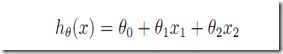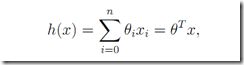stanford机器学习 实验1
决定系统学习下机器学习了,以stanford课件为主线。
notes1是关于回归的部分http://www.stanford.edu/class/cs229/notes/cs229-notes1.pdf
1.线性回归
举例是对于房子价格的预测,它这个数据很遗憾网上找不到,那么就暂时用5个数据点做下实验吧。
准备house.txt,5个数据记录大小,卧室数目,价格。
area bedrooms price
2104 3 400
1600 3 330
2400 3 369
1416 2 232
3000 4 540
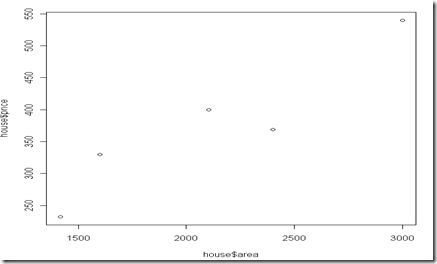
用R展示下数据
> house = read.table('house.txt', header=T)
> house
area bedrooms price
1 2104 3 400
2 1600 3 330
3 2400 3 369
4 1416 2 232
5 3000 4 540
> house$area
[1] 2104 1600 2400 1416 3000
> plot(house$area, house$price)
>
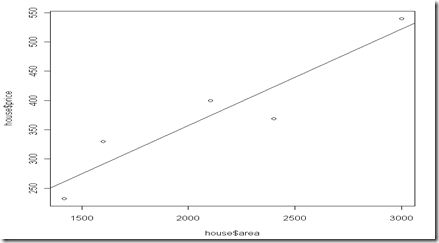
> fit = lm(house$price~house$area) //尝试线性回归 price = w*area + b
> abline(fit)
> summary(fit)
Call:
lm(formula = house$price ~ house$area)
Residuals:
1 2 3 4 5
25.80 39.02 -54.08 -28.60 17.85
Coefficients:
Estimate Std. Error t value Pr(>|t|)
(Intercept) 26.78988 78.20681 0.343 0.7545
house$area 0.16512 0.03588 4.602 0.0193 *
---
Signif. codes: 0 ‘***’ 0.001 ‘**’ 0.01 ‘*’ 0.05 ‘.’ 0.1 ‘ ’ 1
Residual standard error: 45.64 on 3 degrees of freedom
Multiple R-squared: 0.8759, Adjusted R-squared: 0.8345
F-statistic: 21.18 on 1 and 3 DF, p-value: 0.01929
因此R解出来的拟合公式是
price = 26.78988 + 0.16512 * area
如果我们同时考虑area, bedrooms两个因素对房价造成的影响
利用R的多元回归
> fit = lm(house$price~house$area + house$bedrooms)
> summary(fit)
Call:
lm(formula = house$price ~ house$area + house$bedrooms)
Residuals:
1 2 3 4 5
25.80 -12.02 -24.10 5.16 5.16
Coefficients:
Estimate Std. Error t value Pr(>|t|)
(Intercept) -70.43460 59.50462 -1.184 0.358
house$area 0.06384 0.04458 1.432 0.288
house$bedrooms 103.43605 40.09826 2.580 0.123
Residual standard error: 26.87 on 2 degrees of freedom
Multiple R-squared: 0.9713, Adjusted R-squared: 0.9426
F-statistic: 33.87 on 2 and 2 DF, p-value: 0.02868
price = –70.43 + 0.06384 * area + 103.43605 * bedrooms
这个和课件上出入都很大,主要还是这边数据集合太小了,只有5个数据点。
C++实验
考虑到上面的回归其实本质上都是最小二乘问题。如果从线性代数角度求解最小二乘AX=b,这里用eigen做下实验,分别对应上面的1元和多元线性回归两个例子。
始终是1, 对应试area, 如果是二元回归 对应 price
/** * ============================================================================== * * \file stanford1.cc * * \author chenghuige * * \date 2011-02-27 15:27:07.614842 * * \Description: stanford 机器学习实验 * area bedrooms price 2104 3 400 1600 3 330 2400 3 369 1416 2 232 3000 4 540 * ============================================================================== */ #define private public #define protected public #include <iostream> #include <string> #include <vector> #include <fstream> #include <algorithm> #include <boost/progress.hpp> #include <glog/logging.h> #include <gflags/gflags.h> #include "debug_help.h" #include "utils/matrix_help.h" using namespace std; DEFINE_string(type, "simple", ""); vec linear_regression(const mat& A, const vec& b) { //Ax=b least squar sort or other method return x return A.jacobiSvd(ComputeThinU | ComputeThinV).solve(b); } void run() { mat data(5, 4); //5data points, each with 3 attrib with a const attrib data << 1, 2104, 3, 400, 1, 1600, 3, 330, 1, 2400, 3, 369, 1, 1416, 2, 232, 1, 3000, 4, 540; cout << "实验数据如下: \n" << data << endl; cout << "一元线性回归结果如下,对应常系数和area系数: " << endl; cout << linear_regression(data.leftCols(2), data.col(3)) << endl; //一元线性回归 cout << "二元线性回归结果如下,对应常系数和area系数和bedrooms系数: " << endl; cout << linear_regression(data.leftCols(3), data.col(3)) << endl; //二元线性回归 } int main(int argc, char *argv[]) { FLAGS_logtostderr = true; google::InitGoogleLogging(argv[0]); google::InstallFailureSignalHandler(); int s = google::ParseCommandLineFlags(&argc, &argv, false); boost::progress_timer timer; run(); return 0; }
[chg@localhost bin]$ ./stanford1
实验数据如下:
1 2104 3 400
1 1600 3 330
1 2400 3 369
1 1416 2 232
1 3000 4 540
一元线性回归结果如下,对应常系数和area系数:
26.7899
0.165119
二元线性回归结果如下,对应常系数和area系数和bedrooms系数:
-70.4346
0.0638434
103.436
0.00 s
可以看到和R的结果是一致的。