CityEngine2016-学习笔记(2)Shape Operations
CityEngine2016-学习笔记(2)Shape Operations
这是学习CGA规则的笔记,版本是cityengine 2016.0,参考help文件。
CityEngine Help Manual > Rule-based Modeling > Shape Operations
1 Extrusion 拉伸
一般用法:
Lot -->
extrude(10) Building.
另外,可以用世界坐标:
Lot -->
extrude(world.up, 30)
这里采用了world坐标,的up方向。
【延伸】extrude()用法:
extrude(distance)
extrude(extrusionType, distance)
Param:
extrusionType:
world.up:世界坐标系向上
word.up.flatTop:世界坐标系向上,但是生成平头
face.normal:默认垂直于面的法线
vertex.normal:Extrudes face vertices along their normals.
实际出来的效果,face.normal和vertex.normal没啥区别。。。
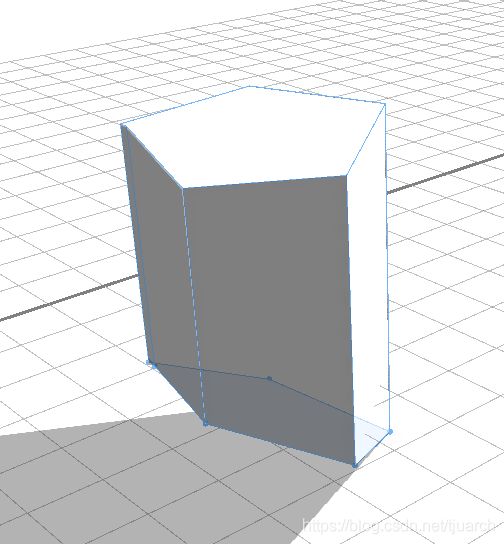
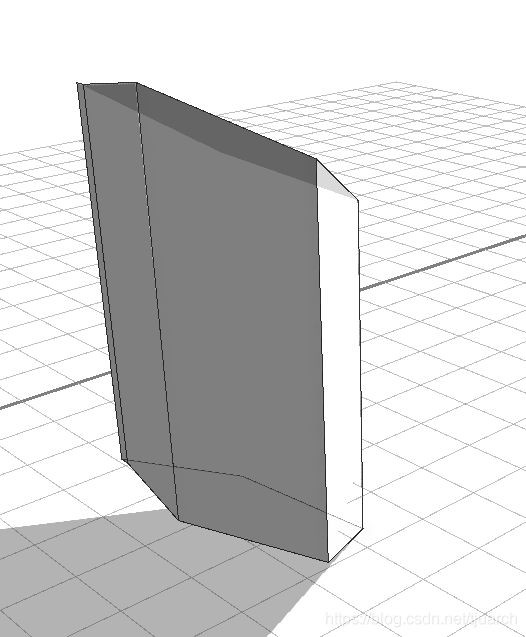

【延伸】taper()
一般用法:
taper(height)
Params:
height: float, 拉伸的距离,也可以是负数,向反拉,不过这时的scope.sy是负的。
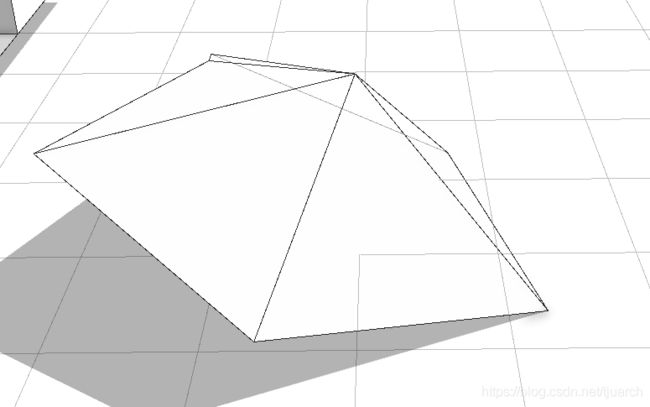
2 Transformations 变换
t(tx, ty, tz) 沿着模型scope轴变换位置
r(rx, ry, rz) 沿着模型scope的轴(向量scope.r
)旋转角度。也可以写成r(scopeCenter, rx, ry, rz),围绕scope center旋转。
![]() s(sx, sy, sz)设定模型向量scope.s的比例,与t、r操作不同,这里的参数是“重写”模型的比例。参数sx、sy、sz是绝对值。
s(sx, sy, sz)设定模型向量scope.s的比例,与t、r操作不同,这里的参数是“重写”模型的比例。参数sx、sy、sz是绝对值。
相对操作符
s、t操作可以使用相对操作符 ’ :
s('0.5, '1, '1) 等同于 s(0.5scope.sx, 1scope.sy, 1scope.sz)
t('2, 0, '3) 等同于 t(2scope.sx, 0scope.sy, 3scope.sz)
举栗:
相对比例缩放
Lot -->
s(’0.8, ’1, ’0.8)
center(xz)
extrude(20)
Lot -->
extrude(20)
split(y) {
2: r(scopeCenter, 0, 360*split.index/split.total, 0) X
}*
坐标系统 coordinate system
omni…
From Volume to Surface with the Component Split 各部分部件的划分
从一个建筑体块划分为不同的形状(shapes),操作上使用comp(),一般来说酱紫:
comp(comp-selector) {selector: operations | selector: operations ... }
把一个物体依据它的几何(geometry)关系划分成部件(components),然后在每一个部件上进行进一步的操作。
参数comp-selector指定划分的类型,可以是f、e、v,分别是面faces,边edges,点vertices。
参数selector定义部件如何划分/选取。举栗:
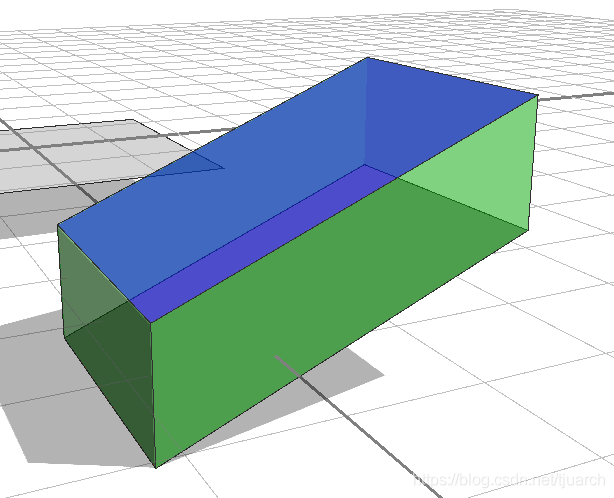
A --> comp(f) {all: B}
从A创建了一个新的shape B,包括A的每个面。
A --> comp(e) {all: C}
A --> comp(v) {all: D}
创建C、D,分别包含A的边和点。
也可以用数字指定具体的部件,如comp(f){3 : B},这里特指第三个面。但是也可以用预定的关键词(semantic selection)来选取: Building --> comp(f) { side : Facade }
预定的关键词:
-front, back, left, right, top, bottom,根据方向来确定形状(shape)
-vertical, horizontal, aslant, nutant:相对于当前形状的局部坐标系的xz平面分析y法线。 例如,如果y法线平行于xz平面,则垂直匹配;否则,垂直匹配。 如果法线或多或少垂直,则为水平匹配; 如果法线和xz平面之间的角度为正,则aslant匹配;如果中间角度为负,则nutant相匹配。
-side: 选取除了水平(horizontal)方向的部件
-all: 选取全部部件。
栗子:
attr red = "#FF0000"
attr green = "#00FF00"
attr blue = "#0000FF"
Lot -->
extrude(world.up, 10) A
A -->
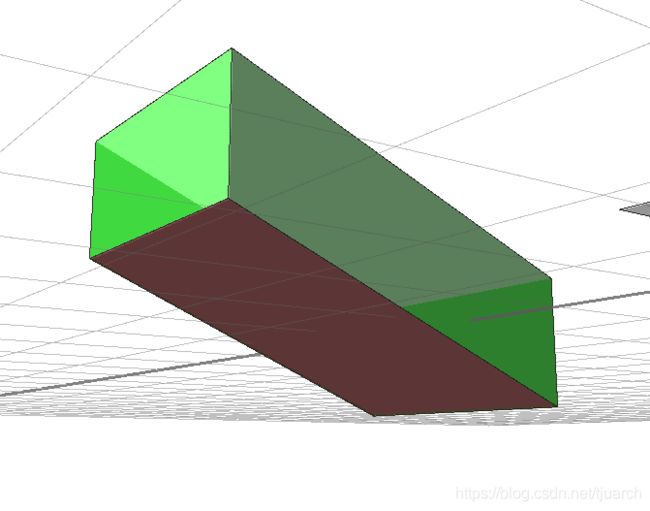
comp(f) {aslant : B | nutant : C | all : D}
B -->
color(blue)
C -->
color(red)
D -->
color(green)
3 the subdivision split 细分
一般形式:
split(axis) { selector : operation }
引用帮助文件:
split(splitAxis) { size1 : operations1 | size2 : operations2 | ... | sizen-1 : operationsn-1 }
split(splitAxis) { size1 : operations1 | size2 : operations2 | ... | sizen-1 : operationsn-1 }*
split(splitAxis, adjustSelector) { size1 : operations1 | ... | sizen-1 : operationsn-1 }
split(splitAxis, adjustSelector) { size1 : operations1 | ... | sizen-1 : operationsn-1 }*
参数:
splitAxis(selstring)
(x | y | z)-要沿其拆分的轴的名称。 这是相对于局部坐标系(即范围)而言的。
AdjustSelector
(adjust | noAdjust)-可选的选择器,用于控制所计算形状的范围计算:默认值是将范围调整到几何的边界框; noAdjust避免了这种情况,因此,最终形状的范围将无间隙地填充父级的范围。
建模的时候,一般来说,学会基本的推拉、移动、缩放、细分等操作足够可以应付大多数场景了。在cga建模也是一样,所以这方面多费点笔墨来详细叙述也是值得的。
(1)simple resize
栗子:
attr red = "#ff0000"
attr green = "#00ff00"
attr blue = "#0000ff"
attr yellow = "#ffff00"
attr orange = "#ffa500"
attr length = 5
Lot -->
s(length, 1, 1)
primitiveCube()
color(red)
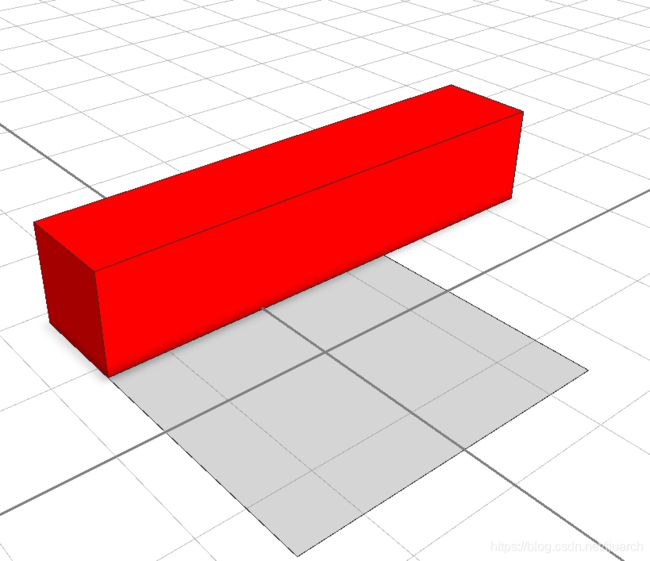
解释:定义三个颜色变量,拉出一个长5,截面1x1的长方体,颜色定义为红色。
栗子:
attr length = 5
Lot -->
s(length, 1, 1)
primitiveCube()
Split_ex
Split_ex -->
split(x) { 3 : X }
X -->
color(blue)

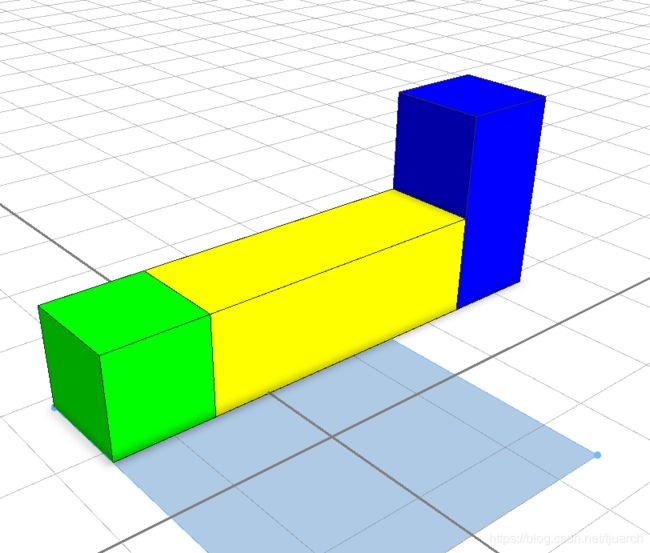
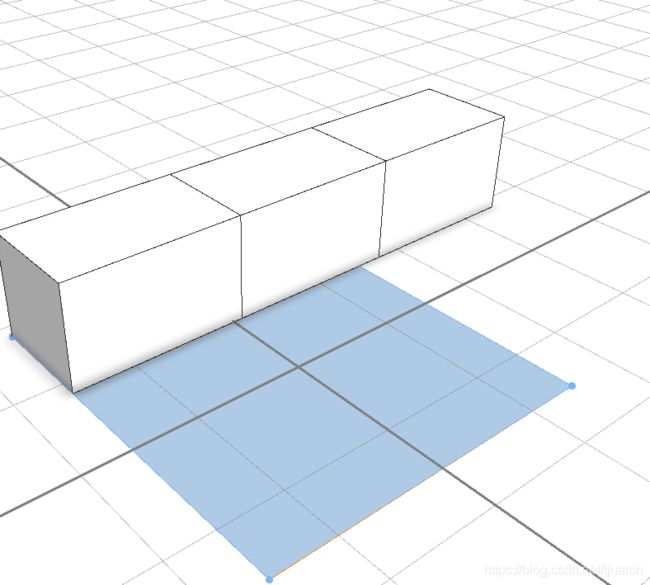
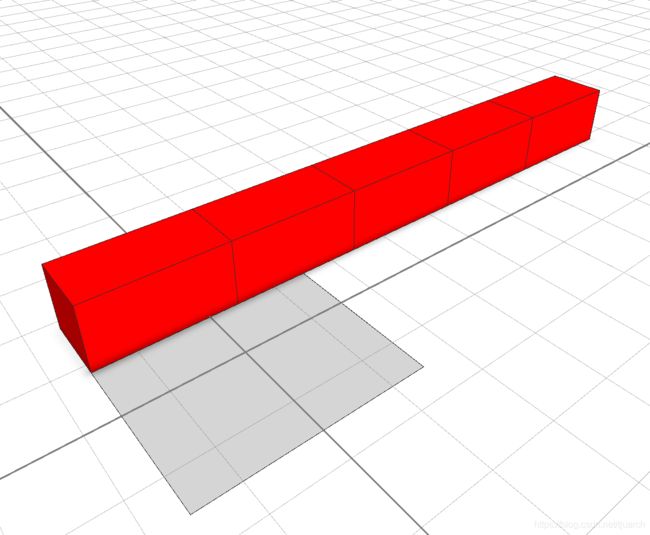
解释:5个长的矩形,沿着x轴切出来一个3个的蓝色,剩下的就没了,截掉了。
栗子:
Split_ex -->
split(x) { 3 : X | ~1 : X(2) }
X -->
color(green)
X(h) -->
color(red)
s('1, h, '1)
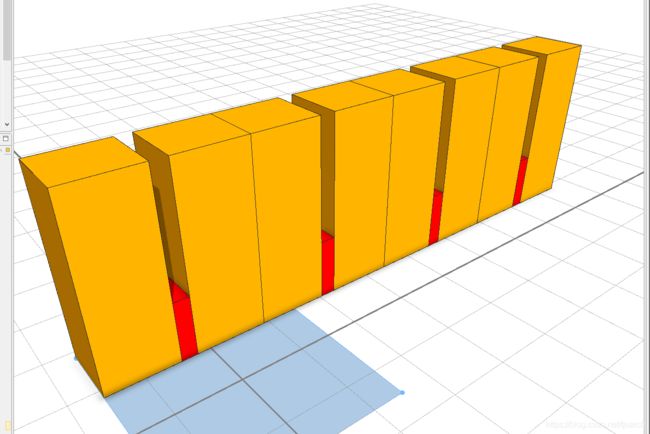
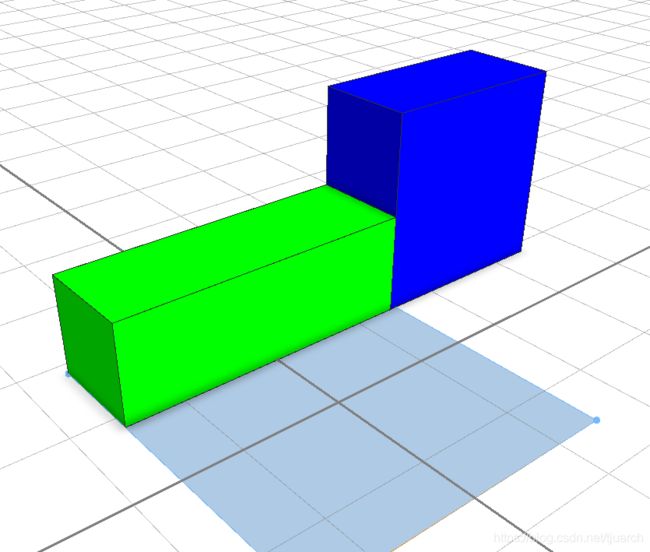 解释:5个长的巨型,切了一个3个的绿色,然后剩下的“~1”部分切了2个长,2个高的部分。“~1”的意思就是“剩下的都是他的”,“~”是一个可变的变量。
解释:5个长的巨型,切了一个3个的绿色,然后剩下的“~1”部分切了2个长,2个高的部分。“~1”的意思就是“剩下的都是他的”,“~”是一个可变的变量。
栗子:
Split_ex -->
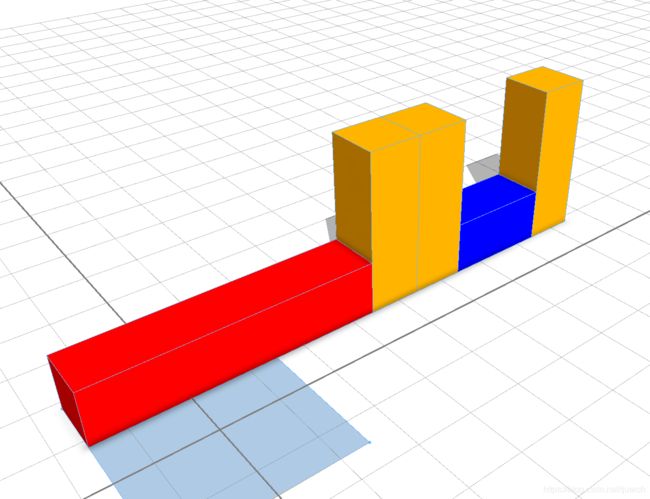
split(x) { 1 : X | ~100 : Y | 1 : X(2) }
Y -->
color(yellow)
Split_ex -->
split(x) { 3 : X | ~1 : X(0.5) | ~1 : X(0.5) | ~1 : X(0.5) }
(2)repeat split 重复
simple repeat 简单重复
栗子:
attr red = "#ff0000"
attr green = "#00ff00"
attr blue = "#0000ff"
attr yellow = "#ffff00"
attr orange = "#ffa500"
attr length = 10
Lot -->
s(length, 1, 1)
primitiveCube()
color(yellow)
Repeat_ex
Repeat_ex -->
split(x) { ~2 : X } *
栗子:
attr red = "#ff0000"
attr green = "#00ff00"
attr blue = "#0000ff"
attr yellow = "#ffff00"
attr orange = "#ffa500"
attr length = 10
Lot -->
s(length, 1, 1)
primitiveCube()
color(yellow)
Repeat_ex
Repeat_ex -->
split(x) { { 2 : X }* | ~1 : X(2) }
X -->
color(red)
X(h) -->
s( '1, h, '1)
Repeat_ex -->
split(x) { ~1 : X(2) | { 2 : X }* }
解释:图像和上面一样。要先满足后面的固定数值,但是下面又不一样了。
Repeat_ex -->
split(x) { ~1 : X(2) | { 2 : X }* | ~1 : X(2)}
repeat pattern 重复样式
Repeat_ex -->
split(x) { ~1 : Y | 0.25 : X | ~1 : Y }*
Y -->
s('1, '3, '1)
color(orange)
rhythm 节奏重复
attr length = 15
Lot -->
s(length, 1, 1)
primitiveCube()
color(yellow)
Rhythm_ex
Rhythm_ex -->
split(x){ ~5: X(2) | { ~1: Y | { ~1: Y | ~1: Z }* }* }*
Z -->
color(blue)
Y -->
s('1, '3, '1)
color(orange)
X -->
color(red)
X(h) -->
s( '1, h, '1)
relative split 相对细分
按比例切分,栗子:
attr red = "#ff0000"
attr green = "#00ff00"
attr blue = "#0000ff"
attr yellow = "#ffff00"
attr orange = "#ffa500"
attr length = 10
Lot -->
s(length, 1, 1)
primitiveCube()
color(yellow)
R_ex
R_ex -->
split(x) { '0.5 : X | { ~1 : Y }* | 2 : Z | { ~1 : Y }* }*
R_ex -->
split(x) { '0.382 : A | '0.618 : B}
A -->
R_ex
B -->
R_ex
不要这样写,内存溢出,哈哈哈,触及了死循环的递归,CE崩溃,连带着浏览器也崩溃。
CE重启,卡到初始化licence阶段,这时的处理办法是删掉project目录中的.metadata目录,打开后,项目要重新导入并且重新设置鼠标,导入后切记打开cga之前删掉预览,否则还得崩溃。。。