使用栈结构对表达式进行求值的C++实现
使用栈结构对表达式进行求值的C++实现
栈的显著特点就是后进先出(LIFO),因此可以用作表达式求值。我们习惯性输入的表达式是中缀式,一般含有+、-、*、/、%、^等运算符号以及左右括号,计算机并不好处理。但是如果把中缀式转化为后缀式(也称逆波兰式),我们就可以很轻易地求出其值。
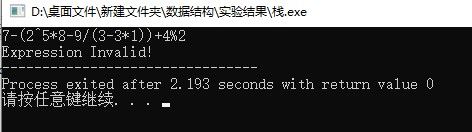
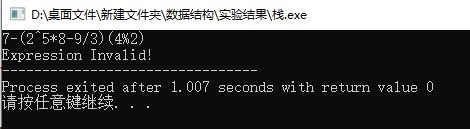
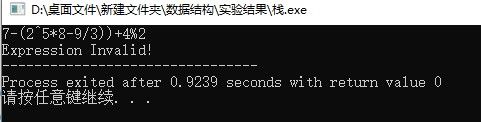
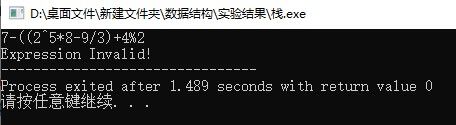
恰巧的是,中缀式转化成后缀式的过程和求后缀式的过程都可以借助栈结构来实现。我在做数据结构的实验时,按照老师的要求自己定义了一个栈,并通过优先级机制实现了0~9之间包含括号的+、-、*、/、%、^等运算,在C++实训的简易计算器实验中通过Qt平台(修改了一些兼容的地方,去掉了括号的匹配)将算法略作改进使之能够处理多位数的运算(时间原因只实现了+、-、×、/,并且不包括浮点数)。
C++有自带的stack,但是自己设计实现一个栈有助于更好的地理解栈结构:
struct Stack{
double num;
char c;
Stack *next;
/* 结构体构造函数 */
Stack(){
next = NULL;
}
Stack(char c,Stack *S){
this->c = c;
next = S->next;
}
Stack(double num,Stack *S){
this->num = num;
next = S->next;
}
};
使用的链式存储,这里考虑到之后的使用需要分别创建符栈和数栈,所以进行了整合。当然可以选择编写两个Stack(或者使用模板),设计一个栈类实现顺序栈也可以。
栈的一些必要的基本操作的函数声明:
/* push和pop因为有两个栈所以进行了重载,最后一个pop用于仅删除栈顶元素 */
void Push(Stack *S,char c);
void Push(Stack *S,double num);
void Pop(Stack *S,char &poper);
void Pop(Stack *S,double &operand);
void Pop(Stack *S);
/* 置空 */
void Clear(Stack *S);
bool isEmpty(Stack *S);
/* 主要用于符栈的获取栈顶元素 */
char getTop(Stack *S);
函数实现:
/* 部分语句已经在构造函数中实现了 */
void Push(Stack *S,char c){
Stack *temp = new Stack(c,S);
S->next = temp;
}
void Push(Stack *S,double num){
Stack *temp = new Stack(num,S);
S->next = temp;
}
void Pop(Stack *S,char &poper){
if(!isEmpty(S))
{
poper = (S->next)->c;
Stack *t = S->next;
S->next = (S->next)->next;
delete t;
}
}
void Pop(Stack *S,double &operand){
if(!isEmpty(S))
{
operand = (S->next)->num;
Stack *t = S->next;
S->next = (S->next)->next;
delete t;
}
}
void Pop(Stack *S){
Stack *t = S->next;
S->next = (S->next)->next;
delete t;
}
void Clear(Stack *S){
while(S!=NULL)
{
Stack *t = S;
S = S->next;
delete t;
}
}
bool isEmpty(Stack *S){
if(S->next==NULL)
return true;
else
return false;
}
char getTop(Stack *S){
if(isEmpty(S))
return '0';
else
return (S->next)->c;
}
然后是计算的函数,包括中缀转后缀、计算后缀的结合过程,为了让结构更清晰一点分离成几个函数:
/* 栈内/外优先级函数 */
int Isp(char c);
int Osp(char c);
/* 以Compute为主,Calculate用于取出当前数栈栈顶的两个元素,以符栈的栈顶元素进行运算后将结果重新push进数栈 */
void Compute(string &expr,bool &isInvalid,double &result);
void Calculate(char op,Stack *Operand,bool &isInvalid);
实现部分:
int Isp(char op){
/*stand for the priority level of characters inside stack*/
switch(op){
case '#': return 0;
case '(': return 1;
case '+': return 3;
case '-': return 3;
case '*': return 5;
case '/': return 5;
case '%': return 5;
case '^': return 7;
case ')': return 8;
}
}
int Osp(char op){
/*stand for the priority level of characters outside stack*/
switch(op){
case '#': return 0;
case '(': return 8;
case '+': return 2;
case '-': return 2;
case '*': return 4;
case '/': return 4;
case '%': return 4;
case '^': return 6;
case ')': return 1;
}
}
void Calculate(char op,Stack *Operand,bool &isInvalid){
/*used to simplify function Compute()*/
double num1,num2,M; /*M: the result of the calculation of two operands*/
Pop(Operand,num2);
Pop(Operand,num1); /*the first operand is num2, second is num1*/
switch(op){
case '+': M = num1 + num2; break;
case '-': M = num1 - num2; break;
case '*': M = num1 * num2; break;
case '/':
if(num2!=0)
{
M = num1 / num2; break; }
else
{
isInvalid = true; return; } /*when num2=0, the expression is invalid*/
case '%':
if(num1!=(int)num1||num2!=(int)num2){
isInvalid = true; return;
} /*when one of them isn’t an integer, the expression is invalid*/
else
{
int a = int(num1);
int b = int(num2);
M = a % b;
break; /*operands of modular must be integer*/
}
case '^': M = pow(num1,num2);break;
default: {
isInvalid = true; return; } /*operator is invalid*/
}
Push(Operand,M);
}
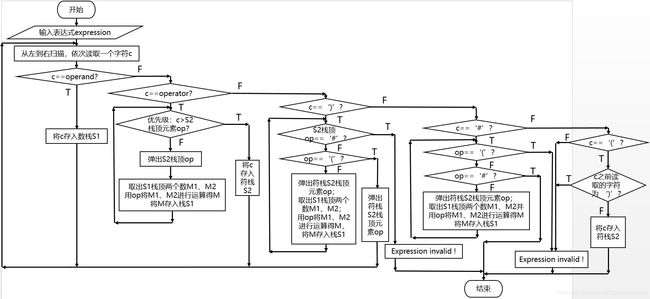
void Compute(string &expr,bool &isInvalid,double &result){
Stack *Operand = new Stack;
Stack *Operator = new Stack; /*head node chain*/
expr += '#'; /*a symbol in the last stand for ending*/
Push(Operator,'#'); /* used for a pair of the last '#' */
/*c: every character be got of expression; */
/*op: the top operator of the stack for operators ; */
/*opBefore: to check if the character before '(' is ')'. (invalid expression)*/
char c, op, opBefore;
for(int i=0;i<expr.length();i++)
{
c = expr[i];
if(c<=57&&c>=48) /* c is a number */
{
double x = int(c) - 48; /*change c to an double number*/
Push(Operand,x);
}
else if(c=='+'||c=='-'||c=='*'||c=='/'||c=='%'||c=='^'||c=='(')
{
if( c=='('&&opBefore==')')
{
isInvalid = true;
break; /*if the character before '(' is ')', expression is invalid*/
}
if( Osp(c)<Isp(getTop(Operator)) ){
while( Osp(c)<Isp(getTop(Operator)) ){
Pop(Operator,op);
/*take two operands out of stack and calculate them according to the top character op*/
Calculate(op,Operand,isInvalid);
}
}
if( Osp(c)>Isp(getTop(Operator)) )
Push(Operator,c);
}
else if(c==')')
{
while(getTop(Operator)!='('){
if(getTop(Operator)=='#'){
isInvalid = true;
break; /*expression is invalid because ')' is extra*/
}
Pop(Operator,op);
Calculate(op,Operand,isInvalid);
}
if(getTop(Operator)=='(')
Pop(Operator);
opBefore = c; /*to check whether the character before '(' is ')' */
}
else if(c=='#'){
while(getTop(Operator)!='#'){
if(getTop(Operator)=='(' ) {
isInvalid = true;
break; /*expression is invalid because '(' is extra*/
}
Pop(Operator,op);
Calculate(op,Operand,isInvalid);
}
if(getTop(Operator)=='#') /*compute of the expression is ended*/
{
Pop(Operator);
Pop(Operand,result); /*the last number in stack is result*/
break;
}
}
}
Clear(Operand);
Clear(Operator); /*release space of two chains*/
}
在Qt平台上,QString的功能更为健壮,所以依托此类对算法可以有个小改进,使其能运算多位整数。在c为数字时设置一个循环,如果下一个字符也为数字则对c进行字符串拼接,然后判断下下个字符,如果不为数字则退出循环,类似的,浮点数的计算也可以如此设计。
这里给出Qt平台上改进后的Compute、Calculate作为示例(只包括+、-、*、/),优先级函数同上:
double Compute(QString &expr,bool &isInvalid){
QStack <double> Operand;
QStack <QString> Operator; //使用QStack类更为方便
expr += "#";
Operator.push("#");
QString c, op, next;
for(int i=0;i<expr.length();i++)
{
c = expr.mid(i,1); //获取子串
if(i<expr.length()-1)
next = expr.mid(i+1,1);
else
next = "";
if(c<=57&&c>=48)
{
QString cc = "";
cc += c;
/* 循环字符串拼接 */
while(next<=57&&next>=48&&i<expr.length()-1){
cc += next;
if(i<expr.length()-2){
i++;
next = expr.mid(i+1,1); //特殊情况,多位数在表达式末尾
}
}
bool ok;
double x = cc.toDouble(&ok);
if(ok)
Operand.push(x);
}
else if(c=='+'||c=='-'||c=='*'||c=='/')
{
if( Osp(c)<Isp(Operator.top()) )
{
while( Osp(c)<Isp(Operator.top()) ){
op = Operator.pop();
Calculate(op,Operand,isInvalid);
}
}
if( Osp(c)>Isp(Operator.top()) )
Operator.push(c);
}
else if(c=="#")
{
while(Operator.top()!='#')
{
op = Operator.pop();
Calculate(op,Operand,isInvalid);
}
if(Operator.top()=='#')
{
Operator.pop();
expr.remove(expr.length()-1,1);
return Operand.pop();
}
}
}
}
void Calculate(QString &op,QStack<double> &Operand,bool &isInvalid){
double num1,num2,M;
num2 = Operand.pop();
num1 = Operand.pop();
int i=0;
if(op=="+") i=1;
else if(op=="-") i=2;
else if(op=="*") i=3;
else if(op=="/") i=4; //因为Qt的switch语句好像仅仅支持整型,不得已只好这样了
switch(i){
case 1: M = num1 + num2;break;
case 2: M = num1 - num2;break;
case 3: M = num1 * num2;break;
case 4:
if(num2!=0)
{
M = num1 / num2;break; }
else
{
isInvalid = true; return; }
default: {
isInvalid = true; return; }
}
Operand.push(M);
}
新人,很笨,写博客做个记录。
如有意见不同之处欢迎交流讨论。