判断内容是否相同
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (this == o) {
return true;}
if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()){
return false;}
Student student = (Student) o;
return num == student.num &&
Objects.equals(use, student.use);
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return Objects.hash(num, use);
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student{" +
"num=" + num +
", use='" + use + '\'' +
'}';
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Student o) {
return this.num-o.num;
}
}
TreeSet
TreeSet 可以按照元素的自然顺序排序
底层是红黑树
public static void main(String[] args) {
TreeSet<String> t = new TreeSet<String>();
t.add("1");
t.add("2");
t.add("1");
t.add("4");
t.add("3");
System.out.println(t);
}
创建一个学生类
public class Student implements Comparable<Student>{
private int num;
private String use;
public Student(int num, String use) {
this.num = num;
this.use = use;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student{" +
"num=" + num +
", use='" + use + '\'' +
'}';
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Student o) {
return this.num-o.num;
}
}
test类
public static void main(String[] args) {
TreeSet<Student> t = new TreeSet<Student>();
Student s1= new Student(10,"我丢");
Student s2= new Student(11,"通话");
Student s3= new Student(11,"重地");
Student s4= new Student(10,"我丢");
t.add(s1);
t.add(s2);
t.add(s3);
t.add(s4);
System.out.println(t);
}
Set遍历方法
public static void main(String[] args) {
TreeSet<String> t = new TreeSet<String>();
t.add("1");
t.add("2");
t.add("1");
t.add("4");
t.add("3");
/* t.stream().forEach((a)->System.out.print(a));*/
/*
增强for
for (String s : t) {
System.out.println(s);
}*/
/*
迭代器遍历
Iterator it = tset.iterator();
while(it.hasNext()){
String e = it.next();
System.out.println(e);
}*/
}