Coursera Algorithm Ⅱ week4 编程作业 Boggle
代码地址:https://github.com/RedemptionC/CourseraAlgorithms/tree/master/boggle
本题基本与leetcode212 单词搜索Ⅱ(https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/word-search-ii/)相同,实现trie的时候还可以把208 实现trie(208. 实现 Trie (前缀树))做了~
要求是给出一个board,上面每一个格子之上都有一个字母,题目会给出一个字典,里面有一些预定的单词,我们要做的是找出board相邻(上下左右对角线)的格子上的字母,如果能组成字典里的单词,就计分
所以本质上是个搜索问题:我们可以建立一个set,把字典里的单词都加入,然后在board上搜索,如果当前连成的单词在字典里,就积分
关键在于,要实现高效的查字典,我们不能直接用hashset里的contains,应该用startwith这种函数,一旦字典里没有当前这种字符串作为开头的单词,马上返回
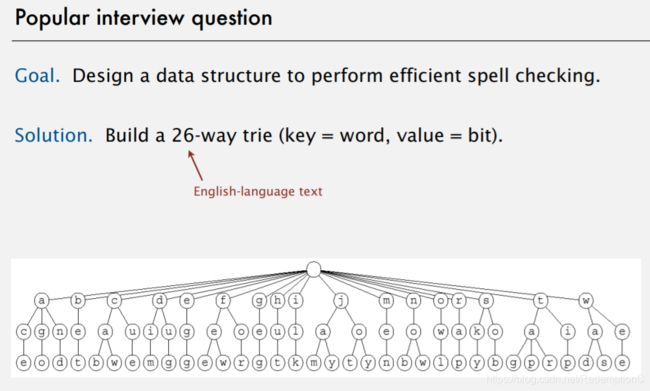
这里我们要实现trie(字典树),来实现高效的查询
因为本题里的元素都是大写字母,只有26种,为了简单起见,我实现的是26 way trie
差不多就是这种:
上代码:
Trie
public class Trie {
private class Node {
private Integer value;
private Node[] next = new Node[26];
}
private Node root;
private int count;// for setting value
/** Initialize your data structure here. */
public Trie() {
root = new Node();
count = 0;
}
private Node insert(String word, int val, Node node, int d) {
if (node == null) {
node = new Node();
}
if (d == word.length()) {
node.value = val;
return node;
}
int c = word.charAt(d) - 'A';
node.next[c] = insert(word, val, node.next[c], d + 1);
return node;
}
/** Inserts a word into the trie. */
public void insert(String word) {
insert(word, count, root, 0);
count++;
}
private boolean search(String word, Node node, int d) {
if (node == null) {
return false;
}
if (d == word.length()) {
if (node.value == null)
return false;
else
return true;
}
int c = word.charAt(d) - 'A';
return search(word, node.next[c], d + 1);
}
/** Returns if the word is in the trie. */
public boolean search(String word) {
return search(word, root, 0);
}
// 注意,这里是判断是否有以prefix为前缀的字符串在trie里,所以当d==len后,下一步是判断node.next是否有不为null
private boolean startsWith(String prefix, Node node, int d) {
if (d > prefix.length()) {
return false;
}
if (node == null) {
return false;
}
// 按说这里不能只根据next[i]不为空就判断存在,但是因为这里没有delete,所以只要next[i]不为空
// 那么对应的value也不为空(也就是不会被删除)
if (d == prefix.length()) {
return true;
}
int c = prefix.charAt(d) - 'A';
return startsWith(prefix, node.next[c], d + 1);
}
/** Returns if there is any word in the trie that starts with the given prefix. */
public boolean startsWith(String prefix) {
return startsWith(prefix, root, 0);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Trie trie = new Trie();
trie.insert("APPLE");
System.out.println(trie.search("APPLE")); // 返回 true
System.out.println(trie.search("APP")); // 返回 false
System.out.println(trie.startsWith("APP")); // 返回 true
trie.insert("APP");
System.out.println(trie.search("APP")); // 返回 true
}
}
/**
* Your Trie object will be instantiated and called as such:
* Trie obj = new Trie();
* obj.insert(word);
* boolean param_2 = obj.search(word);
* boolean param_3 = obj.startsWith(prefix);
*/
boardSolver
import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.In;
import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.SET;
import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.StdOut;
public class BoggleSolver {
private Trie set;
private int rows, cols;
private BoggleBoard boggleBoard;
private boolean[][] marked;
// 上下左右,左上,右上,左下,右下
private final int[] drow = { -1, 1, 0, 0, -1, -1, 1, 1 };
private final int[] dcol = { 0, 0, -1, 1, -1, 1, -1, 1 };
// Initializes the data structure using the given array of strings as the dictionary.
// (You can assume each word in the dictionary contains only the uppercase letters A through Z.)
public BoggleSolver(String[] dictionary) {
set = new Trie();
for (String s : dictionary) {
set.insert(s);
}
}
private boolean outOfBound(int row, int col) {
return row < 0 || row >= rows || col < 0 || col >= cols;
}
private void dfs(SET rs, int row, int col, StringBuilder sb) {
char c = boggleBoard.getLetter(row, col);
sb.append(c == 'Q' ? "QU" : c);
if (!set.startsWith(sb.toString())) {
return;
}
marked[row][col] = true;
if (sb.length() >= 3) {
String t = sb.toString();
if (set.search(t)) {
rs.add(t);
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < 8; i++) {
int tRow = row + drow[i];
int tCol = col + dcol[i];
if (outOfBound(tRow, tCol) || marked[tRow][tCol]) {
continue;
}
dfs(rs, tRow, tCol, new StringBuilder(sb));
marked[tRow][tCol] = false;
// if (row == 0 && col == 0)
// printMarked();
}
}
private void printMarked() {
for (int i = 0; i < rows; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < cols; j++) {
System.out.printf("%b ", marked[i][j]);
}
System.out.println();
}
}
// Returns the set of all valid words in the given Boggle board, as an Iterable.
public Iterable getAllValidWords(BoggleBoard board) {
SET rs = new SET<>();
boggleBoard = board;
//dfs:以所有的点作为起点,然后向左右,上下,对角线,搜索
rows = board.rows();
cols = board.cols();
for (int i = 0; i < rows; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < cols; j++) {
// FIXTHIS:这里是可以仅new一次的
marked = new boolean[rows][cols];
dfs(rs, i, j, new StringBuilder());
}
}
return rs;
}
// Returns the score of the given word if it is in the dictionary, zero otherwise.
// (You can assume the word contains only the uppercase letters A through Z.)
public int scoreOf(String word) {
if (!set.search(word))
return 0;
int len = word.length();
if (len < 3)
return 0;
if (len == 3 || len == 4)
return 1;
if (len == 5)
return 2;
if (len == 6)
return 3;
if (len == 7)
return 5;
// if (len >= 8)
return 11;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
In in = new In(args[0]);
String[] dictionary = in.readAllStrings();
BoggleSolver solver = new BoggleSolver(dictionary);
BoggleBoard board = new BoggleBoard(args[1]);
int score = 0;
for (String word : solver.getAllValidWords(board)) {
StdOut.println(word);
score += solver.scoreOf(word);
}
StdOut.println("Score = " + score);
// System.out.println(solver.scoreOf("STONES"));
}
}