前言:
KCP是一个可靠的协议,它的延迟率比起tcp低很多。在游戏和视频推流领域广泛使用。
在TCP是为流量设计的(每秒内可以传输多少KB的数据),讲究的是充分利用带宽。而 KCP是为流速设计的(单个数据包从一端发送到一端需要多少时间),以10%-20%带宽浪费的代价换取了比 TCP快30%-40%的传输速度。
文章中内容解析了整个kcp的传输数据数据包组成。
系统: mac OS 10.14.3
golang: go1.12 darwin/amd64
抓包工具:tcpdump
kcp协议介绍
KCP是一个快速可靠协议,能以比 TCP浪费10%-20%的带宽的代价,换取平均延迟降低 30%-40%,且最大延迟降低三倍的传输效果。纯算法实现,并不负责底层协议(如UDP)的收发,需要使用者自己定义下层数据包的发送方式,以 callback的方式提供给 KCP。 连时钟都需要外部传递进来,内部不会有任何一次系统调用。
(一)rpcx的kcp实现源码
代码可以在github中获取:
https://github.com/rpcx-ecosystem/rpcx-examples3/tree/master/kcp
client端:
package main
import (
"context"
"crypto/sha1"
"flag"
"fmt"
"log"
"net"
"time"
example "github.com/rpcx-ecosystem/rpcx-examples3"
"github.com/smallnest/rpcx/client"
kcp "github.com/xtaci/kcp-go"
"golang.org/x/crypto/pbkdf2"
)
var (
addr = flag.String("addr", "localhost:8972", "server address")
)
const cryptKey = "rpcx-key"
const cryptSalt = "rpcx-salt"
func main() {
flag.Parse()
pass := pbkdf2.Key([]byte(cryptKey), []byte(cryptSalt), 4096, 32, sha1.New)
bc, _ := kcp.NewAESBlockCrypt(pass)
option := client.DefaultOption
option.Block = bc
d := client.NewPeer2PeerDiscovery("kcp@"+*addr, "")
xclient := client.NewXClient("Arith", client.Failtry, client.RoundRobin, d, option)
defer xclient.Close()
// plugin
cs := &ConfigUDPSession{}
pc := client.NewPluginContainer()
pc.Add(cs)
xclient.SetPlugins(pc)
args := &example.Args{
A: 10,
B: 20,
}
start := time.Now()
//for i := 0; i < 10000; i++ {
// reply := &example.Reply{}
// err := xclient.Call(context.Background(), "Mul", args, reply)
// if err != nil {
// log.Fatalf("failed to call: %v", err)
// }
// //log.Printf("%d * %d = %d", args.A, args.B, reply.C)
//}
reply := &example.Reply{}
err := xclient.Call(context.Background(), "Mul", args, reply)
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("failed to call: %v", err)
}
log.Printf("%d * %d = %d", args.A, args.B, reply.C)
dur := time.Since(start)
qps := 10000 * 1000 / int(dur/time.Millisecond)
fmt.Printf("qps: %d call/s", qps)
}
type ConfigUDPSession struct{}
func (p *ConfigUDPSession) ConnCreated(conn net.Conn) (net.Conn, error) {
session, ok := conn.(*kcp.UDPSession)
if !ok {
return conn, nil
}
session.SetACKNoDelay(true)
session.SetStreamMode(true)
return conn, nil
}server端:
package main
import (
"crypto/sha1"
"flag"
"net"
example "github.com/rpcx-ecosystem/rpcx-examples3"
"github.com/smallnest/rpcx/server"
kcp "github.com/xtaci/kcp-go"
"golang.org/x/crypto/pbkdf2"
)
var (
addr = flag.String("addr", "localhost:8972", "server address")
)
const cryptKey = "rpcx-key"
const cryptSalt = "rpcx-salt"
func main() {
flag.Parse()
pass := pbkdf2.Key([]byte(cryptKey), []byte(cryptSalt), 4096, 32, sha1.New)
bc, err := kcp.NewAESBlockCrypt(pass)
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
s := server.NewServer(server.WithBlockCrypt(bc))
s.RegisterName("Arith", new(example.Arith), "")
cs := &ConfigUDPSession{}
s.Plugins.Add(cs)
err = s.Serve("kcp", *addr)
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
}
type ConfigUDPSession struct{}
func (p *ConfigUDPSession) HandleConnAccept(conn net.Conn) (net.Conn, bool) {
session, ok := conn.(*kcp.UDPSession)
if !ok {
return conn, true
}
session.SetACKNoDelay(true)
session.SetStreamMode(true)
return conn, true
}client端和server端使用了AESBlockCrypt加密,密钥对应const cryptKey = "rpcx-key" 和 const cryptSalt = "rpcx-salt"。
kcp支持:Salsa20、sm4、Twofish、Triple_DES、CAST-128、Blowfish、AES、TEA、XTEA等加密方式。
(二)抓包
还是抓回环链路,捕获8972端口数据
tcpdump -i lo0 port 8972 -S -XX这一块不会抓包的可以看看《【协议分析】rpcx网络协议分析之kcp》 那篇文章。
或者去官网学习下:
www.us.tcpdump.org/manpages/tcpdump.1.html
数据包数据如下:
22:00:28.410752 IP localhost.63488 > localhost.8972: UDP, length 115
0x0000: 0200 0000 4500 008f 3b55 0000 4011 0000 ....E...;U..@...
0x0010: 7f00 0001 7f00 0001 f800 230c 007b fe8e ..........#..{..
0x0020: dd9f 8ab0 5984 b839 5bd3 6dbe c94f ac6a ....Y..9[.m..O.j
0x0030: 8429 1745 cd66 7630 47d7 289d d743 84f7 .).E.fv0G.(..C..
0x0040: 9726 b1f2 d45a 5092 b27f 1135 2b12 4ad9 .&...ZP....5+.J.
0x0050: cf0b 49e2 f611 3a7a cf06 f328 3ca6 42fc ..I...:z...(<.B.
0x0060: b9f2 1930 0dfd 5269 5ef7 b439 2d1e 9a92 ...0..Ri^..9-...
0x0070: 64db 2eaf 95a6 95dc 3af3 eb46 5294 252e d.......:..FR.%.
0x0080: 1d3c e49c a8f9 e6d1 0bd0 cc58 fe71 6aa5 .<.........X.qj.
0x0090: 24b7 e2 $..
22:00:28.411010 IP localhost.8972 > localhost.63488: UDP, length 52
0x0000: 0200 0000 4500 0050 3e9c 0000 4011 0000 ....E..P>...@...
0x0010: 7f00 0001 7f00 0001 230c f800 003c fe4f ........#....<.O
0x0020: 52fb 130d 850f 90d8 1b04 7a7e 855b e4b1 R.........z~.[..
0x0030: 4173 c282 a462 f211 6aaf 18a2 92e5 5c4e As...b..j.....\N
0x0040: a738 c934 c707 71ba c72f 19e1 4caf 56ec .8.4..q../..L.V.
0x0050: 5b1f e7d4 [...
22:00:28.411180 IP localhost.8972 > localhost.63488: UDP, length 104
0x0000: 0200 0000 4500 0084 0e44 0000 4011 0000 ....E....D..@...
0x0010: 7f00 0001 7f00 0001 230c f800 0070 fe83 ........#....p..
0x0020: a99c 6f57 4549 66bb c8b9 5f72 07c7 d697 ..oWEIf..._r....
0x0030: 3656 afd3 2eed 21cd 69b1 321b 85cf 3840 6V....!.i.2...8@
0x0040: 2ec9 9aea 8e3c 4cbe bd2d ed4f b357 2106 ..... localhost.8972: UDP, length 52
0x0000: 0200 0000 4500 0050 06a8 0000 4011 0000 ....E..P....@...
0x0010: 7f00 0001 7f00 0001 f800 230c 003c fe4f ..........#..<.O
0x0020: 8408 27a6 f032 f202 f717 9f88 8e8e c915 ..'..2..........
0x0030: f1c5 12c7 0e57 5152 c471 de8c 5a5a f388 .....WQR.q..ZZ..
0x0040: 9391 d2d6 5f9f 95e8 7518 e02e a8f1 7536 ...._...u.....u6
0x0050: 74e4 370b t.7. (三)解析UDP协议包与KCP协议包
3.1 UDP数据解析
解析数据包内容
22:00:28.410752 IP localhost.63488 > localhost.8972: UDP, length 115
0x0000: 0200 0000 4500 008f 3b55 0000 4011 0000 ....E...;U..@...
0x0010: 7f00 0001 7f00 0001 f800 230c 007b fe8e ..........#..{..
0x0020: dd9f 8ab0 5984 b839 5bd3 6dbe c94f ac6a ....Y..9[.m..O.j
0x0030: 8429 1745 cd66 7630 47d7 289d d743 84f7 .).E.fv0G.(..C..
0x0040: 9726 b1f2 d45a 5092 b27f 1135 2b12 4ad9 .&...ZP....5+.J.
0x0050: cf0b 49e2 f611 3a7a cf06 f328 3ca6 42fc ..I...:z...(<.B.
0x0060: b9f2 1930 0dfd 5269 5ef7 b439 2d1e 9a92 ...0..Ri^..9-...
0x0070: 64db 2eaf 95a6 95dc 3af3 eb46 5294 252e d.......:..FR.%.
0x0080: 1d3c e49c a8f9 e6d1 0bd0 cc58 fe71 6aa5 .<.........X.qj.
0x0090: 24b7 e2 $..网络传输中的字节码都是大端读取的,这个是为了兼容CPU架构。所以在编程中需要转换网络字节码,其实就是小端转成大端。
就像我们的02 00 。
/UDP头定义,共8个字节/
typedef struct _UDP_HEADER
{
unsigned short m_usSourPort; // 源端口号16bit
unsigned short m_usDestPort; // 目的端口号16bit
unsigned short m_usLength; // 数据包长度16bit
unsigned short m_usCheckSum; // 校验和16bit
}__attribute__((packed))UDP_HEADER, *PUDP_HEADER;3.2 KCP数据解析
根据上面分析我们可以得知,我们的数据部分应该是从第33个字节开始。原因: 4字节(回环链路层) + 20字节(IP层) + 8字节(UDP层) = 32字节。
刚好是如下部分:
0x0020: dd9f 8ab0 5984 b839 5bd3 6dbe c94f ac6a ....Y..9[.m..O.j
0x0030: 8429 1745 cd66 7630 47d7 289d d743 84f7 .).E.fv0G.(..C..
0x0040: 9726 b1f2 d45a 5092 b27f 1135 2b12 4ad9 .&...ZP....5+.J.
0x0050: cf0b 49e2 f611 3a7a cf06 f328 3ca6 42fc ..I...:z...(<.B.
0x0060: b9f2 1930 0dfd 5269 5ef7 b439 2d1e 9a92 ...0..Ri^..9-...
0x0070: 64db 2eaf 95a6 95dc 3af3 eb46 5294 252e d.......:..FR.%.
0x0080: 1d3c e49c a8f9 e6d1 0bd0 cc58 fe71 6aa5 .<.........X.qj.
0x0090: 24b7 e2 $..dd9f 8ab0 5984 b839 5bd3 6dbe c94f ac6a 因为我们是针对与传输数据时使用了AESBlockCrypt加密,所以我们可以编写一段go代码对数据包部分做一下解密工作。
代码如下:
package main
import (
"crypto/sha1"
"fmt"
"github.com/xtaci/kcp-go"
"golang.org/x/crypto/pbkdf2"
)
const cryptKey = "rpcx-key"
const cryptSalt = "rpcx-salt"
func main() {
pass := pbkdf2.Key([]byte(cryptKey), []byte(cryptSalt), 4096, 32, sha1.New) //加密令牌
bc, err := kcp.NewAESBlockCrypt(pass)
if err != nil {
fmt.Println(err)
return
}
//数据包
var dst []byte = []byte{
0xdd, 0x9f, 0x8a, 0xb0, 0x59, 0x84, 0xb8, 0x39, 0x5b, 0xd3, 0x6d, 0xbe, 0xc9, 0x4f, 0xac, 0x6a,
0x84, 0x29, 0x17, 0x45, 0xcd, 0x66, 0x76, 0x30, 0x47, 0xd7, 0x28, 0x9d, 0xd7, 0x43, 0x84, 0xf7,
0x97, 0x26, 0xb1, 0xf2, 0xd4, 0x5a, 0x50, 0x92, 0xb2, 0x7f, 0x11, 0x35, 0x2b, 0x12, 0x4a, 0xd9,
0xcf, 0x0b, 0x49, 0xe2, 0xf6, 0x11, 0x3a, 0x7a, 0xcf, 0x06, 0xf3, 0x28, 0x3c, 0xa6, 0x42, 0xfc,
0xb9, 0xf2, 0x19, 0x30, 0x0d, 0xfd, 0x52, 0x69, 0x5e, 0xf7, 0xb4, 0x39, 0x2d, 0x1e, 0x9a, 0x92,
0x64, 0xdb, 0x2e, 0xaf, 0x95, 0xa6, 0x95, 0xdc, 0x3a, 0xf3, 0xeb, 0x46, 0x52, 0x94, 0x25, 0x2e,
0x1d, 0x3c, 0xe4, 0x9c, 0xa8, 0xf9, 0xe6, 0xd1, 0x0b, 0xd0, 0xcc, 0x58, 0xfe, 0x71, 0x6a, 0xa5,
0x24, 0xb7, 0xe2}
dec := make([]byte, len(dst))
fmt.Println("加密数据:")
for i := 0;i < len(dst) ;i++ {
fmt.Printf("%02x ", dst[i])
if (i + 1) % 16 == 0{
fmt.Printf("\n")
}
}
bc.Decrypt(dec,dst) //解密
fmt.Println("\n")
fmt.Println("解密数据:")
for i := 0;i < len(dec) ;i++ {
fmt.Printf("%02x ", dec[i])
if (i + 1) % 16 == 0{
fmt.Printf("\n")
}
}
fmt.Println("\n")
}输入数据如下:
加密数据:
dd 9f 8a b0 59 84 b8 39 5b d3 6d be c9 4f ac 6a
84 29 17 45 cd 66 76 30 47 d7 28 9d d7 43 84 f7
97 26 b1 f2 d4 5a 50 92 b2 7f 11 35 2b 12 4a d9
cf 0b 49 e2 f6 11 3a 7a cf 06 f3 28 3c a6 42 fc
b9 f2 19 30 0d fd 52 69 5e f7 b4 39 2d 1e 9a 92
64 db 2e af 95 a6 95 dc 3a f3 eb 46 52 94 25 2e
1d 3c e4 9c a8 f9 e6 d1 0b d0 cc 58 fe 71 6a a5
24 b7 e2
解密数据:
ac d0 ee 1a 3d 48 23 6c 74 27 e2 a4 73 34 ef 78
b9 f2 0f 28 00 00 00 00 f1 00 59 00 dd 36 c5 20
51 00 20 00 0a 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00
3f 00 00 00 08 00 00 30 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00
00 00 00 2f 00 00 00 05 41 72 69 74 68 00 00 00
03 4d 75 6c 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 17 82 a1 41 d3
00 00 00 00 00 00 00 0a a1 42 d3 00 00 00 00 00
00 00 14 KCP数据包组成如下: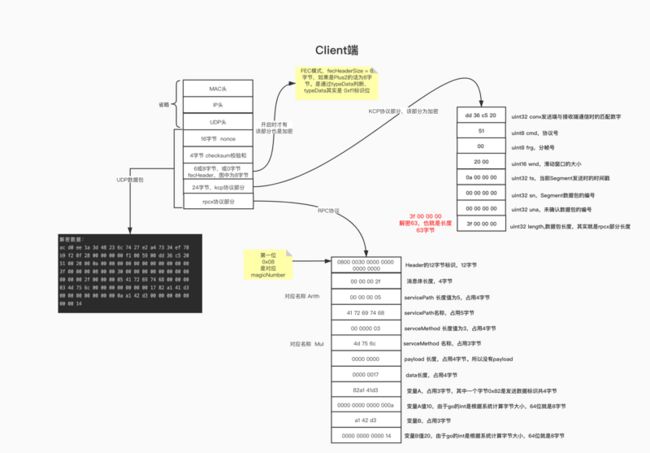
图中UDP数据包,则是上面解密程序的解密数据字节。
kcp协议部分。segment 结构体:
type segment struct {
conv uint32
// 发送端与接收端通信时的匹配数字,发送端发送的数据包中此值与接收端的conv值匹配一致时,接收端才会接受此包
cmd uint8
// 改数据包的协议号,协议号有以下枚举:
// IKCP_CMD_PUSH = 81 // cmd: push data,数据包
// IKCP_CMD_ACK = 82 // cmd: ack,确认包,告诉对方收到数据包
// IKCP_CMD_WASK = 83 // cmd: window probe (ask),询问远端滑动窗口的大小
// IKCP_CMD_WINS = 84 // cmd: window size (tell),告知远端滑动窗口的大小
frg uint8
// 分帧号,由于udp传输有数据包大小的限制,因此,应用层一个数据包可能被分为多个udp包
制自己接下来发送数据的大小wnd uint16
// 滑动窗口的大小
// 当Segment做为发送数据时,此wnd为本机滑动窗口大小,用于告诉远端自己窗口剩余多少
// 当Segment做为接收到数据时,此wnd为远端滑动窗口大小,本机知道了远端窗口剩余多少后,可以控
ts uint32
// timestamp , 当前Segment发送时的时间戳
sn uint32
// Sequence Number,Segment数据包的编号
una uint32
// una即unacknowledged,未确认数据包的编号,表示此编号前的所有包都已收到了。
rto uint32
// rto即Retransmission TimeOut,即超时重传时间,在发送出去时根据之前的网络情况进行设置
xmit uint32
// 基本类似于Segment发送的次数,每发送一次会自加一。用于统计该Segment被重传了几次,用于参考,进行调节
resendts uint32
// 即resend timestamp , 指定重发的时间戳,当当前时间超过这个时间时,则再重发一次这个包。
fastack uint32
// 用于以数据驱动的快速重传机制;
// len uint32 c++版本有数据包的数据长度,go版本无此字段
data []byte // 协议数据的具体内容
}kcp.go,如下为segment协议包组成源码如下:
func (seg *segment) encode(ptr []byte) []byte {
ptr = ikcp_encode32u(ptr, seg.conv) //发送端与接收端通信时的匹配数字,进行加密
ptr = ikcp_encode8u(ptr, seg.cmd) //数据包的协议号,进行加密
ptr = ikcp_encode8u(ptr, seg.frg) //分帧号,进行加密
ptr = ikcp_encode16u(ptr, seg.wnd) //数据包窗口大小,进行加密
ptr = ikcp_encode32u(ptr, seg.ts) //当前Segment发送时的时间戳,进行加密
ptr = ikcp_encode32u(ptr, seg.sn) //Segment数据包的编号,进行加密
ptr = ikcp_encode32u(ptr, seg.una) //未确认数据包的编号,进行加密
ptr = ikcp_encode32u(ptr, uint32(len(seg.data))) //数据长度,进行加密
atomic.AddUint64(&DefaultSnmp.OutSegs, 1)
return ptr
}
代码中的的ikcp_encode32u其实是调用了PutUint32进行加密。
sess.go,数据包输入函数:
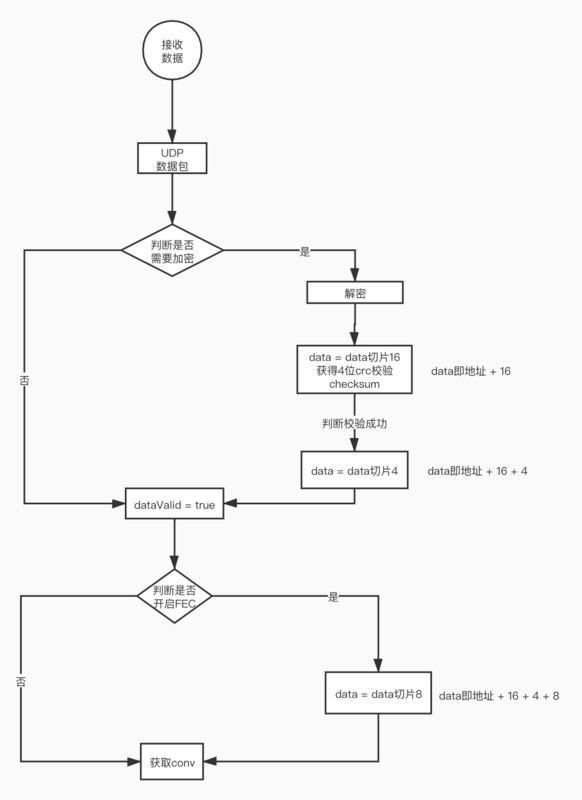
func (l *Listener) packetInput(data []byte, addr net.Addr) {
dataValid := false
if l.block != nil { //判断是否加密
l.block.Decrypt(data, data) //解密数据包
data = data[nonceSize:] //切片16字节,这部分对应的就是图中的nonce。
checksum := crc32.ChecksumIEEE(data[crcSize:]) //获得crc checksum,data原始地址 + 16的4个字节
if checksum == binary.LittleEndian.Uint32(data) {
data = data[crcSize:] //切片4字节,data原始地址 + 16 + 4
dataValid = true
} else {
atomic.AddUint64(&DefaultSnmp.InCsumErrors, 1)
}
} else if l.block == nil {
dataValid = true
}
if dataValid {
l.sessionLock.Lock()
s, ok := l.sessions[addr.String()]
l.sessionLock.Unlock()
if !ok { // new address:port
if len(l.chAccepts) < cap(l.chAccepts) { // do not let the new sessions overwhelm accept queue
var conv uint32
convValid := false
if l.fecDecoder != nil { //判断开启FEC
isfec := binary.LittleEndian.Uint16(data[4:]) //获取2字节FEC type,data原始地址 + 16 + 4 + 4
if isfec == typeData { //判断是否为Plus2,标志位位0xf1
conv = binary.LittleEndian.Uint32(data[fecHeaderSizePlus2:]) //获取conv ,data原始地址 + 16 + 4 + 8
convValid = true
}
} else {
conv = binary.LittleEndian.Uint32(data) //没有开启FEC时直接,获取conv = data原始地址 + 4
convValid = true
}
//...省略
} else {
s.kcpInput(data)
}
}
}根据以上代码我们可以看到获得数据时起时做了一个解密过程Uint32。
总结:
1.kcp支持加密方式:Salsa20、sm4、Twofish、Triple_DES、CAST-128、Blowfish、AES、TEA、XTEA等加密方式。
2.kcp传输数据是通过udp协议。
3.kcp协议部分的segment采用了PutUint和Uint32进行加解密。
参考资料:
tcpdump命令详解:
www.us.tcpdump.org/manpages/tcpdump.1.html
kcp
[https://github.com/skywind300...](https://github.com/skywind300...
)
AESBlockCrypt
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Advanced_Encryption_Standard
Salsa20
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Salsa20
sm4
https://github.com/tjfoc/gmsm/tree/master/sm4
Twofish
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Twofish
Triple_DES
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Triple_DES
Blowfish
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Blowfish_(cipher))